1. The document summarizes key points from a chapter about information systems in business today. It discusses how information systems help businesses achieve six strategic objectives: operational excellence, new products/services, customer intimacy, improved decision making, competitive advantage, and survival.
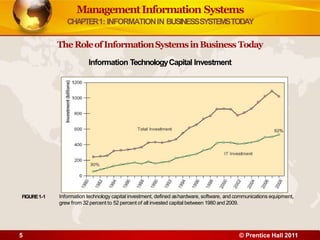
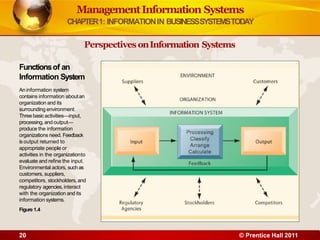
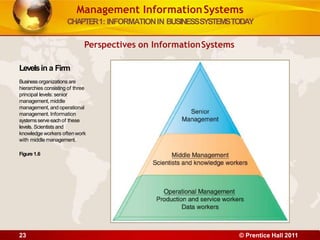
2. It describes an information system as a set of components that collect, process, store, and distribute information to support decision making. Information systems are transforming business through increased use of wireless technology, web tools, cloud computing, and mobile platforms.
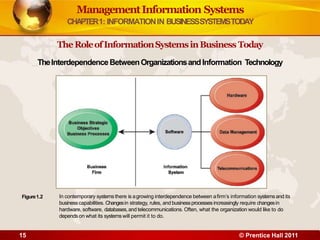
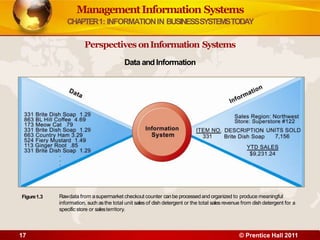
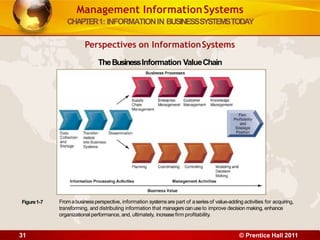
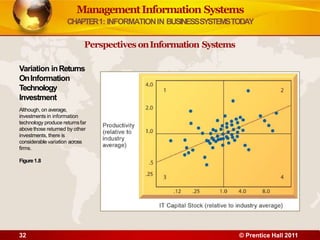
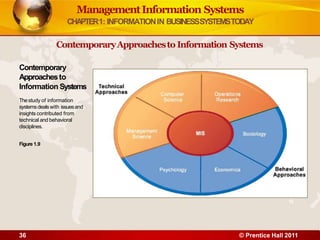
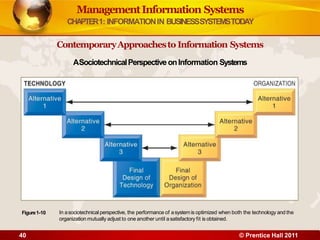
3. The chapter examines the interdependence between organizations and information technology, and how changes in strategy and processes require changes to hardware, software, and networks. It also differentiates between data and information.