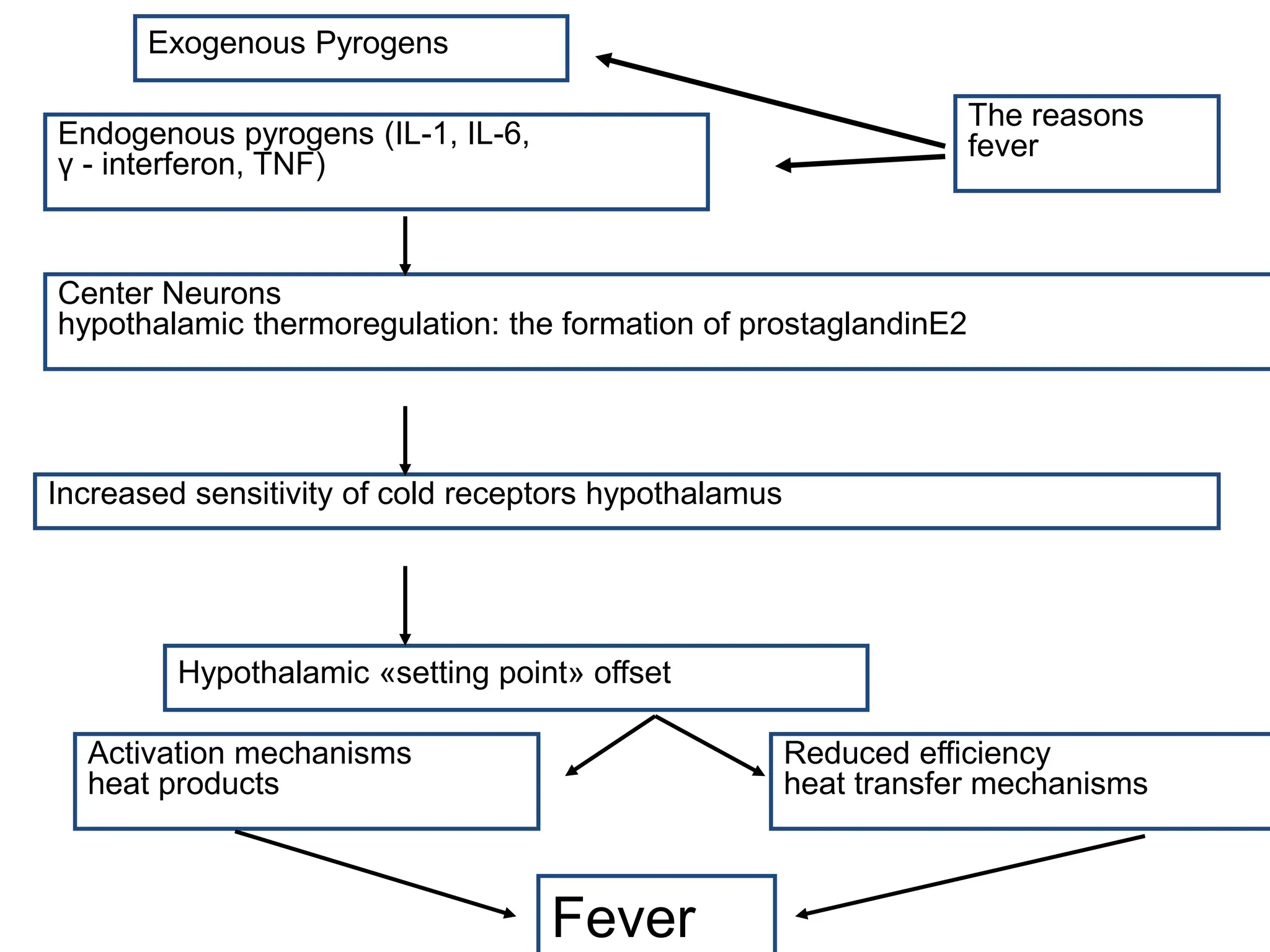
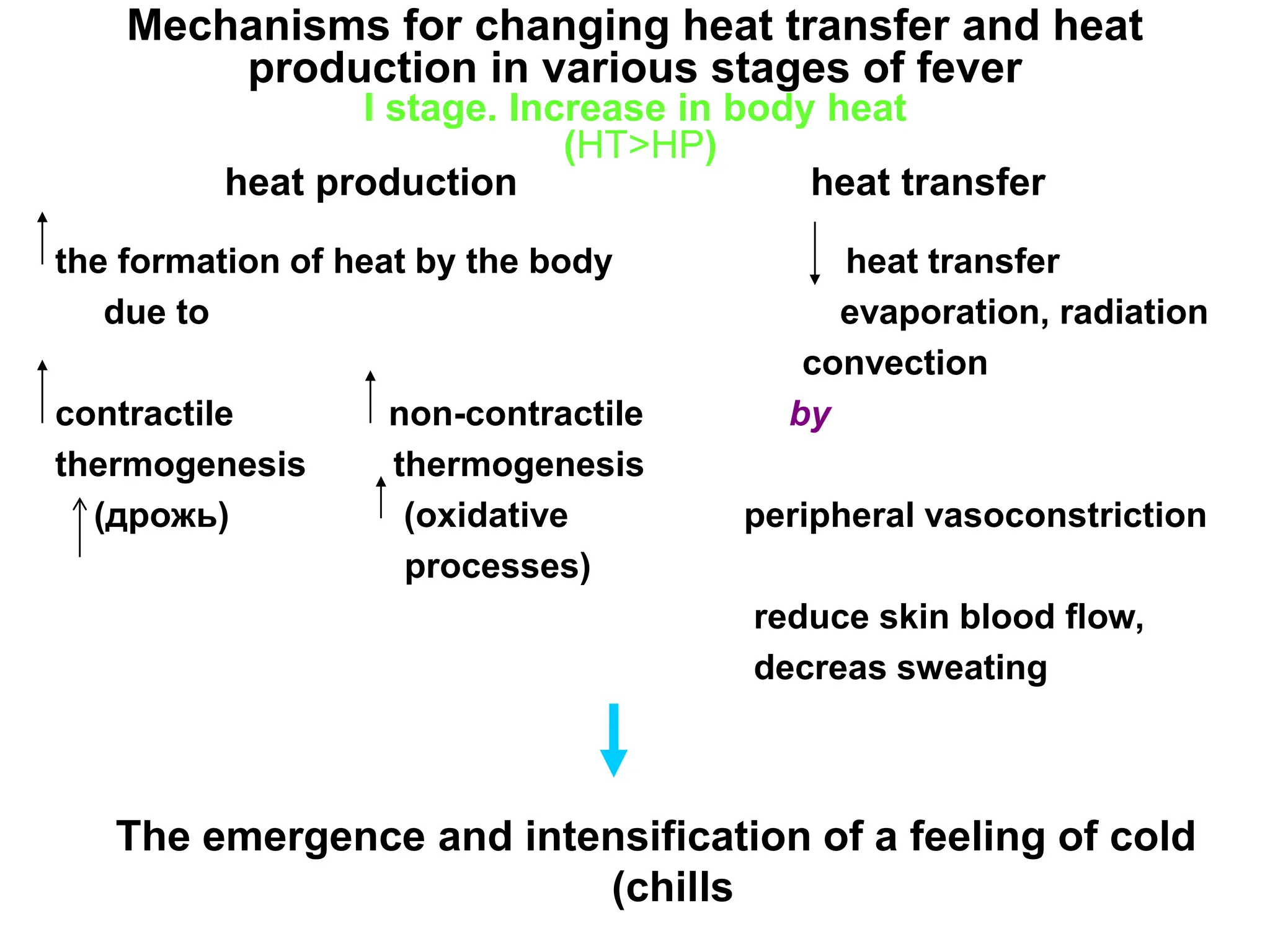
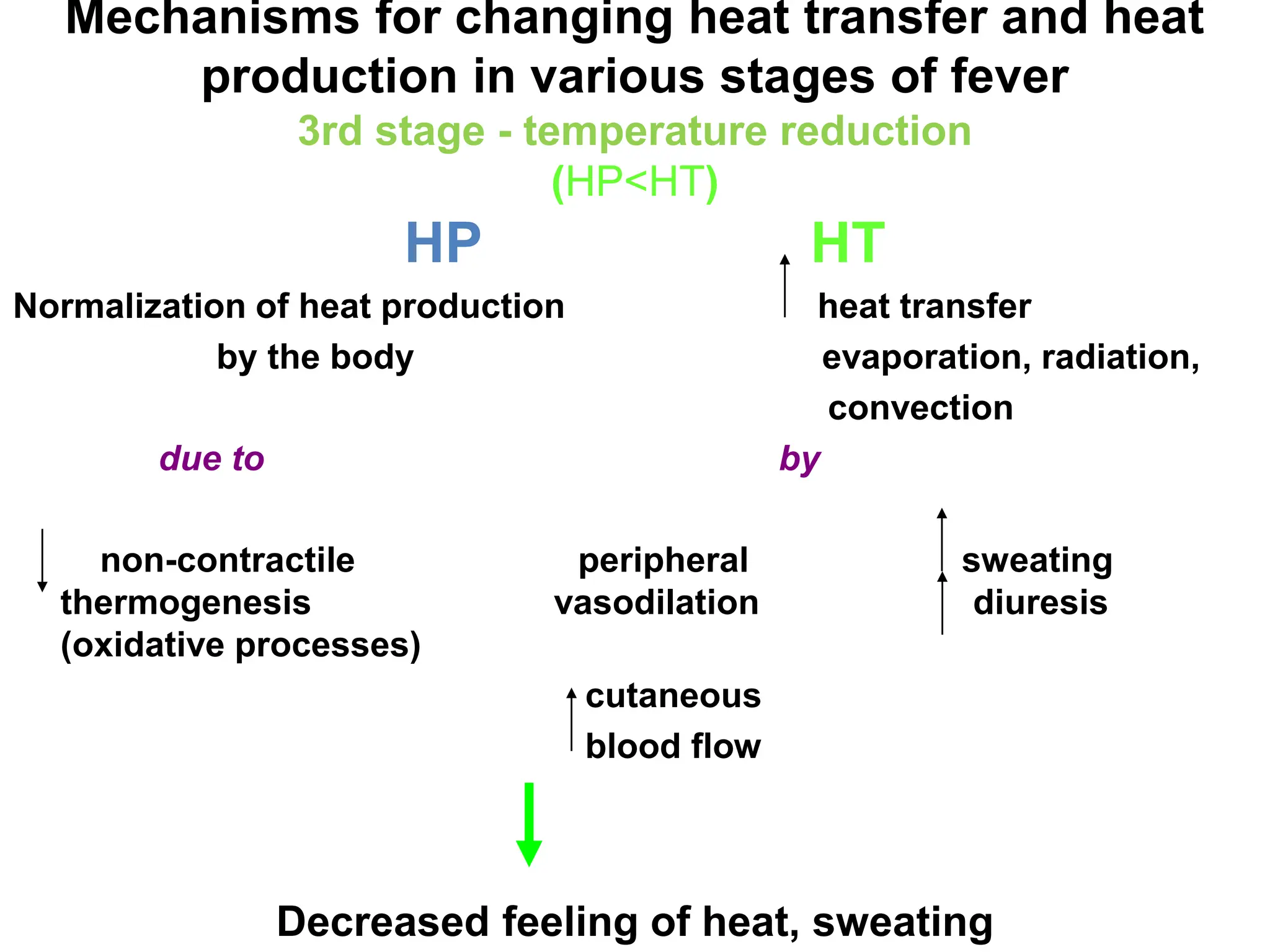
The document discusses the mechanisms of fever and thermoregulation in the hypothalamus. It explains that fever occurs in three stages: 1) increased heat production causes a rise in body temperature and chills, 2) temperature stabilizes as heat production and transfer balance at a higher level, and 3) heat production decreases below transfer levels, reducing temperature through sweating. The hypothalamus contains heat production and transfer centers that are impacted by exogenous and endogenous pyrogens to shift the thermoregulatory set point and trigger the mechanisms of each fever stage.