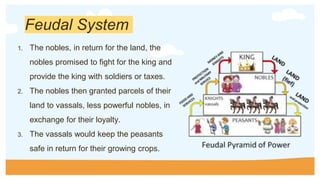
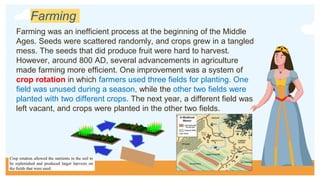
During medieval Europe from 500 to 1400 AD, the feudal system developed out of necessity. Farmers could no longer work their fields without protection from invaders, so they began hiring soldiers to protect their communities. This led to the establishment of a hierarchy with the king at the top granting lands (fiefs) to nobles in exchange for their loyalty and military service. The nobles then granted parts of their lands to lower-ranking vassals, who in turn protected and provided for the peasants living and working on the lands. Peasants gradually became serfs who were bound to work the lands of their lord. Life was organized around manors and centered on the Catholic Church, which was the most powerful institution and