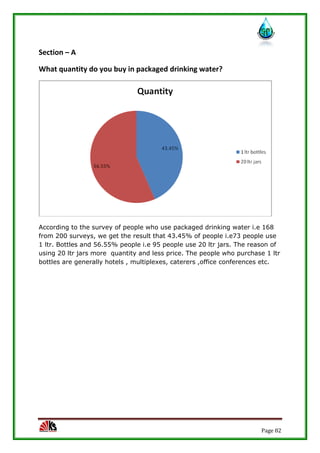
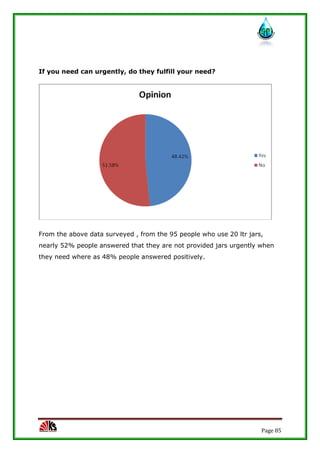
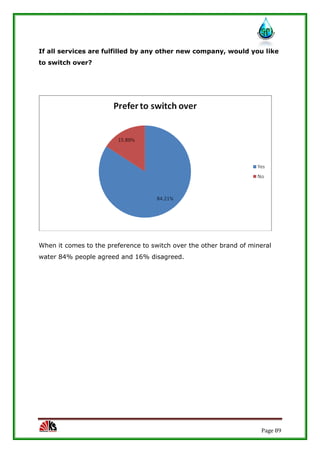
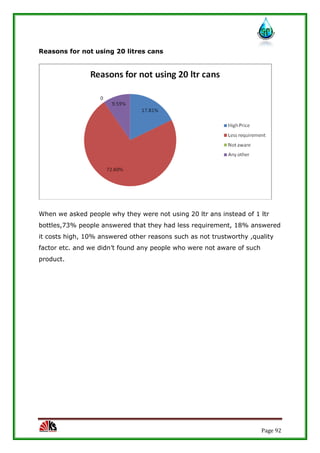
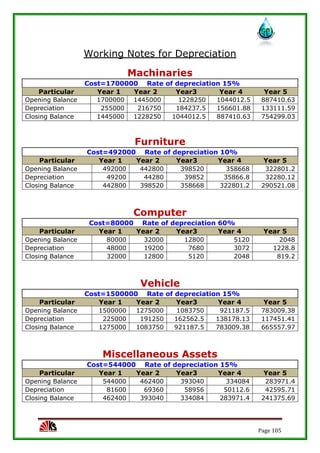
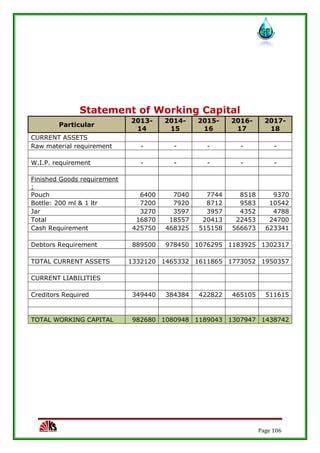
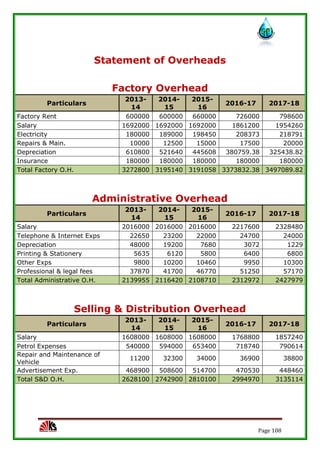
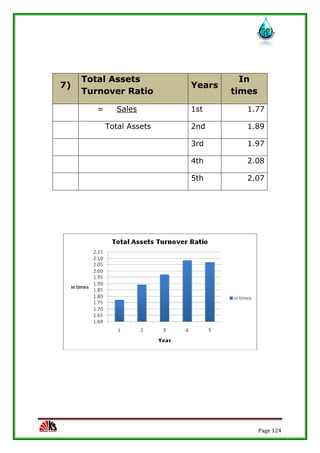
The report assesses the technical, marketing, financial, and legal feasibility of establishing SAP Packaged Drinking Water. It includes details on the proposed location, machinery requirements, manufacturing process, organizational structure, market research results, projected costs and profits. The analysis finds that the project is technically, legally, and financially viable based on the market demand for packaged drinking water in the area.