Extra corporeal medical devices - textiles
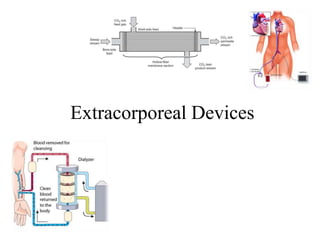
- 2. Extracorporeal devices • Medical devices that are used externally and not implanted with in the body are categorized as extra corporeal. • ECD – Mechanical organs – primarily used for blood purification. • Major organs that purifies blood – lung, liver, kidney and spleen. • Organ failure – supported by artificial organs to save life. • ECD - artificial kidney (dialyzer), the artificial liver, and the mechanical lung (blood oxygenator) – replaces the functions of natural organ – corrects the quality and quantity of blood.
- 3. Artificial Kidney Function of kidney: • ~ 625 mL of plasma flows through each kidney every minute. • Of this 625 mL, each kidney filters ~ 20%, or 125 mL, across the glomerulus - however, only 1 mL⁄min of urine is excreted to the bladder. • After removing so much from the blood, the human kidney then works to reabsorb those substances that are beneficial for homeostasis.
- 4. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) • Malfunction or failure of the kidney Metabolic and dietary waste products gradually accumulate within the body (Uremic Toxins) Results in malfunction of cells and organs CKD - defined by 5 stages of decreasing renal function: from Stage 1, which is defined by a slightly reduced GFR; to Stage 5, which requires medical treatment.
- 5. Current Treatment • Haemodialysis- widely used in the treatment of CKD Artificial removal processes, to mimic the natural function of the kidney. Artificial kidney consists of a semi- permeable membrane, a fine medical textile used to absorb toxins and pures blood (cartridges), on one side of which blood passes while a special dialysate solution is passed along the other. The artificial kidney is made of polyacetate and polysulphone in equal proportions
- 6. Raw Materials and manufacturing Technology • Regenerated cellulose, cellulose triacetate, acrylonitrile copolymer, poly (methyl methacrylate), ethylene-viyl alcohol copolymer, polysulfone and polyamide which can be grouped as cellulose and synthetic polymer systems. • Eighty per cent of the dialyzers use cellulose materials which have excellent permeability for low molecular substances. • Pore sizes of membranes vary between 1 - 3 nm for conventional membranes and 4 - 8 nm for large pore membranes. • Multilayer fibres composed of numerous layers of needle-punched fabrics with varying densities may also be used and are designed to remove the waste materials rapidly and efficiently. The synthetic polymer substitute being experimented with is a polyethylene glycol-polyethylene terephthalate block copolymer membrane which can selectively filter. • The development of artificial kidneys depends on the development of hollow fibre membrane. Polymer can be spun into hollow fibre membrane and can be used for purification.
- 7. Criteria for Hollow Polymer Membrane • Excellent biocompatibility • Effective clearance of target solutes • Larger pore size to aid removal of protein bound uremic toxins and middle to large molecular weight solutes. • High molecular weight cut-off, a sharp cut-off curve and a greater capacity for adsorption. • Loss of < 3 g/session albumin is allowed with a blood flow rate of 200 ml/min and a dialysate flow rate of 500 ml/min.
- 8. How big is the problem? • Found prevalence of CKD as 13–15.04% with stage 1, 2 and 3 as 6.62%, 5.40% and 3.02% respectively in India. • The global estimated prevalence of CKD is 13.4% (11.7-15.1%), and patients with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) needing renal replacement therapy, Only cure- kidney transplantation.
- 9. • Manufacturers • There are no manufacturers of artificial kidney in India presently, except Nipro Corp. Shirwal, Pune (Japanese company ) • India is a net importer of artificial kidney. • The membrane or dialyzers are 100% technical textile products made up of polysulphane and polyacetate. • The Artificial Kidney market industry is projected to grow from USD 0.16 Billion in 2023 to USD 7.00 Billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 60.33% during the forecast period (2023 - 2032). • High time – to look for indigenous artificial kidney for the betterment of patient as well as the Nation.
- 10. Liver & Its Function • Liver - largest and remarkable organ of our body - 1.2-1.6kg. • Hepatic cells (hepatocytes) responsible for liver functions - Make up 80% of the liver • Liver is responsible for up to 500 separate functions Removing/excreting body wastes and hormones as well as drugs and other foreign substances Synthesizing plasma proteins, including those necessary for blood clotting Helping the body fight infection Producing bile to aid in digestion Storing certain vitamins, minerals, and sugars • Regenerative - regenerate after severe trauma like skin – patient can recover from liver disease with only 20 % functional liver as it grows back.
- 11. • Complications – alcohol damage, hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, bile duct infections, cancer, fatty liver, cirrhosis etc – affects severely – lead the condition ‘no return’ in which the liver cannot regenerate – patient – either need a transplant or under support till gets enough liver cells to regenerate or a transplant. • There are 10.4% people affected in the Indian population with diabetes currently. Liver failure & Reasons
- 12. Available Treatments Liver Transplant Pros • Most effective treatment for acute liver failure • High survival rates Cons • Scarcity of donors • Reduced clotting factors • Immunosuppressant's increase risk for infection • Rejection Bio-artificial Liver (BAL) Pros • Keep the patient alive until transplant is available • Aid in the livers regeneration Cons • Are only a temporary fix
- 13. Current Work in BAL’s • Molecular Absorbent Recycling System (MARS), Teraklin - Uses human albumin • Extracorporeal Liver Assist Device (ELAD), Vitagen – Uses immortalized human hepatocytes • HepatAssist 2000 system, Circe Biomedical – Uses porcine hepatocytes • Bioartificial Liver Support System (BLSS), Excorp Medical, Inc., - Uses primary porcine hepatocytes • LIVERX2000 system, Algenix, Inc., - Uses porcine hepatocytes • Modular Extracorporeal Liver System (MELS), Charite Virchow Clinic-Berlin - Uses human hepatocytes • Selective plasma filtration therapy (SEPET) • Single-pass albumin dialysis (SPAD) • Radial Flow Bioreactor (RFB) • TECA-Hybrid Artificial Liver Support System (TECLA-HALSS)
- 14. Challenges & raw Materials • Bio-artificial livers should be able to provide at least 10% of liver functioning – This requires approximately 1010 hepatocytes • Very difficult acquiring this many hepatocyte cells • Controversy over the use of porcine cells due to possible transmission of infections • Hepatocytes and plasma have very different physio-chemical properties – Hepatocytes do not perform well when in contact with plasma – Have a very high oxygen uptake rate • Hepatocyte cells undergo a lot of stress inside of bio-artificial liver – Any stress above 5 dyn/cm2 renders cells useless • Limited volume of the bioreactor – maximum blood/plasma that can be safely drawn out of liver failure patient is one liter – Difficult to achieve 10% of liver functioning within 1 liter • Makes Bio-artificial liver designing very difficult • Membranes used in bio artificial liver systems: Cellulose acetate, Cuprophan, Hemophan, Polyamide, Polypropylene, Polysulfone, Hollow viscose
- 15. Market size & future works • Artificial liver is the fastest growing market segment, at an estimated CAGR of 9.3 % from 2022 to 2030 – 34.3 billion USD to 70.1 billion USD. • Apollo Hospitals have done more than 500 liver transplantation surgeries in India. • Cadaver donation or donation from brain dead patients is still the main source of transplants. • The cost of a liver transplantation is around Rs.25-35 Lakh. • Research in: – Cell sources – Bioreactor design – Filtering techniques – Packaging for implantable devices
- 16. Heart – Lung machine • Heart-Lung Machine – blood pumping machine that takes over the functions of the heart and lungs during surgery (i.e. open-heart surgery). Uses • Coronary artery bypass surgery • Cardiac valve repair or replacement • Repair large septal defects • Repair of congenital heart defects • Transplantation • Repair of large aneurysmns • Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy (PTE) • Pulmonary thrombectomy • Most commonly used to perform a cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) • CPB allows for the heart to stop beating, which makes it easier to operate on, and surgeons can operate in a blood- free area
- 17. Components of Heart & Lung Machine • CBM, “The Pump” • Six main partsCannulae • Reservoir • Oxygenator (medical textile product) • Temperature Control • Filter • Roller/Centripetal Pump • Connected by a series of silicone or PVC tubes
- 18. Oxygenator • Takes place of the lungs • Exchanges O2 for CO2 in the blood pumped from the reservoir • Three types: Bubble Membrane Heparin-coated Heart is Stopped Blood diverted through tubes and is pumped to maintain flow Temperature regulation of blood and gaseous exchange is done Blood circulated systemically bypassing the heart and lungs Principle & Necessity of Oxygenator
- 19. Membrane Oxygenators • Thin gas permeable membrane separates blood and gas flow • The membrane purifies 3-5 L blood / min. • Gas flow is 60% of blood flow • Blood contacts membrane direct oxygenation
- 20. The Future Improvements for the future • Lifebridge B2T • First portable heart-lung machine • Been around since 2007 • Weighs 17.5 kilograms • Can be used by emergency room physicians and paramedics on the site, for critical patients • MiniHLM • Miniaturized heart- lung machine for infants • Functions of the machine are integrated, to make the machine small and compact
- 21. Membrane oxygenators in current use & Market Size • Hollow polypropylene fibre. • Hollow silicone membrane. • The oxygenators market is expected to register a CAGR of 5.4% during the forecast period 2022-2027 • The global oxygenators market size reached US$ 244.2 Million in 2022. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach US$ 348.4 Million by 2028, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% during 2023-2028.
- 22. HME filters • Heat and moisture exchangers (HMEs) are intended to conserve a portion of the patient’s exhaled heat and moisture, and condition inspired gas by warming and humidifying it. • Breathing system filters are intended to reduce the transmission of microbes and other particulate matter in breathing systems • Five types of device are available. • These are: heat and moisture exchanger with no filter (HME) electrostatic filter only pleated filter only electrostatic filter with HME pleated filter with HME.
- 23. HME filters Raw material & Market size • These are the materials used in the manufacturing of HME filters Polyethersulphone (PES) Cellulose Acetate Teflon (Polytetrafluoroethylene) Polyamide (Nylon) Cellulose Nitrate (Collodion) Polycarbonate • The HME filters market is expected to register a CAGR of 4% during the forecast period 2022-2032 and the expected revenue of USD 269.2 million from to cross USD 398.4 million in 2032
- 24. Summary • The Global Artificial Organ Market size is expected to grow from USD 26.21 billion in 2023 to USD 39.83 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 8.73% during the forecast period (2023-2028). • The key drivers of the market for artificial organs and bionics are the increasing number of transplants, coupled with the rising number of people waiting for donors. • As many as 3.17 lakh patients are waiting for a kidney, liver, heart, lung or pancreas transplant in the country as per the data released by the Indian Society of Organ Transplants (ISOT). • Key players Abbott Diabetes Care, Asahi Kasei Kuraray Medical Co. Ltd, Gambro AB, AbioMed, Baxter International, Otto Bock Healthcare, Thoratec Corporation, WorldHeart Corporation, and SynCardia Systems, Inc.
Editor's Notes
- Extracorporeal devices are mechanical organs that are used for blood purification and include the artificial kidney (dialyzer), the artificial liver, and the mechanical lung (blood oxygenator). Blood purification is an effective therapy for incurables such as end-stage renal failure. It is used to correct the abnormality of blood quality and quantity in treating sickness. Use of an artificial organ is a life saving treatment which can restore the spring that does not function, and a dynamic balance can be obtained by organ transplantation to recover health again. The function and performance of extracorporeal devices benefit from fibre and textile technology.
- Usage of dialyzer is depends in the toxin levels of the patients.
- According to the latest WHO data published in may 2014 Liver Disease Deaths in India reached 216,865 or 2.44% of total deaths. The age adjusted Death Rate is 21.96 per 100,000 of population ranks India #61 in the world. Review other causes of death by clicking the links below or choose the full health profile.
- The blood flows inside the strips and oxygen circulated parallel to the central axis that sustains the reel of membrane.