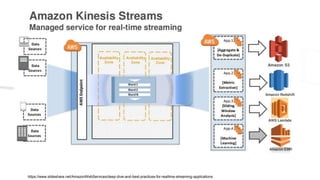
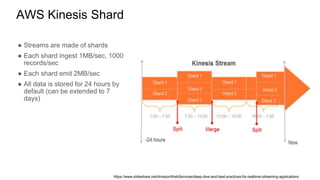
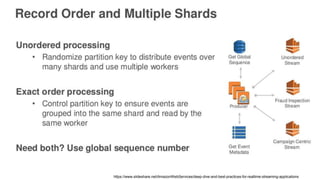
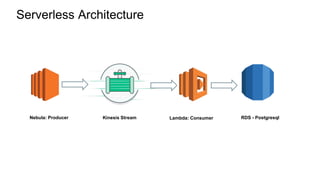
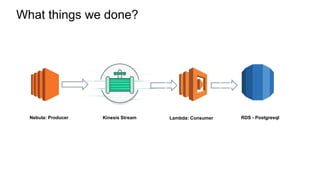
The document discusses experiences with AWS services including Lambda, Kinesis, and PostgreSQL, focusing on architecture, use cases, and enhancements achieved through trial and error. Key insights include methods for optimizing data ingestion and processing, such as managing Kinesis shard limits, utilizing batch processing for updates, and implementing partitioned tables in PostgreSQL. Additionally, lessons learned highlight the importance of evaluating performance resources and understanding concurrency behaviors in serverless architecture.