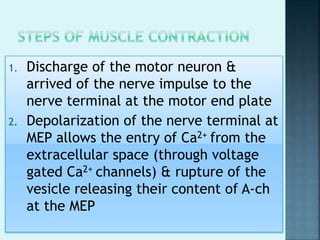
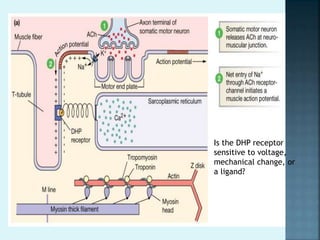
1) An end plate potential (EPP) is generated at the motor end plate when acetylcholine released from the nerve terminal binds to receptors on the muscle fiber membrane, causing sodium influx and partial depolarization.
2) If the EPP reaches threshold, an action potential is triggered and propagates through the muscle fiber via T-tubules.
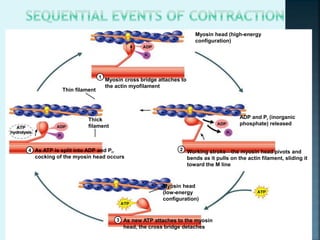
3) The action potential causes calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum via dihydropyridine receptors, which then activates muscle contraction by binding to troponin C and exposing actin binding sites for myosin cross bridges.