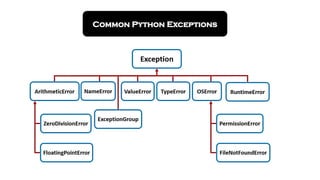
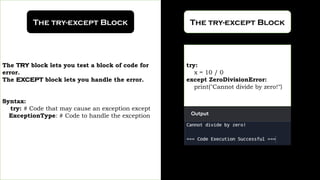
In Python, exceptions are events that disrupt the normal execution flow of a program, often caused by code errors, invalid user input, device failures, or arithmetic errors. Exception handling is crucial for distinguishing between normal and erroneous outcomes, separating error-handling logic from main code, and ensuring stability in multi-threaded applications. Python provides mechanisms like try-except blocks to manage exceptions and handle different error types effectively.



![try:
even_numbers = [2,4,6,8]
print(even_numbers[5])
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Denominator cannot be 0.")
except IndexError:
print("Index Out of Bound.")
# Output: Index Out of Bound
Multiple except
Block
try:
num = int(input("Enter a
number: ")) num % 2 == 0
except:
print("Not an even number!")
else:
print("its a even number")
The else Clause](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandlinginpython-241222112822-648bec77/85/Exception-Handling-in-Python-topic-pptx-6-320.jpg)