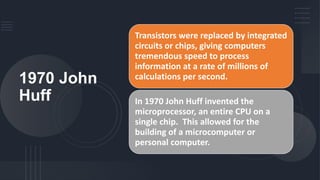
The document traces the history and development of computers from ancient counting devices like the abacus to modern personal computers. It discusses early mechanical calculating machines invented by Pascal and Babbage in the 1600s-1800s. In the 1900s, the first programmable electronic computers were developed using vacuum tubes, including the ENIAC. The invention of the transistor in 1947 and integrated circuits in the 1970s led to smaller, cheaper computers. This paved the way for personal computers like the Altair in 1975 and IBM PC in 1981, making computers accessible to individuals and small businesses. The Macintosh, introduced in 1984, popularized the graphical user interface.