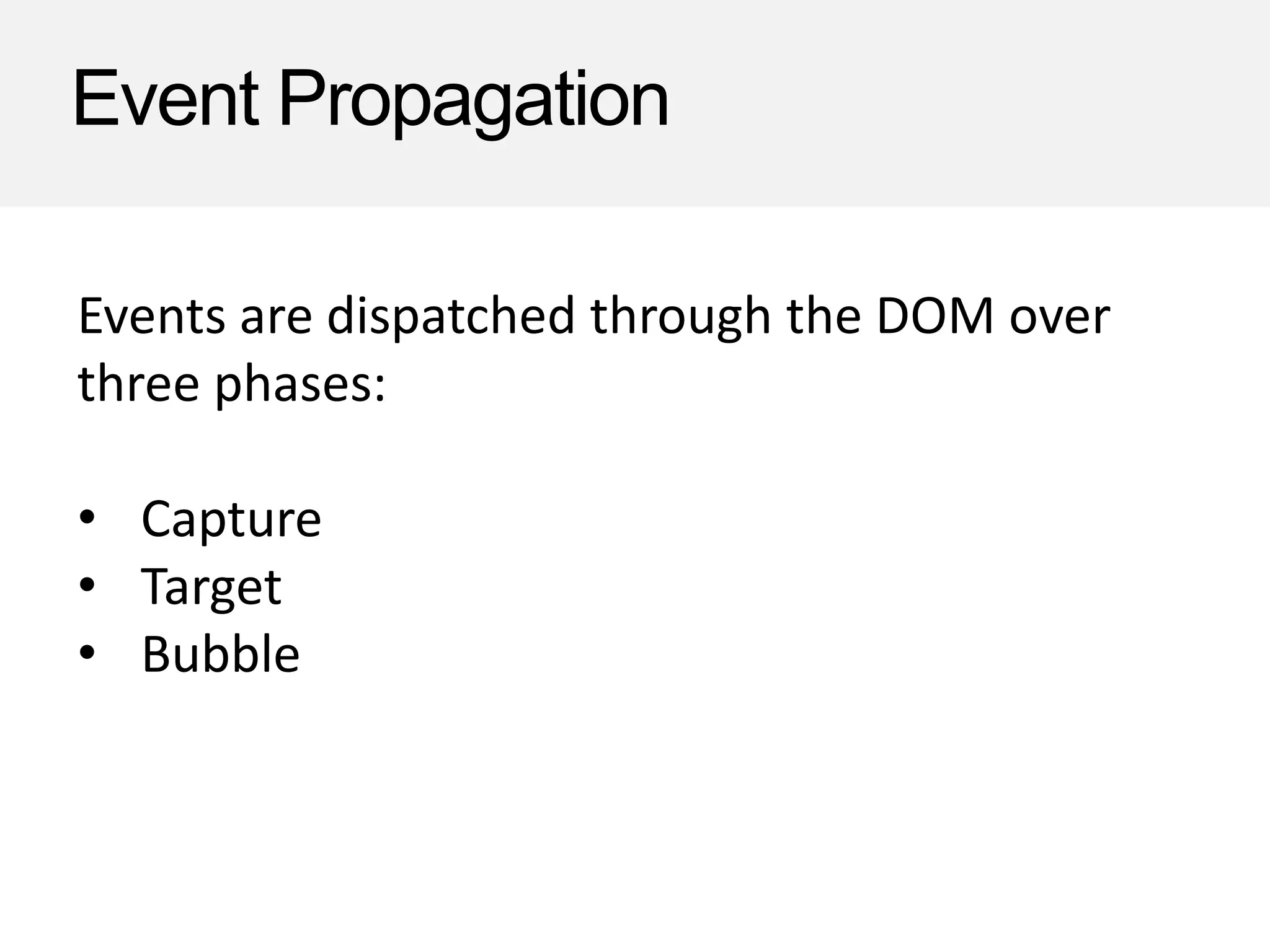
This document provides an overview of JavaScript event handling, including key concepts like default actions, event propagation, and event delegation. It details the methods to prevent default actions, stop propagation, and how to effectively use event listeners in both vanilla JavaScript and jQuery. Additionally, it highlights the advantages of event delegation and common pitfalls to watch out for during implementation.

















![Event Delegation with jQuery
has: function(selector) {
var elements = [];
$.each(this, function(i, el) {
if(el.matches(selector)) {
elements.push(el);
}
});
return $( elements );
}
To check the selector of a DOM element, we will use a
$.fn.has() helper method.
Note: Be sure to check out the answer key for a browser compatible version of this method.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09events-150805144550-lva1-app6892/75/Events-Part-2-20-2048.jpg)
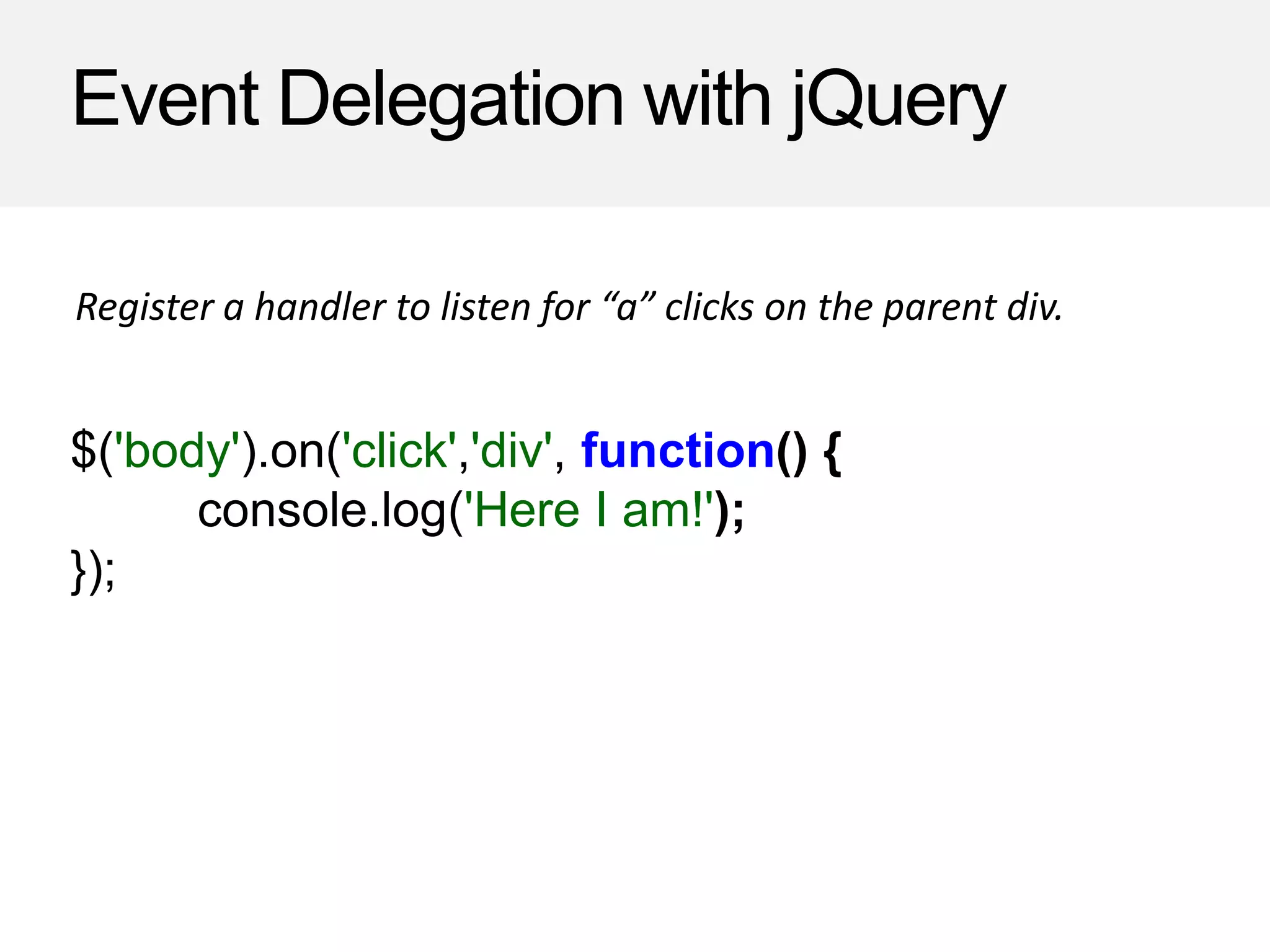
![Event Delegation with jQuery
on: function(eventType, selector, handler) {
return this.bind(eventType, function( ev ){
var cur = ev.target;
do {
if ($([ cur ]).has(selector).length) {
handler.call(cur, ev);
}
cur = cur.parentNode;
} while (cur && cur !== ev.currentTarget);
});
},
A simple $.fn.on() function.
Note: Be sure to check out the answer to handle a corresponding off().](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09events-150805144550-lva1-app6892/75/Events-Part-2-21-2048.jpg)

