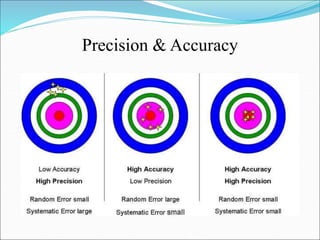
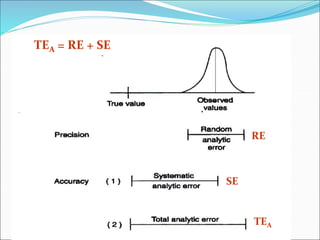
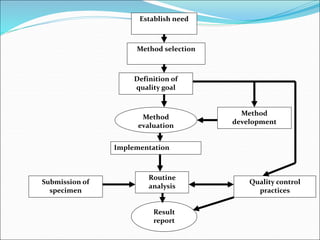
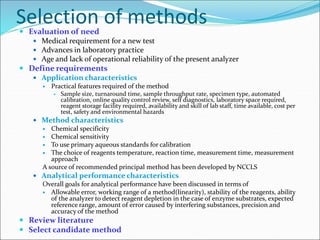
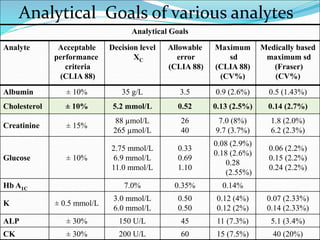
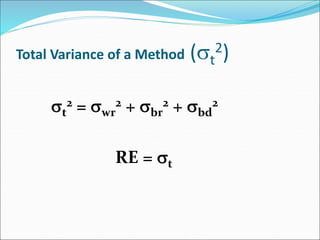
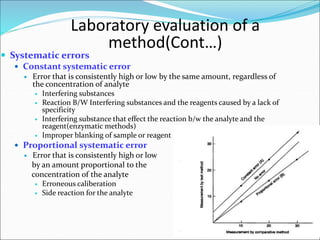
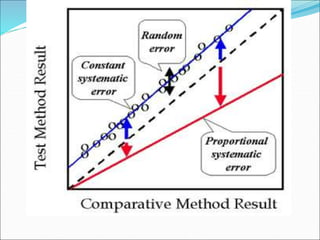
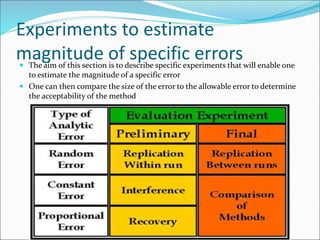
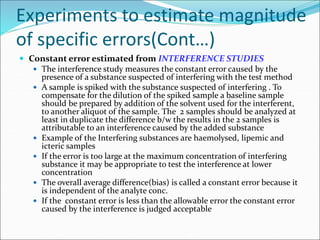
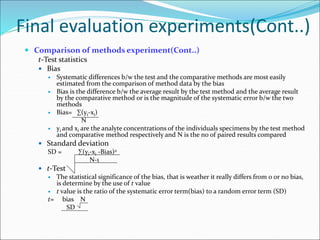
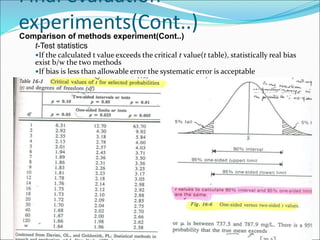
This document defines various terms related to method evaluation in clinical laboratories, including accuracy, precision, bias, systematic and random errors, linearity, and medical decision levels. It discusses the purpose of method evaluation for laboratory, manufacturer and medical requirements. Key aspects of evaluating a new method include assessing stability, linearity, and sources of random and systematic error through experiments. The goal is to determine if a method's total error meets performance criteria for clinical use.