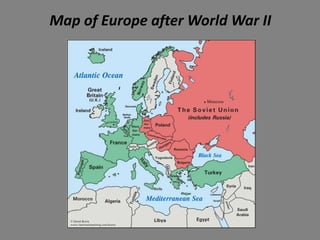
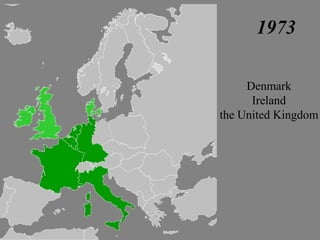
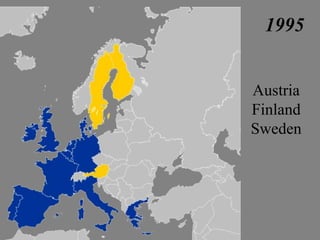
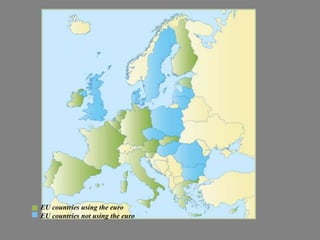
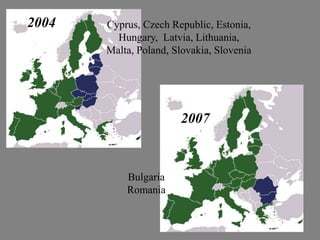
The document provides a brief history of the European Union from World War 2 to present day. Key events include the Yalta Conference in 1945 that discussed post-war Europe, the Marshall Plan in 1948 to rebuild European economies, the Schuman Declaration in 1950 proposing cooperation between France and Germany for coal and steel, and the establishment of the European Coal and Steel Community in 1951 and the European Economic Community and EURATOM in 1957 through the Treaties of Rome. The EU has since expanded to include 27 member countries and introduced the euro currency in 2002.