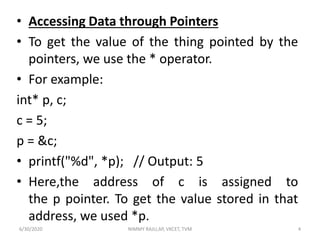
1. Pointers allow accessing and modifying data in memory by storing the memory address of another variable. Pointers must be declared with an asterisk and initialized by assigning the address of the variable.
2. Files can be opened, read from, written to, and closed using standard library functions like fopen(), fread(), fwrite(), and fclose(). Files can be accessed sequentially from beginning to end or randomly by seeking to a specific location.
3. File I/O functions allow reading and writing text and binary data to files, getting file information, and copying or merging file contents. Pointers to open file streams are used to pass file handles to these functions.




![Array Access using Pointers
Write a program to display the content of an array using pointer.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
int i;
int *p = A;
//Variable p of type pointer is pointing to the address of an integer array A.
printf("Array Contentn");
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("%dt",*(p+i));
}
}
Output
Array Content
10 20 30 40 50
6/30/2020 NIMMY RAJU,AP, VKCET, TVM 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module5-200630185407/85/EST-102-Programming-in-C-MODULE-5-7-320.jpg)