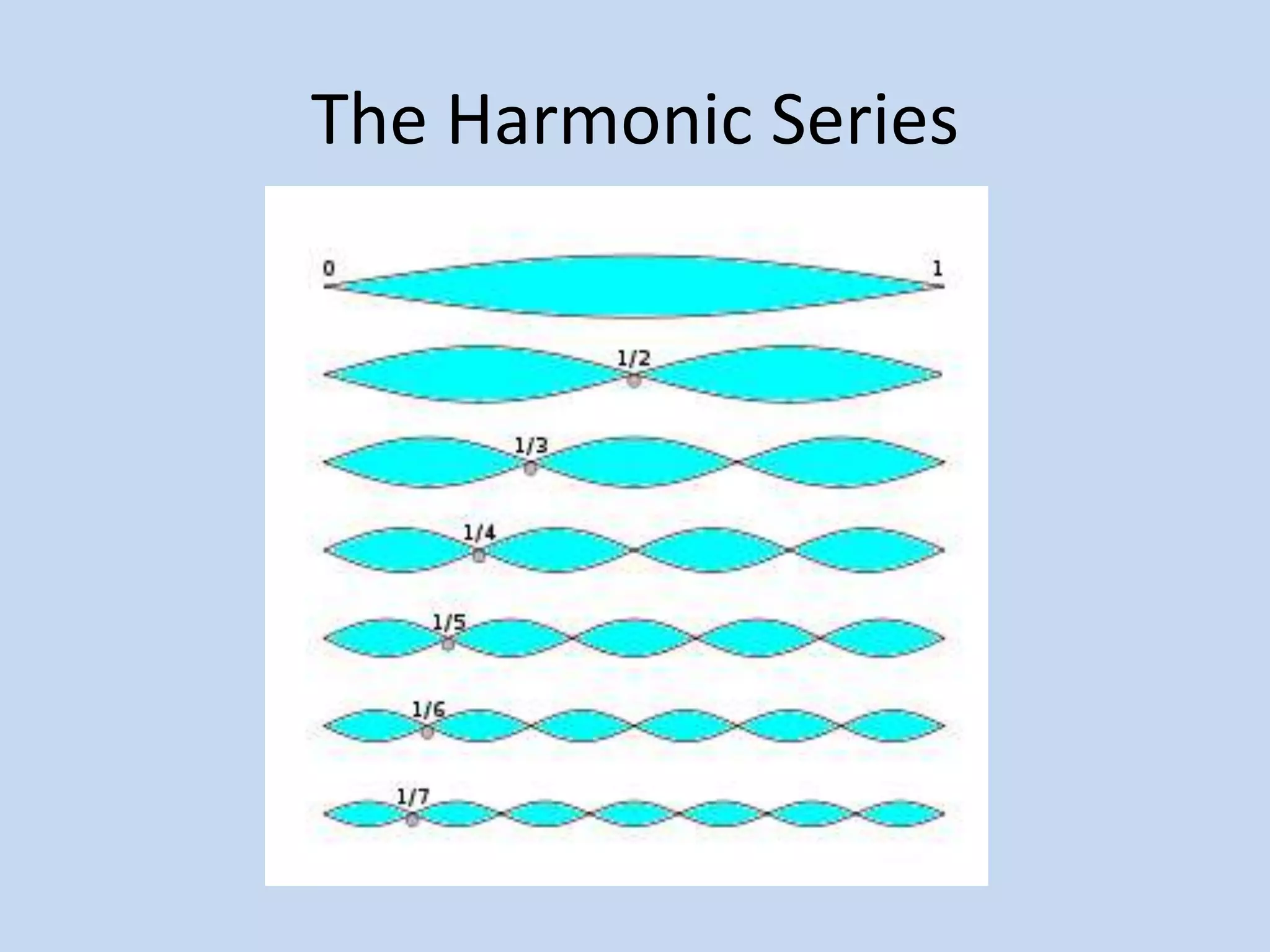
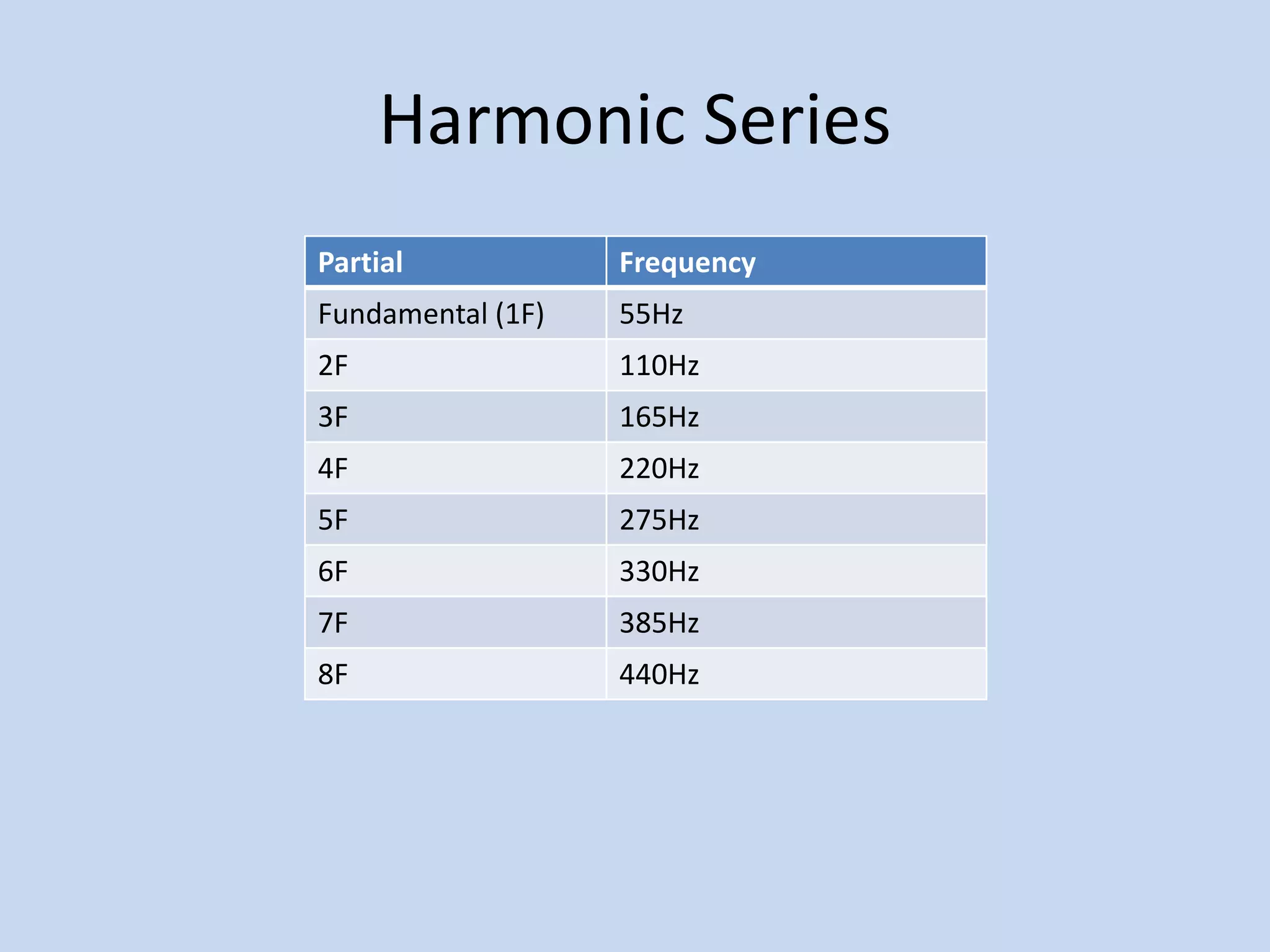
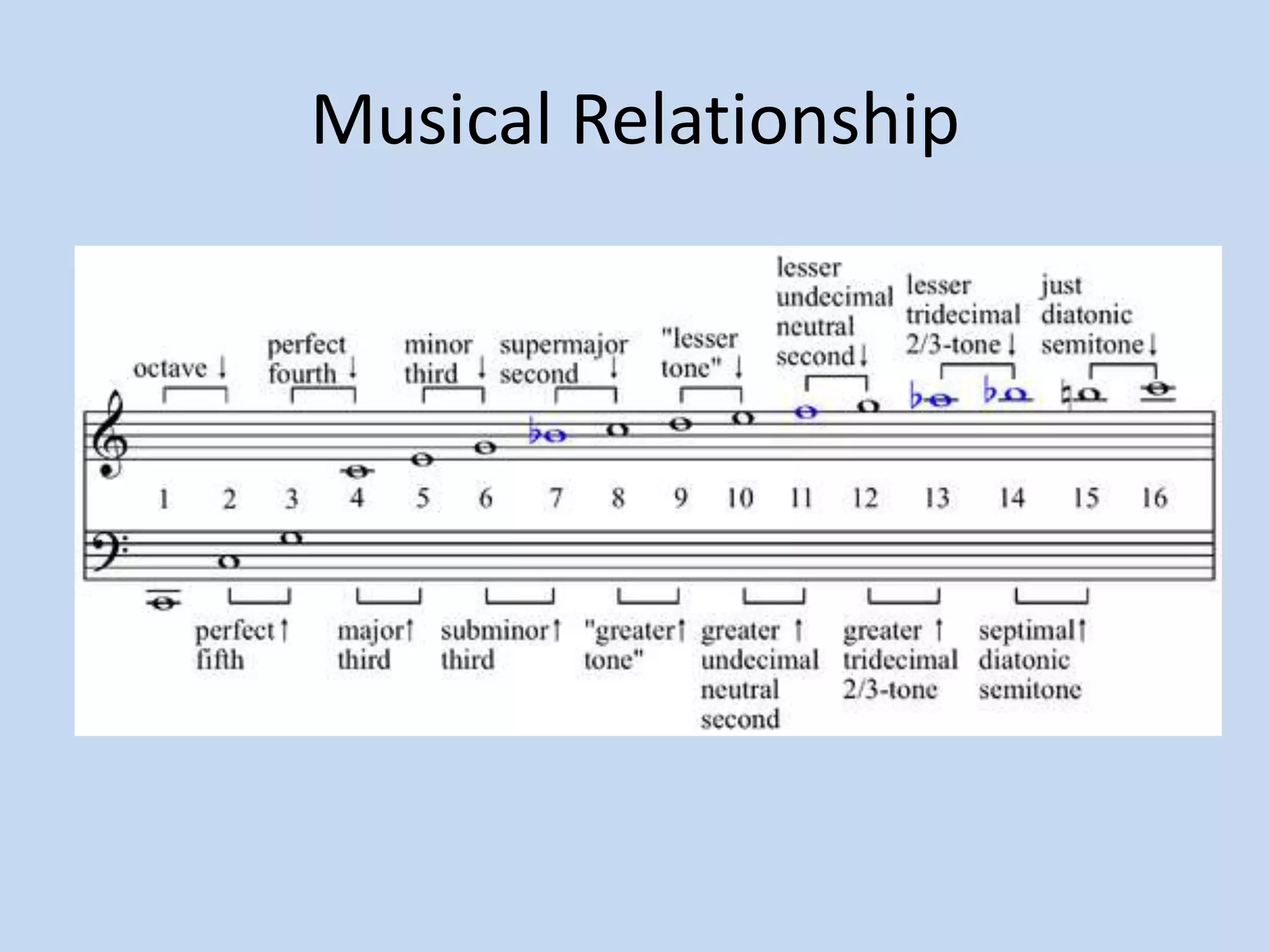
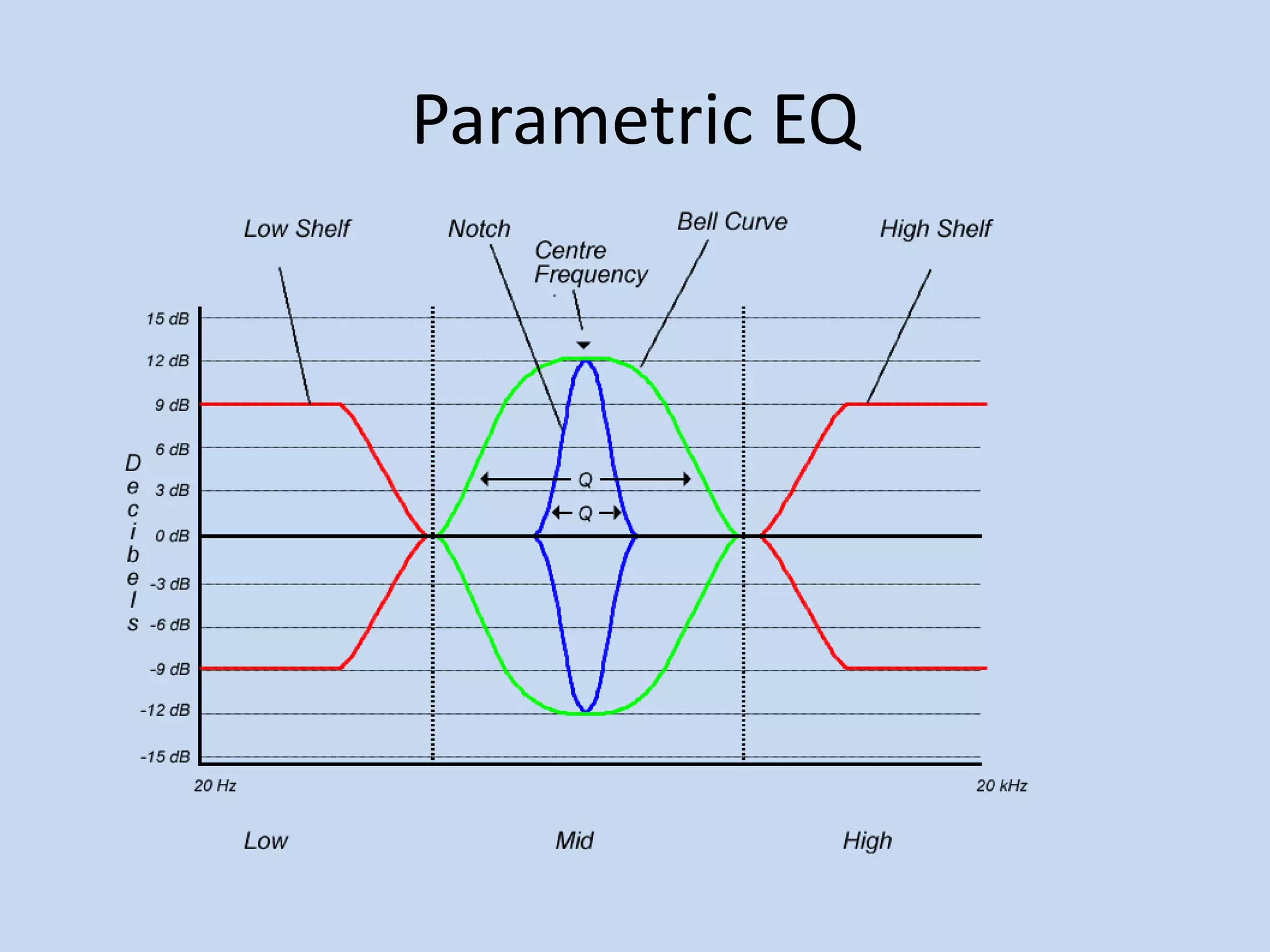
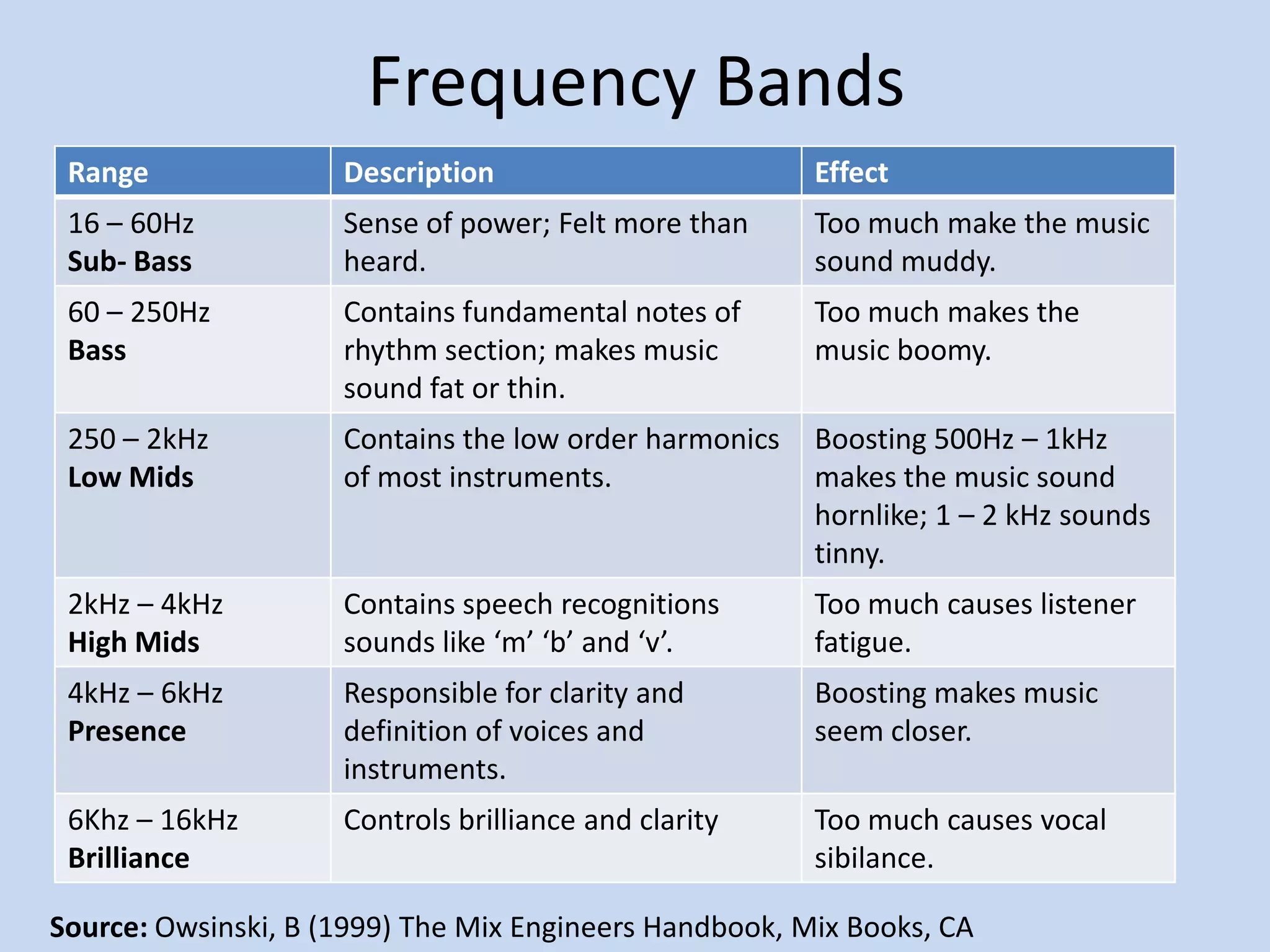
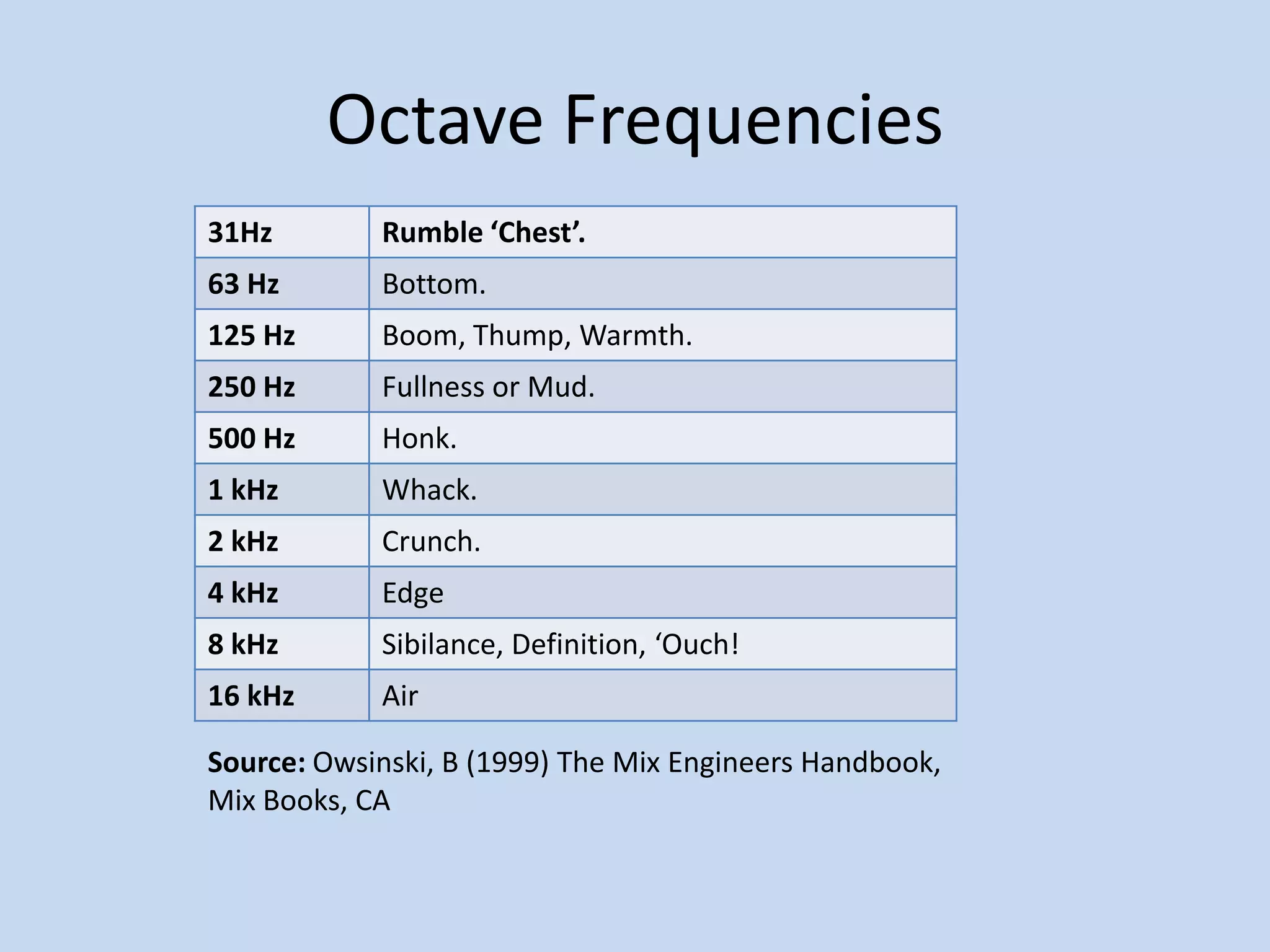
The document provides an introduction to equalizers. It explains that musical instruments produce complex vibrations that can be analyzed as a harmonic series of simpler vibrations, with the simplest being a pure sine wave. An equalizer works by adjusting the balance of these partials and overtones, altering an instrument's tone. The two main types of equalizers are parametric, which target specific frequencies, and graphic, which use overlapping notch filters to hone in on issues. Equalizers can be used correctively, creatively, or to blend sounds effectively.