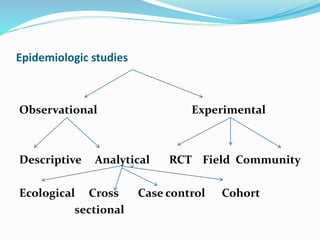
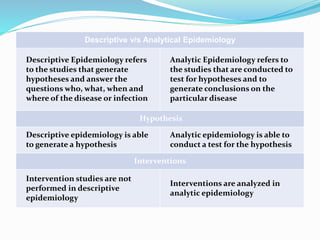
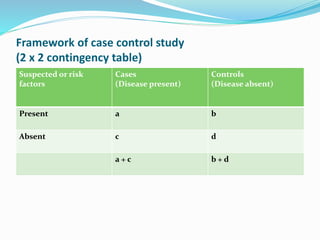
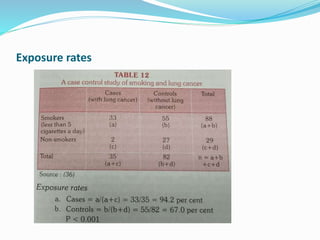
This document discusses descriptive and analytic epidemiology studies. Descriptive studies generate hypotheses and answer questions of who, what, when and where regarding disease. Analytic studies test hypotheses and answer why and how questions. Case control studies are an example of an analytic study. They are retrospective and compare exposure between cases (with disease) and controls (without disease). Exposure rates are calculated and odds ratios are used to estimate disease risk associated with an exposure. Bias can occur from confounding, recall, selection, or information collection.