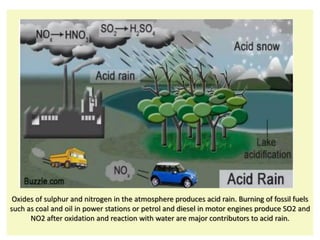
Environmental chemistry deals with studying the interaction of chemicals and their effects on the environment and living things. It covers important areas like personal hygiene, pollution, and health hazards. There are several types of pollution including soil, water, and air pollution. Soil pollution stems from waste dumping, pesticides, urbanization, and mining. Water pollution comes from municipal and industrial discharge as well as other human activities. Air pollution results from the addition of undesirable materials into the atmosphere from natural phenomena and human activities, adversely affecting air quality and life. Common air pollutants include smog from vehicle emissions and power plants as well as acid rain caused by sulfur and nitrogen oxides from burning fossil fuels. Reducing pollution involves following the