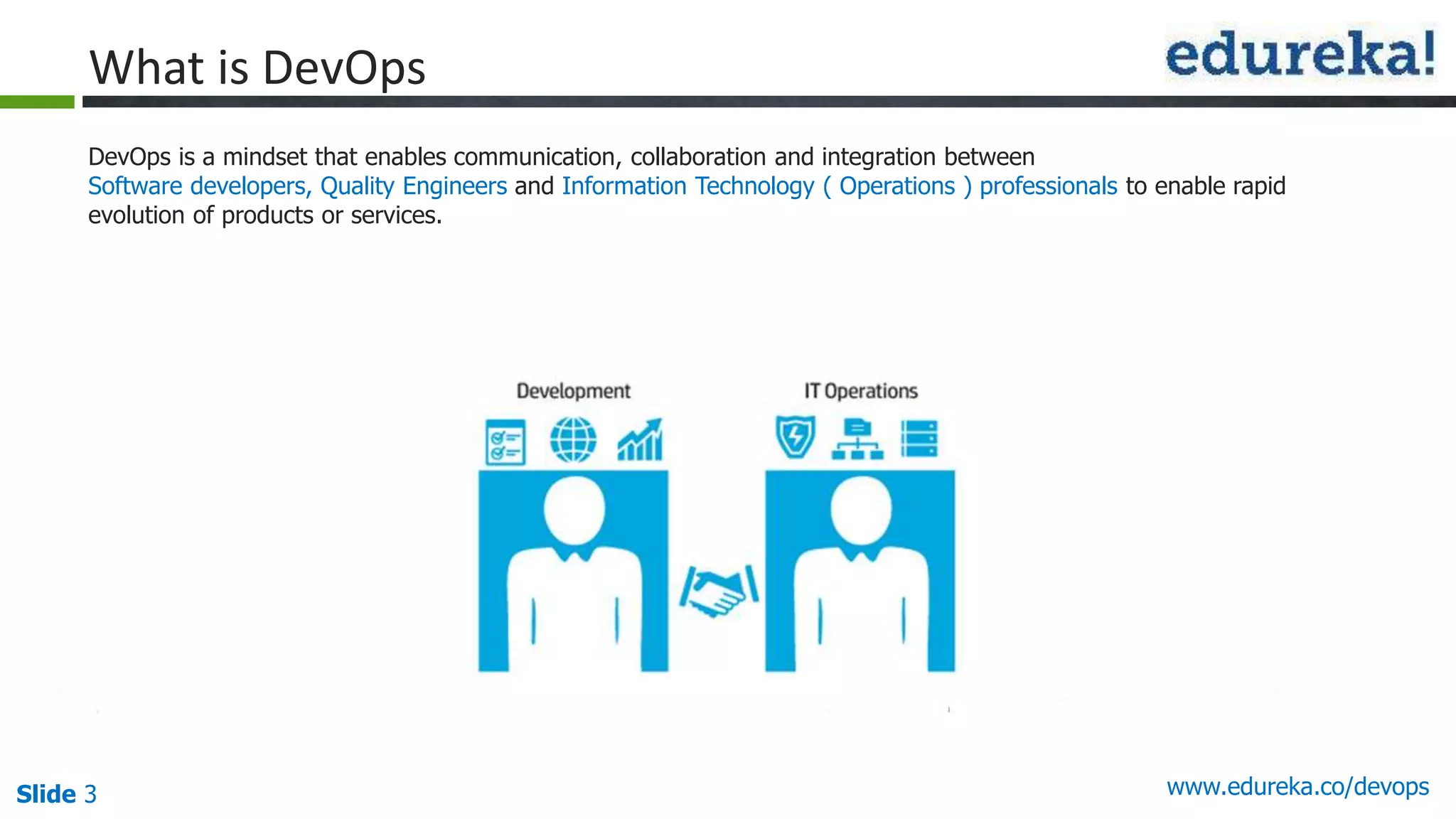
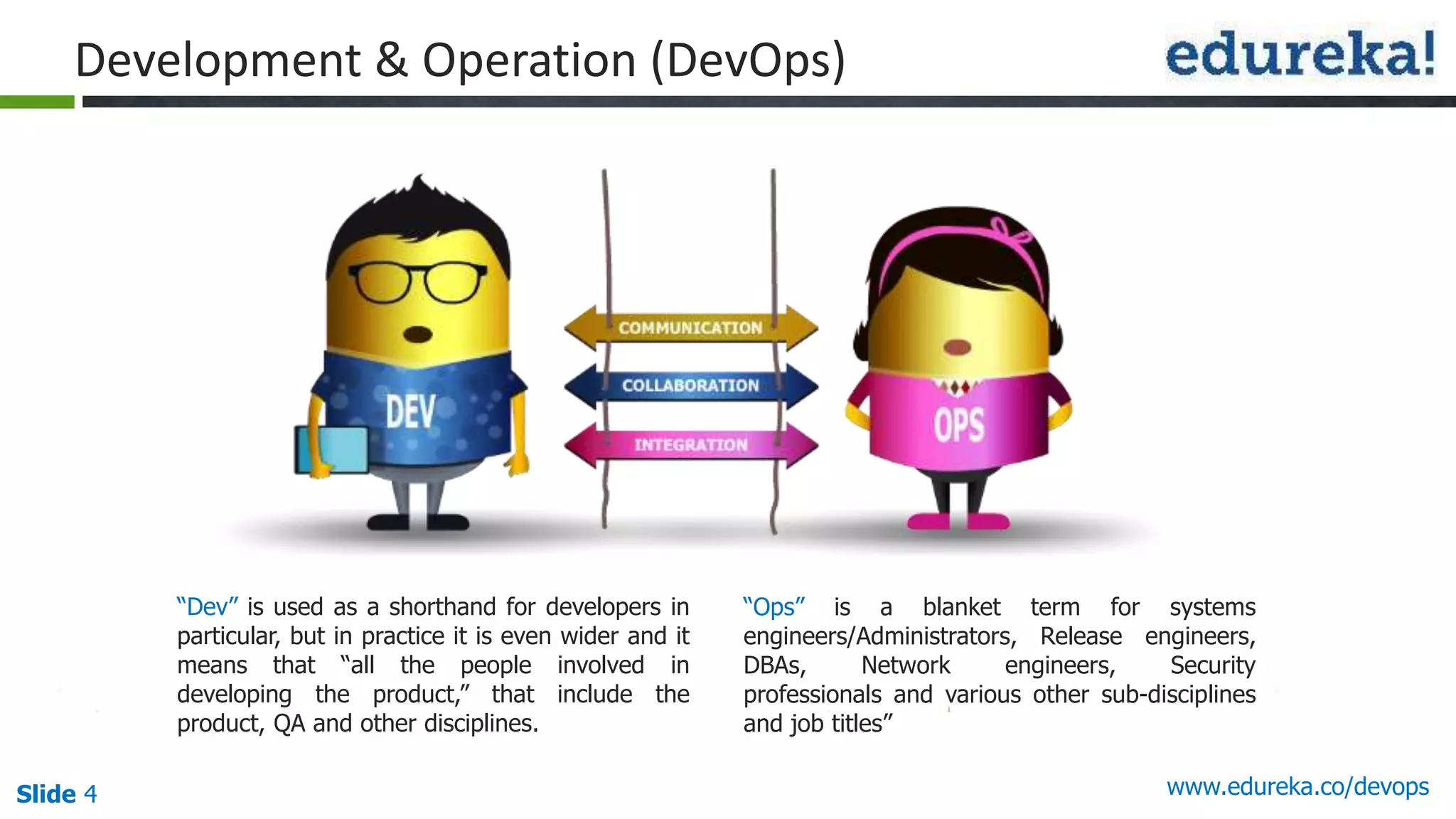
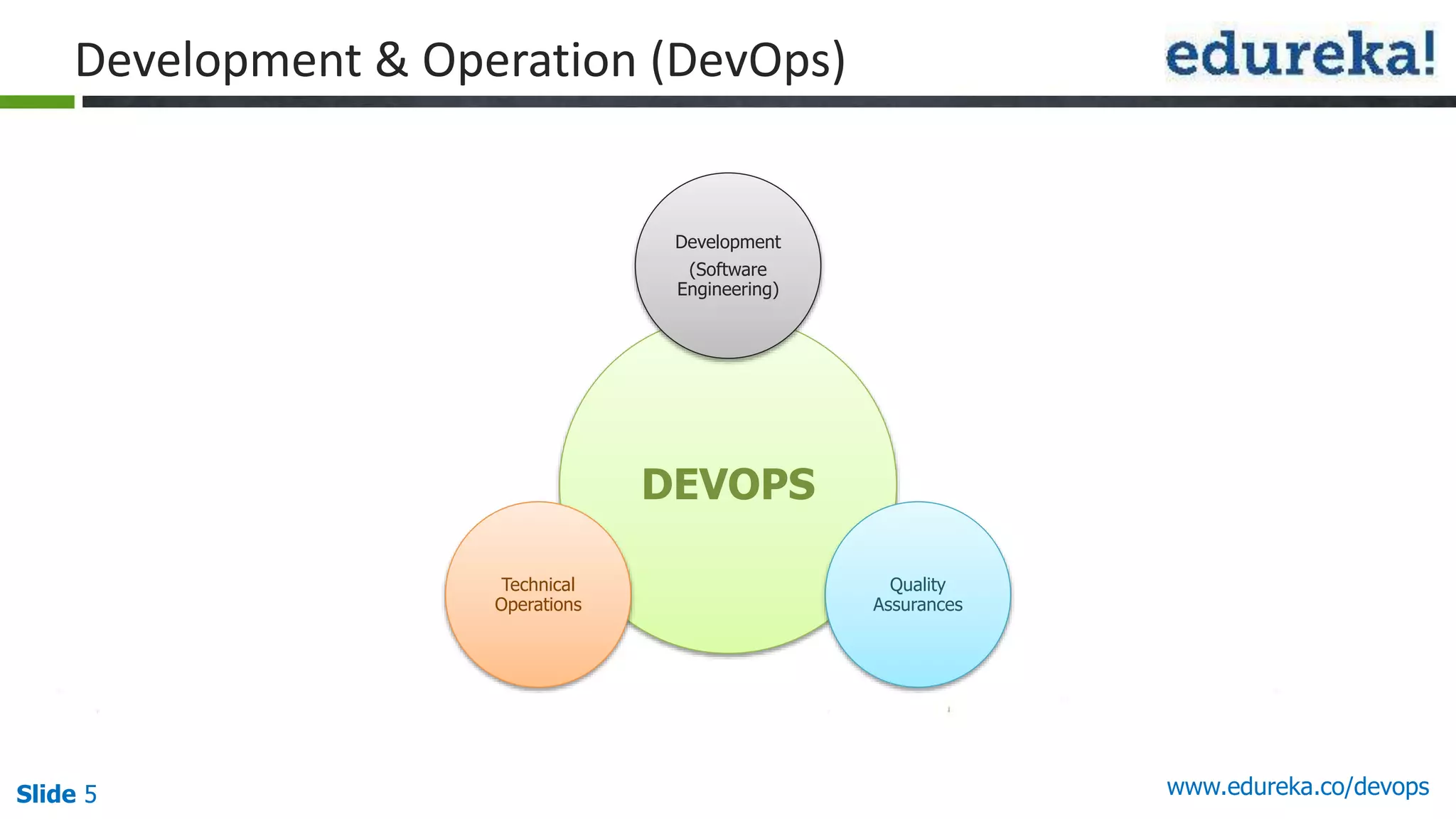
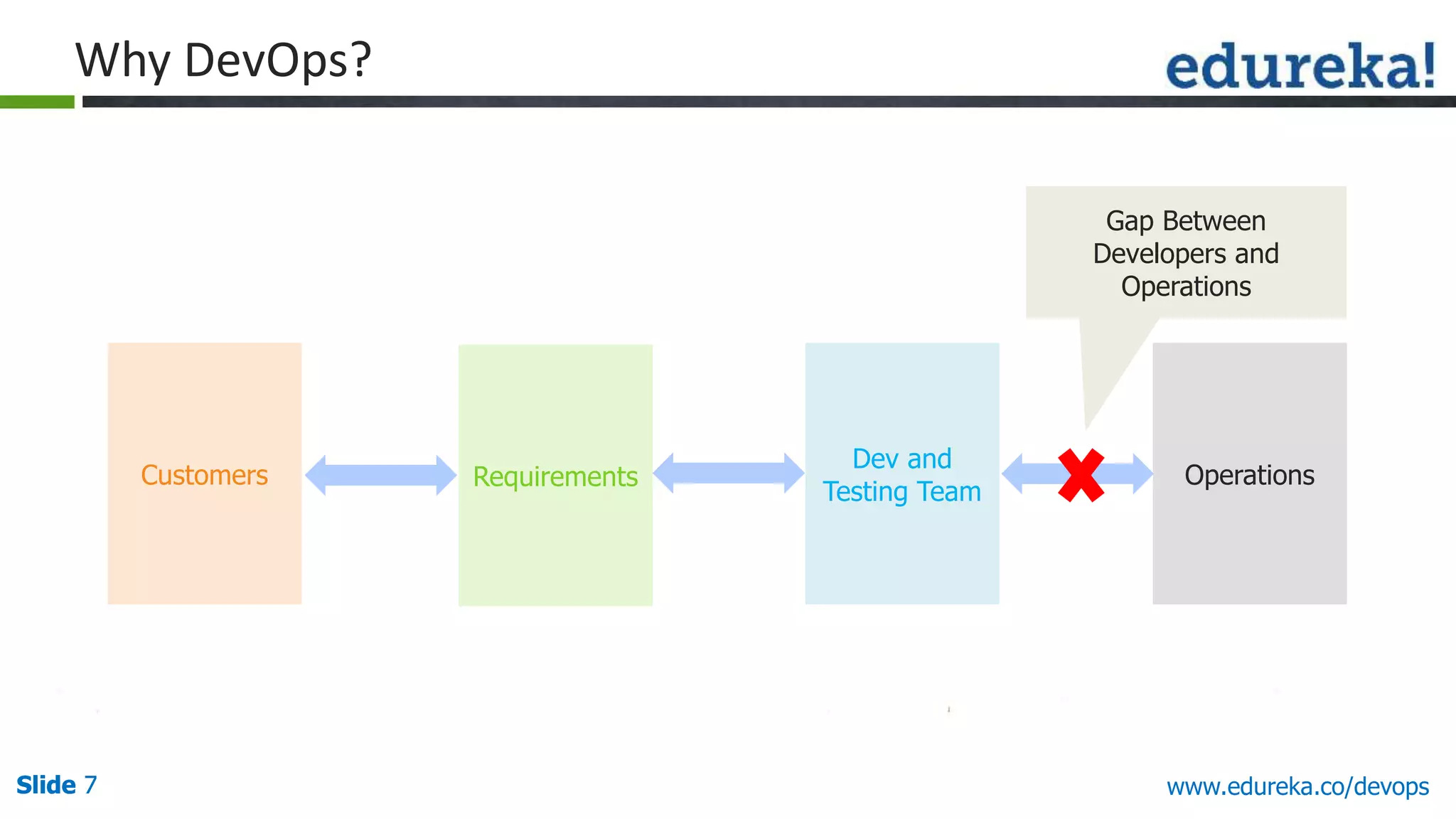
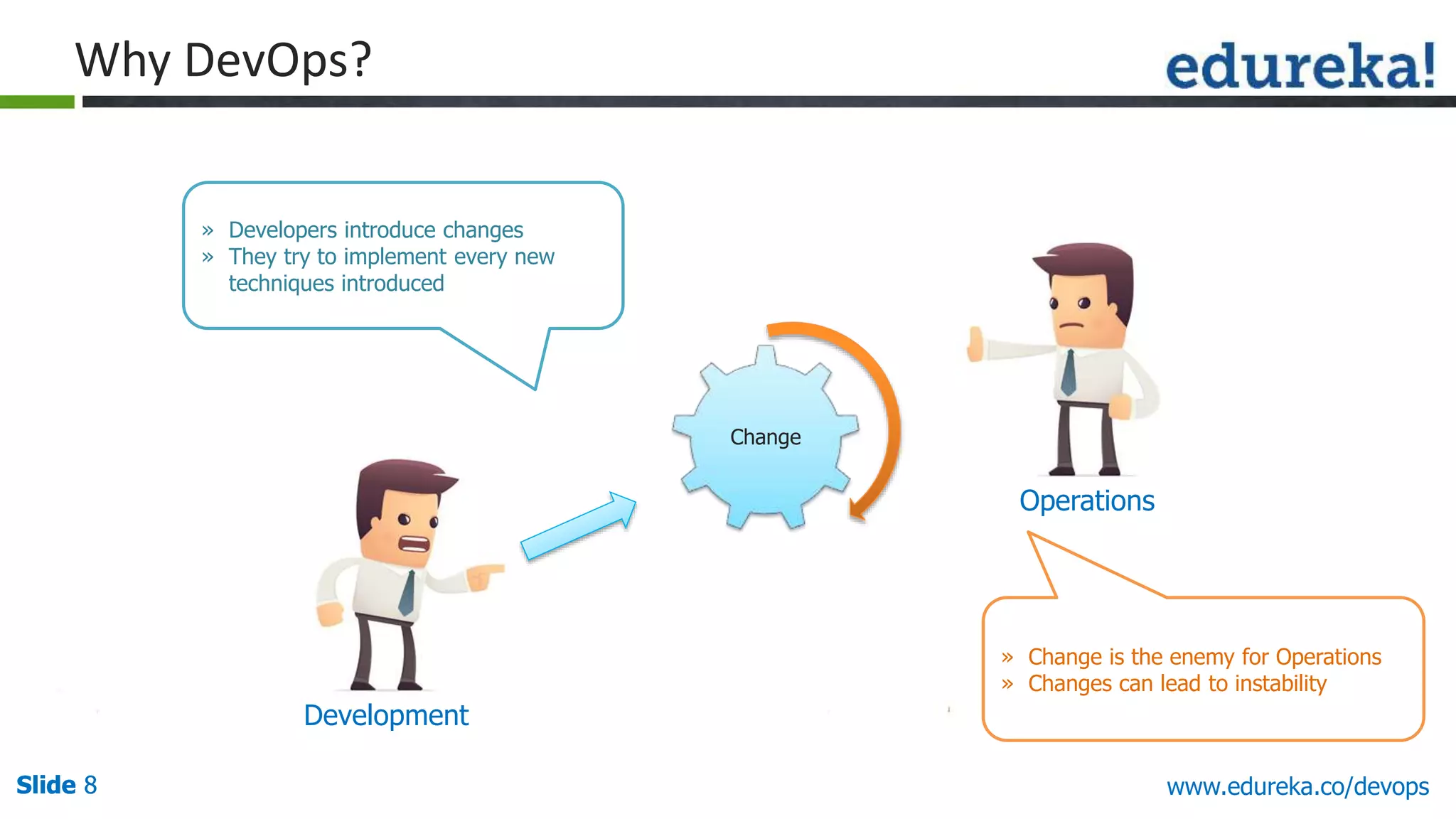
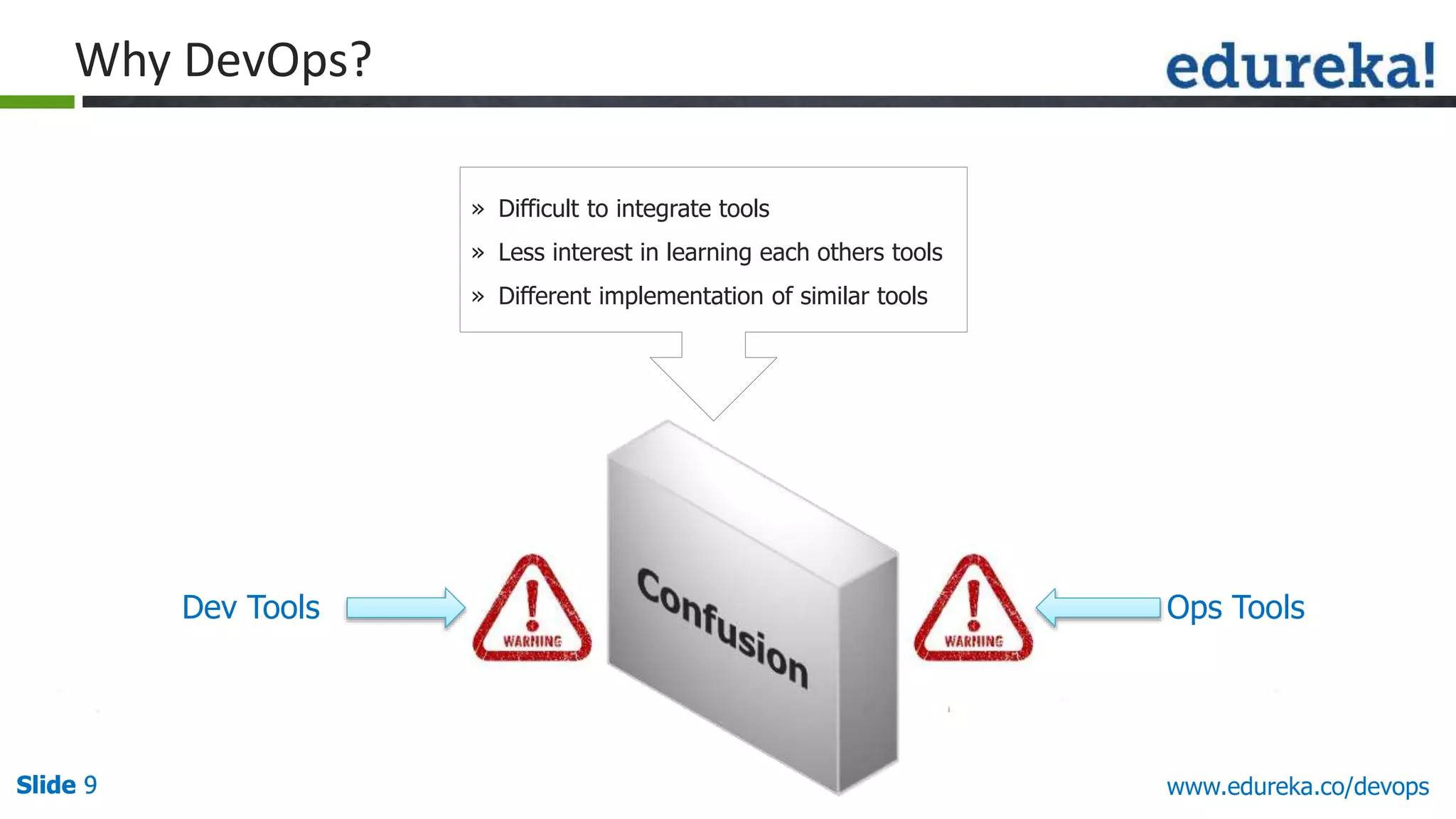
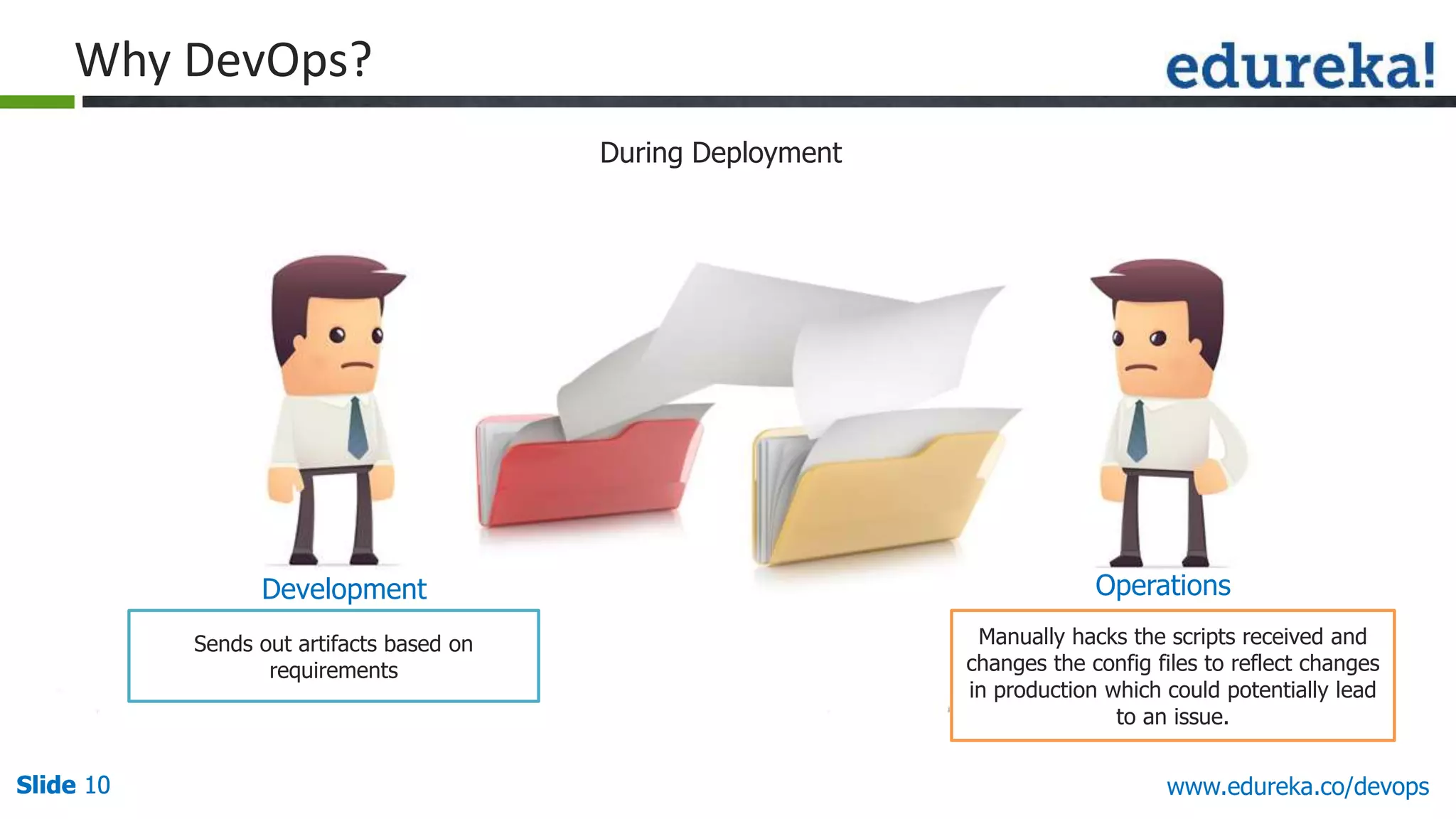
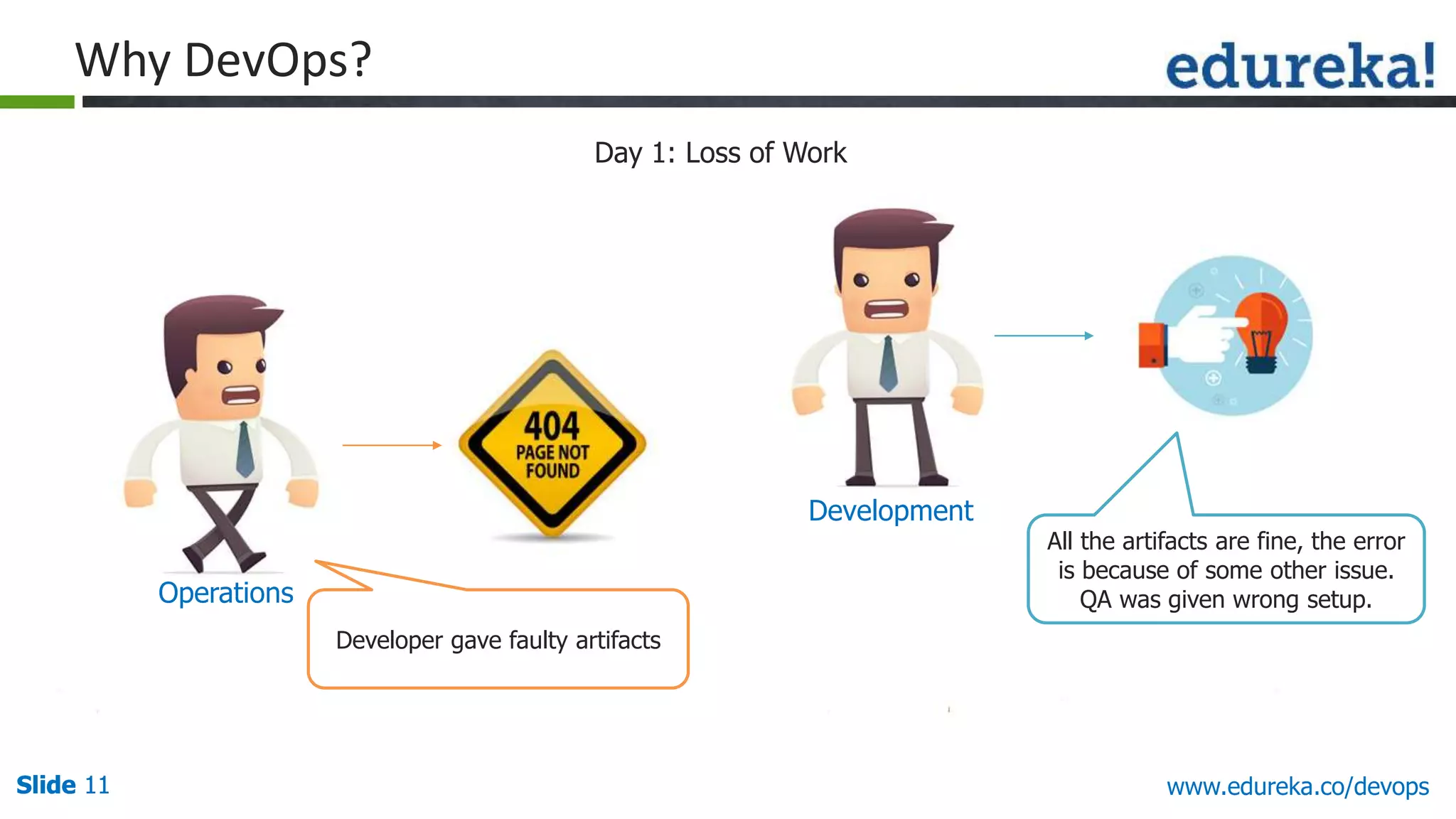
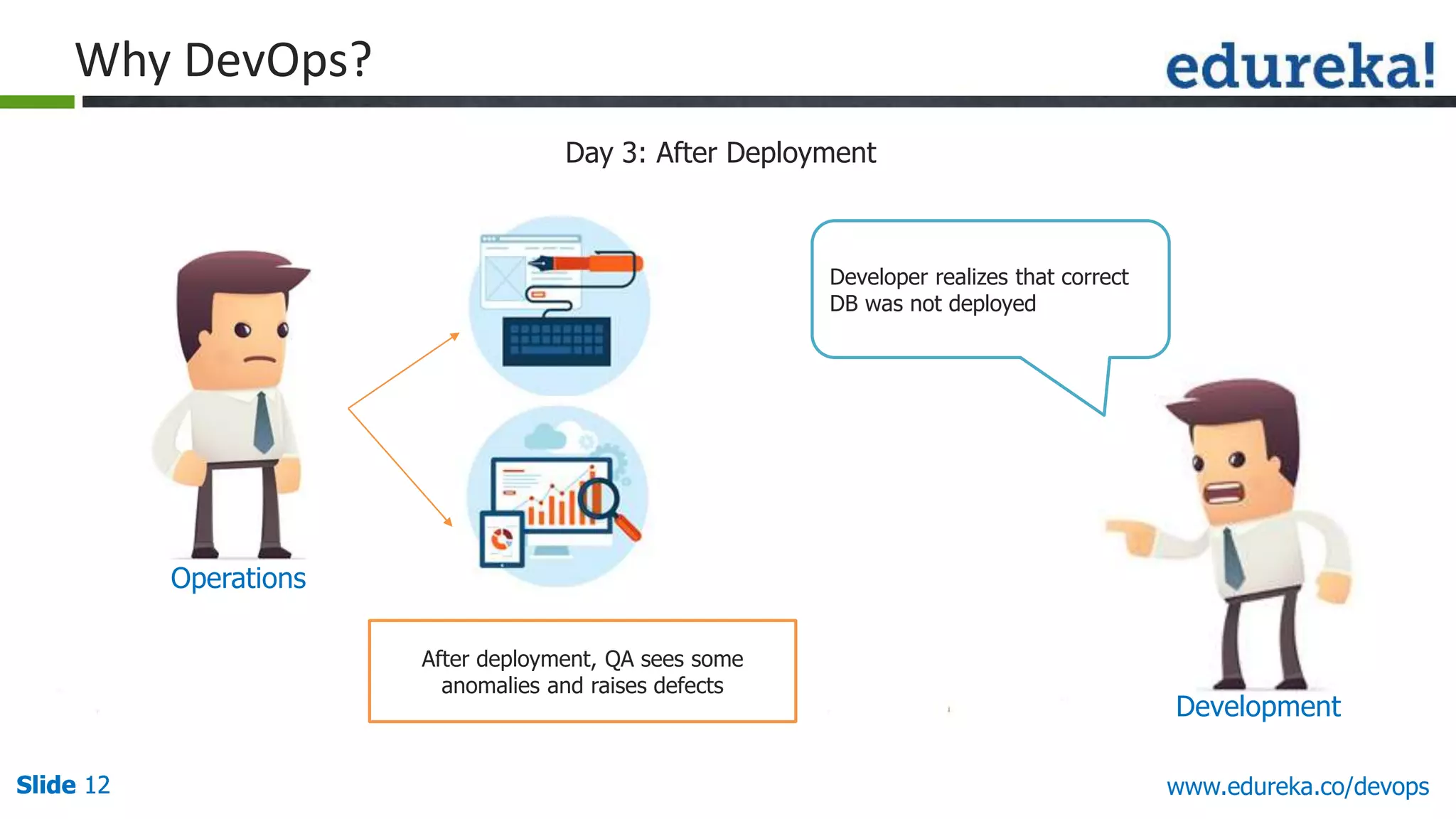
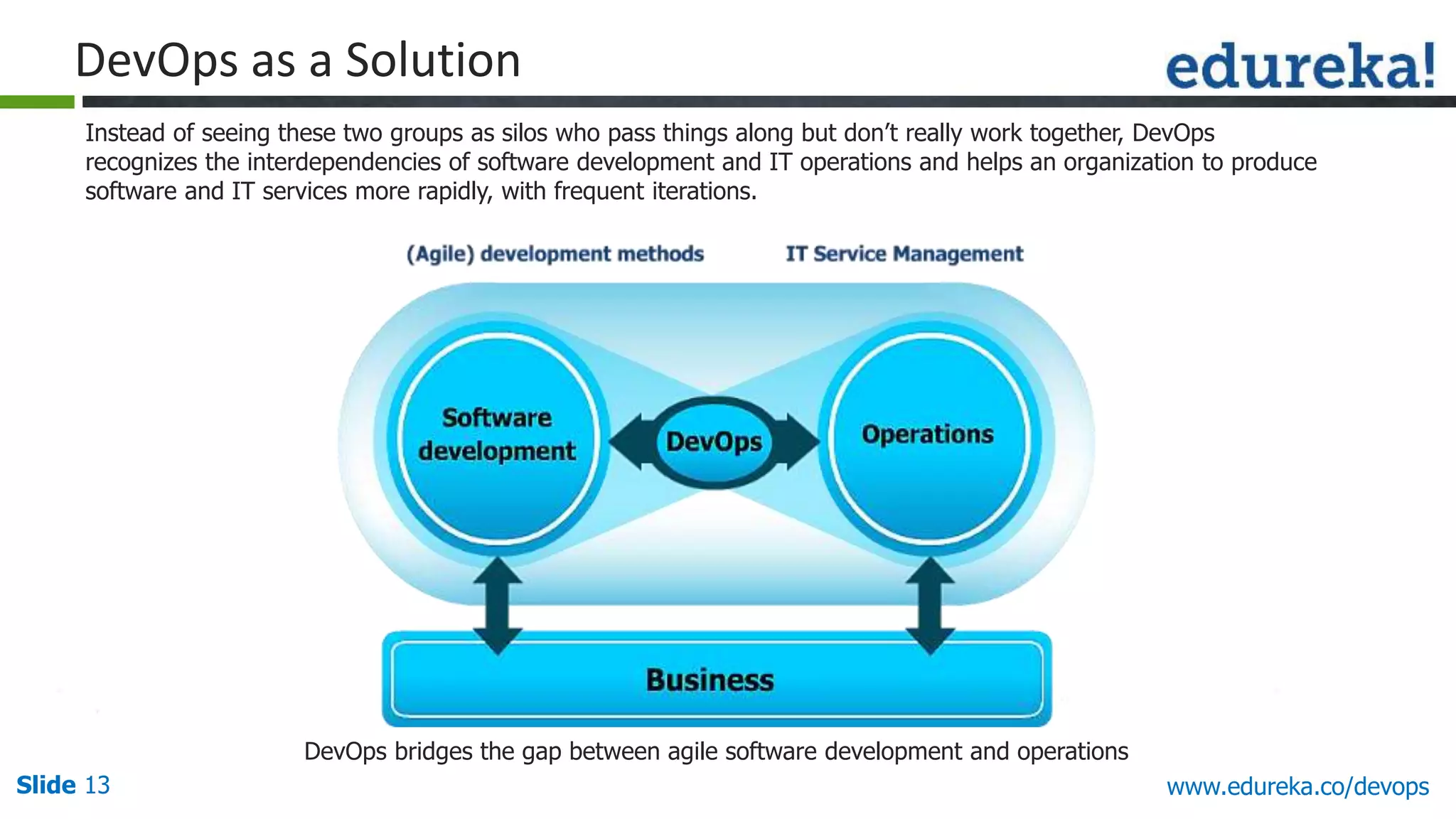
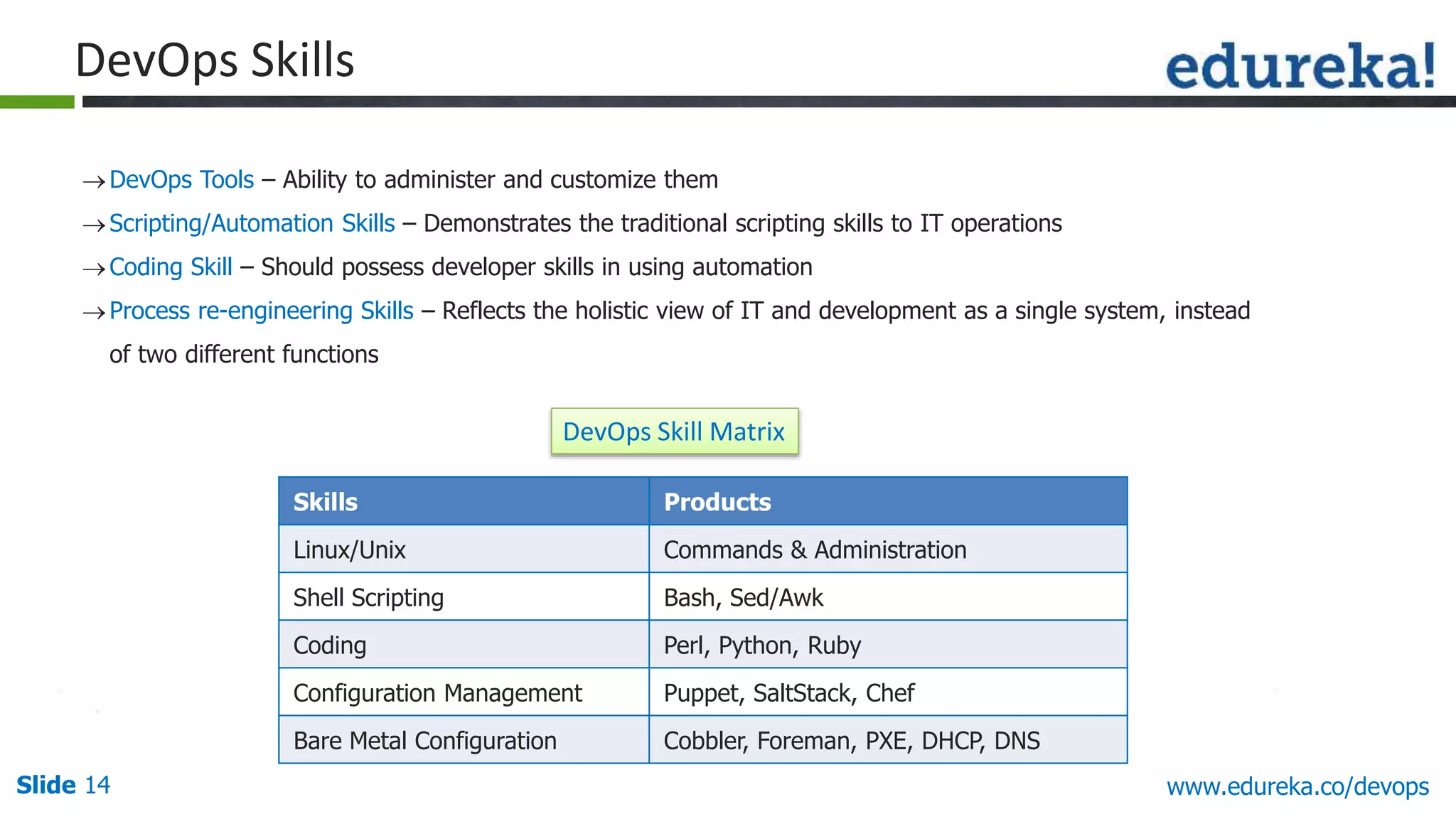
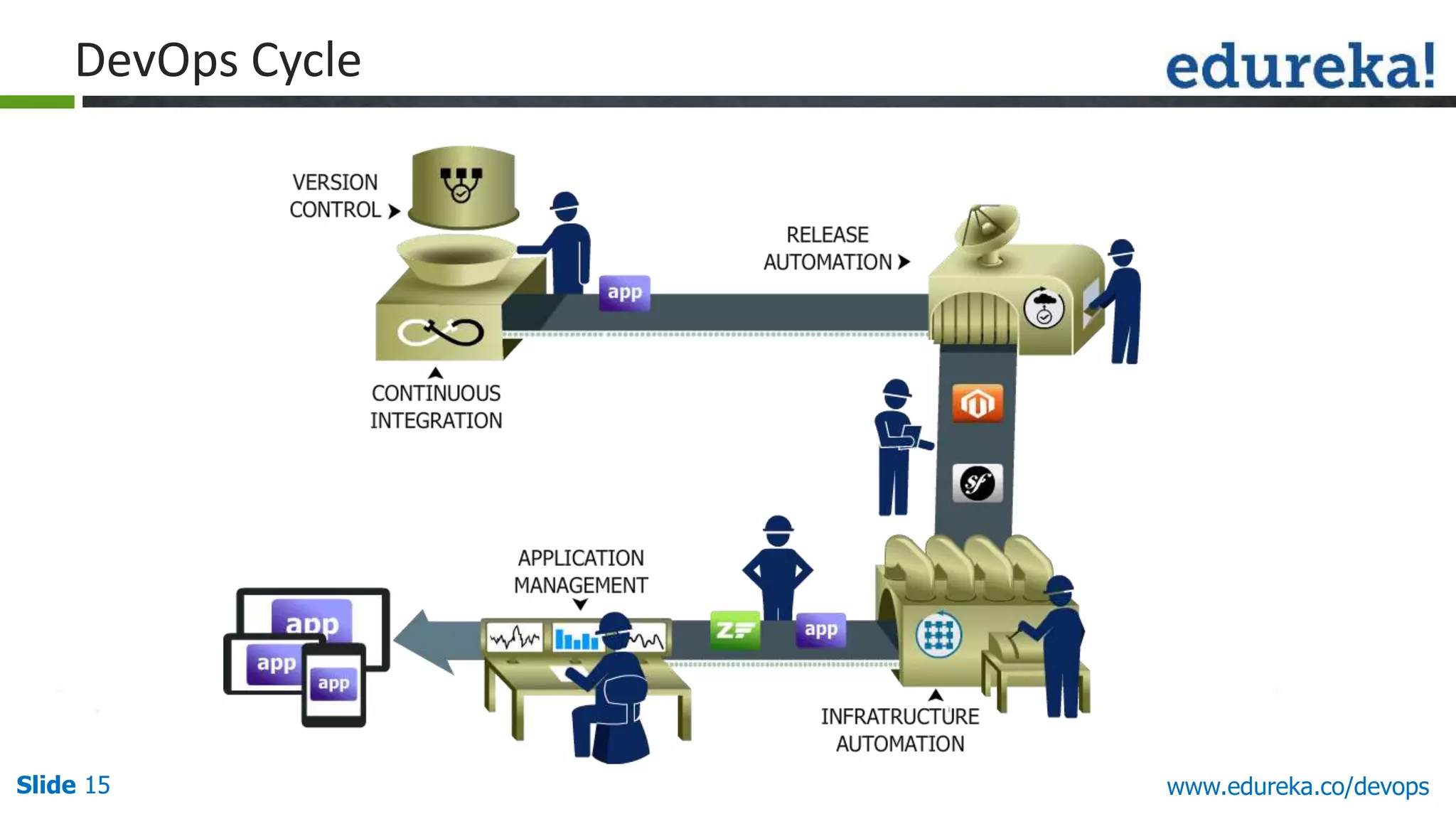
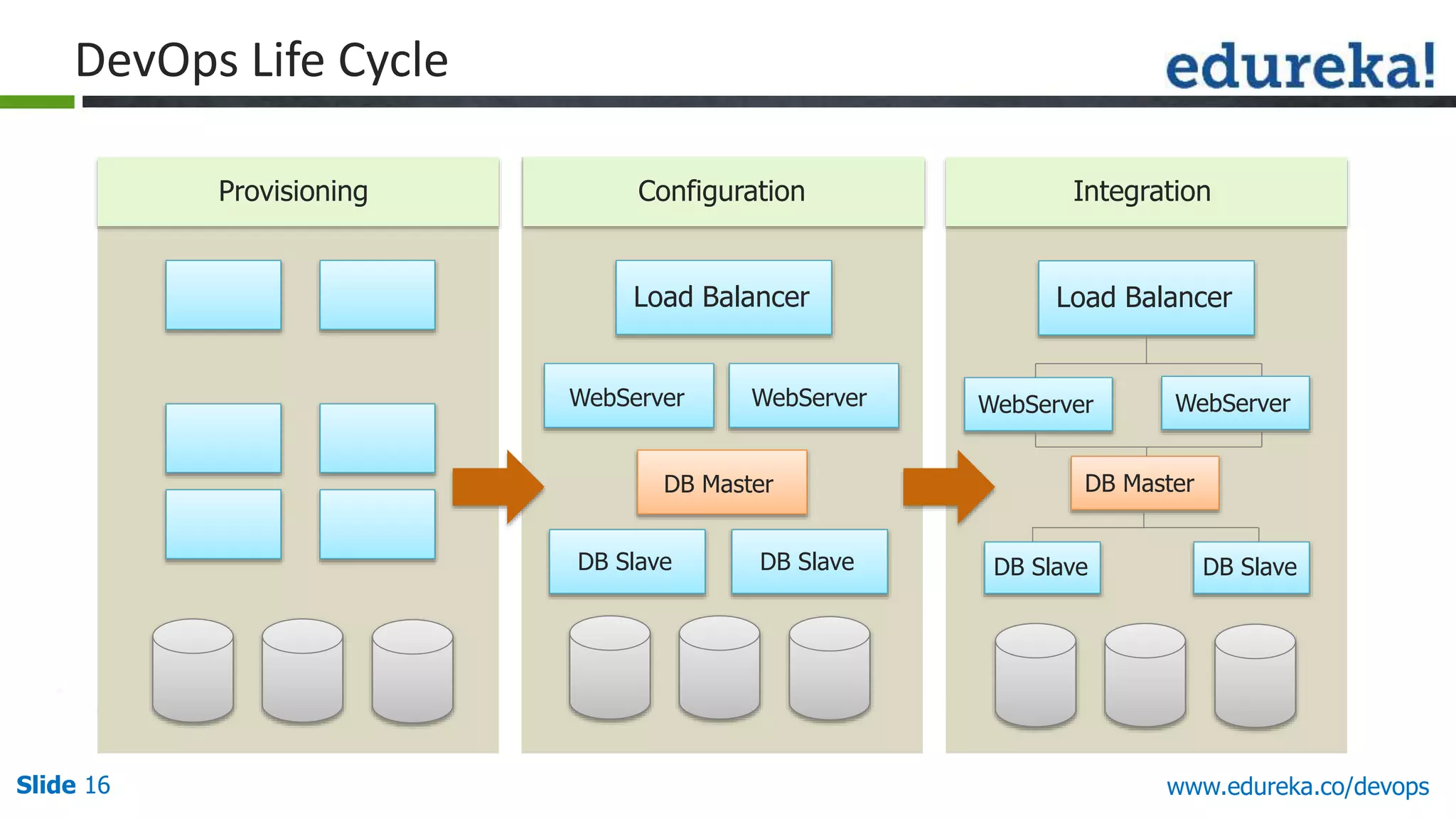
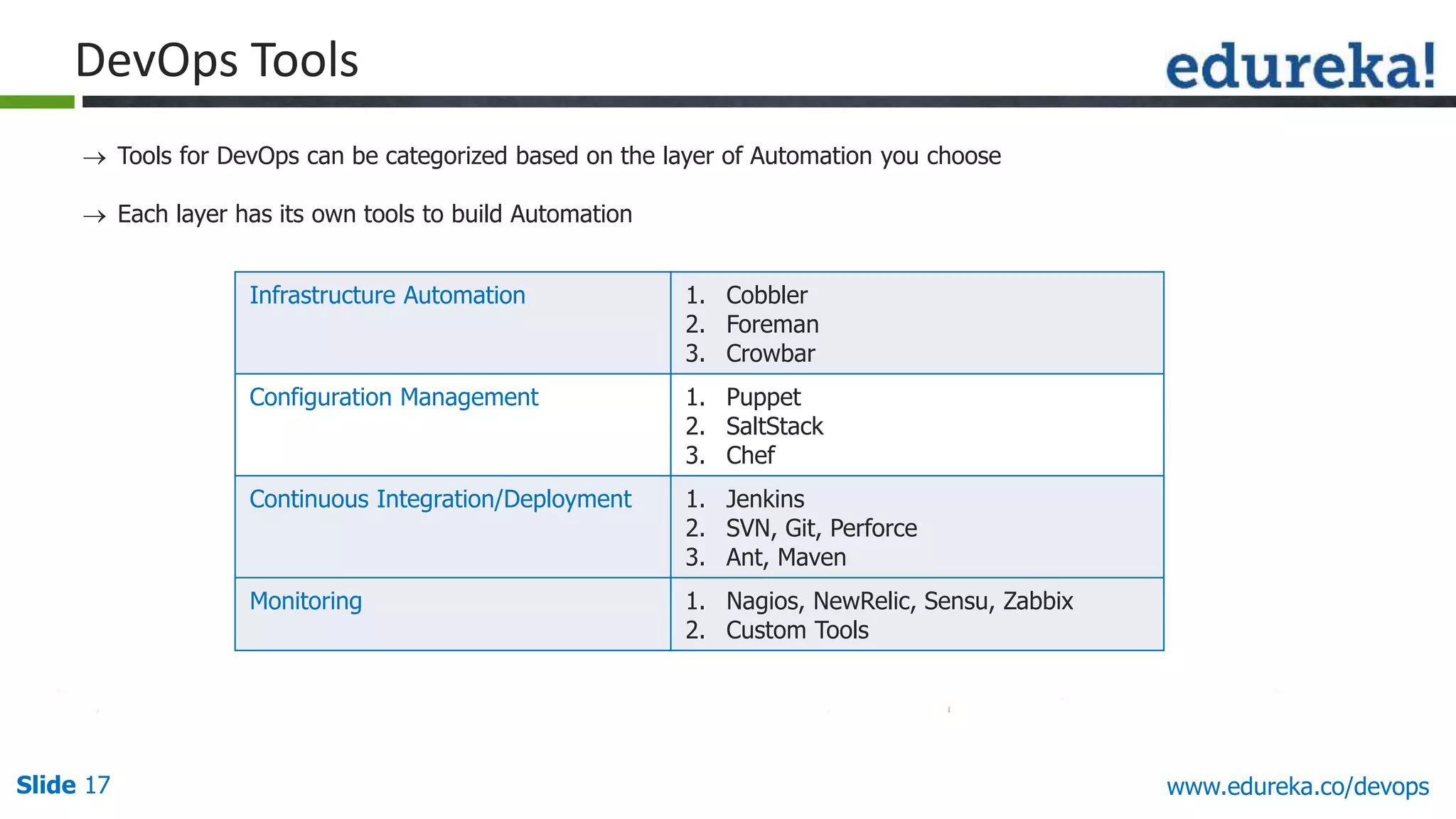
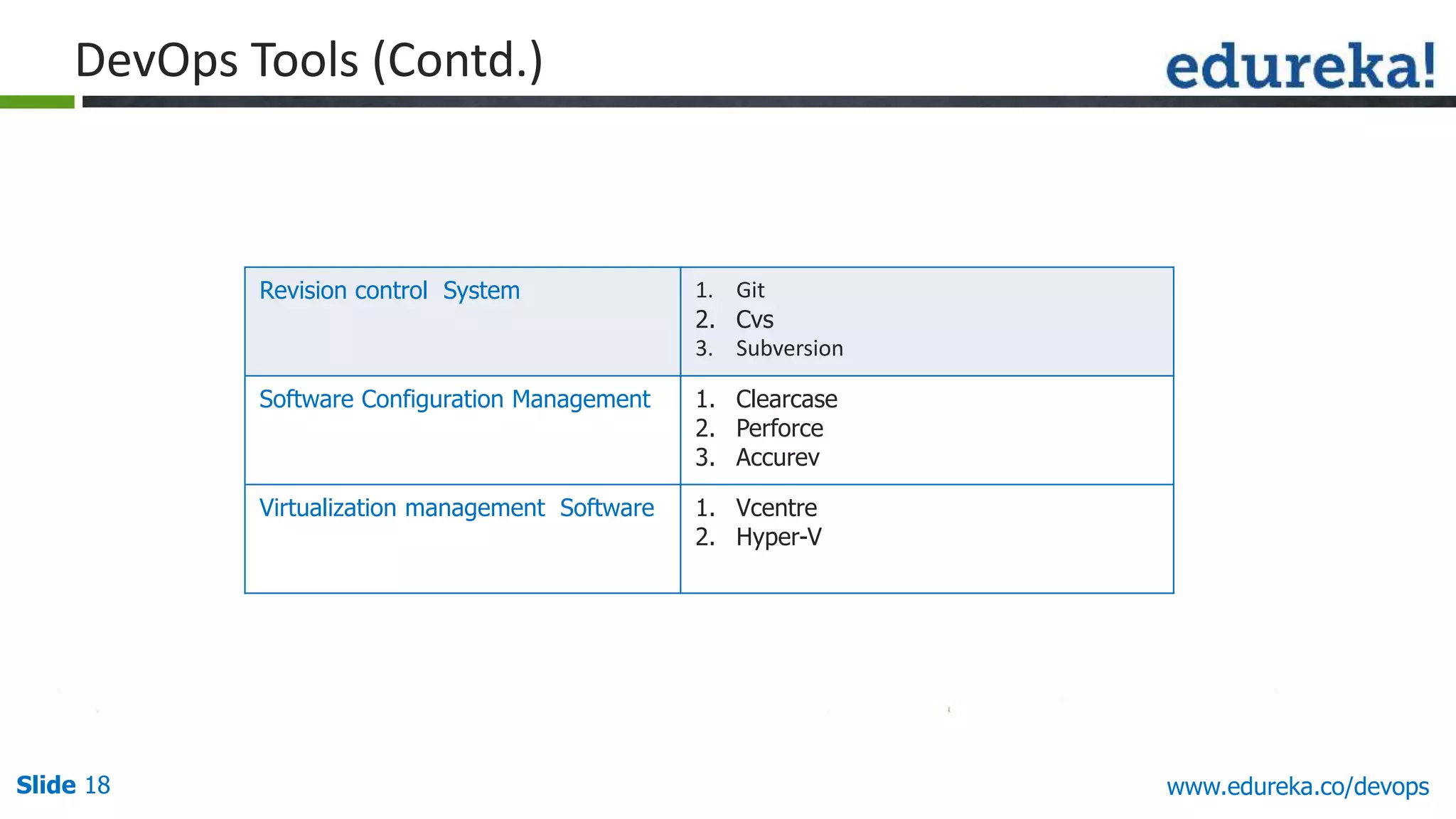
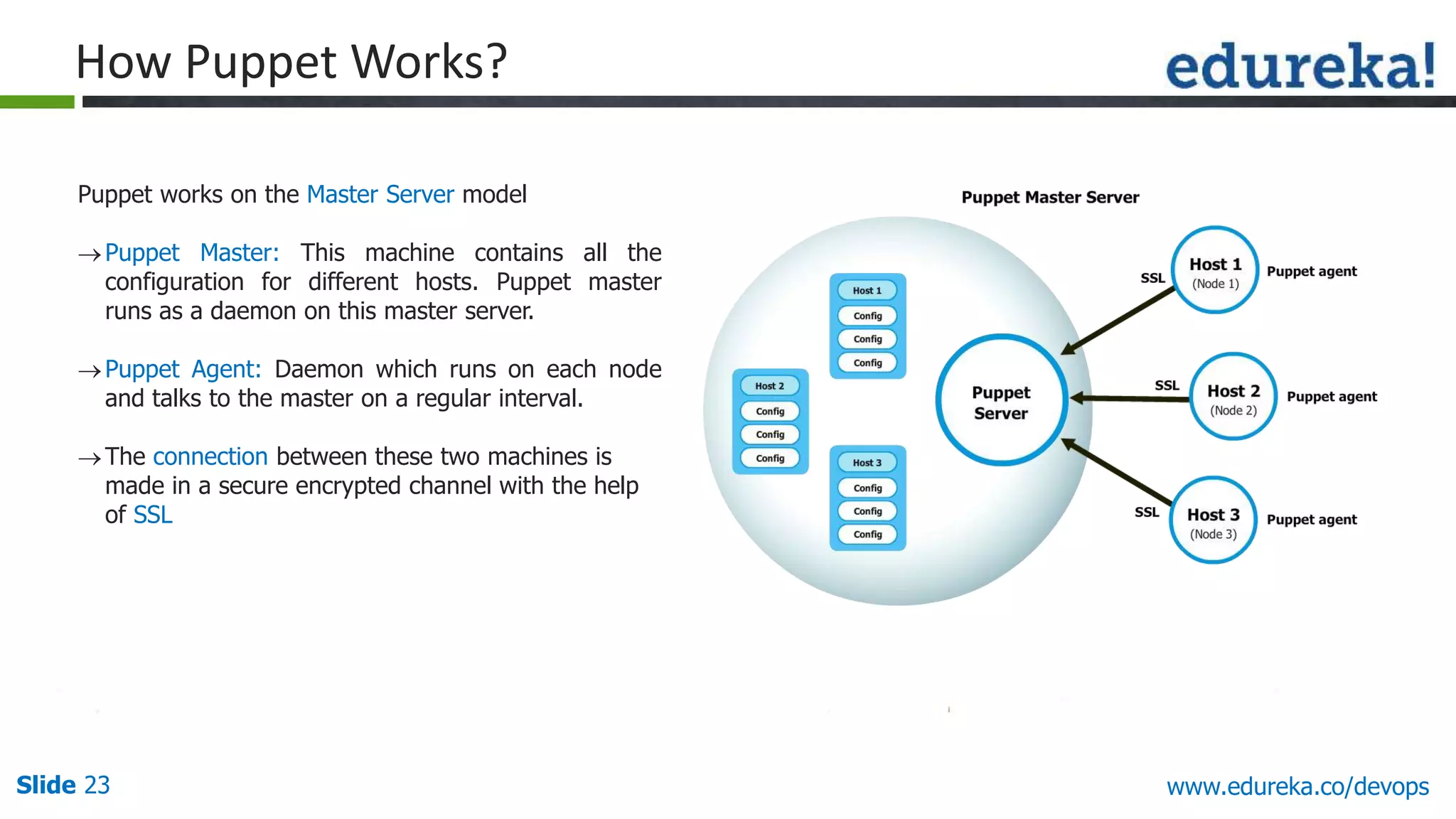
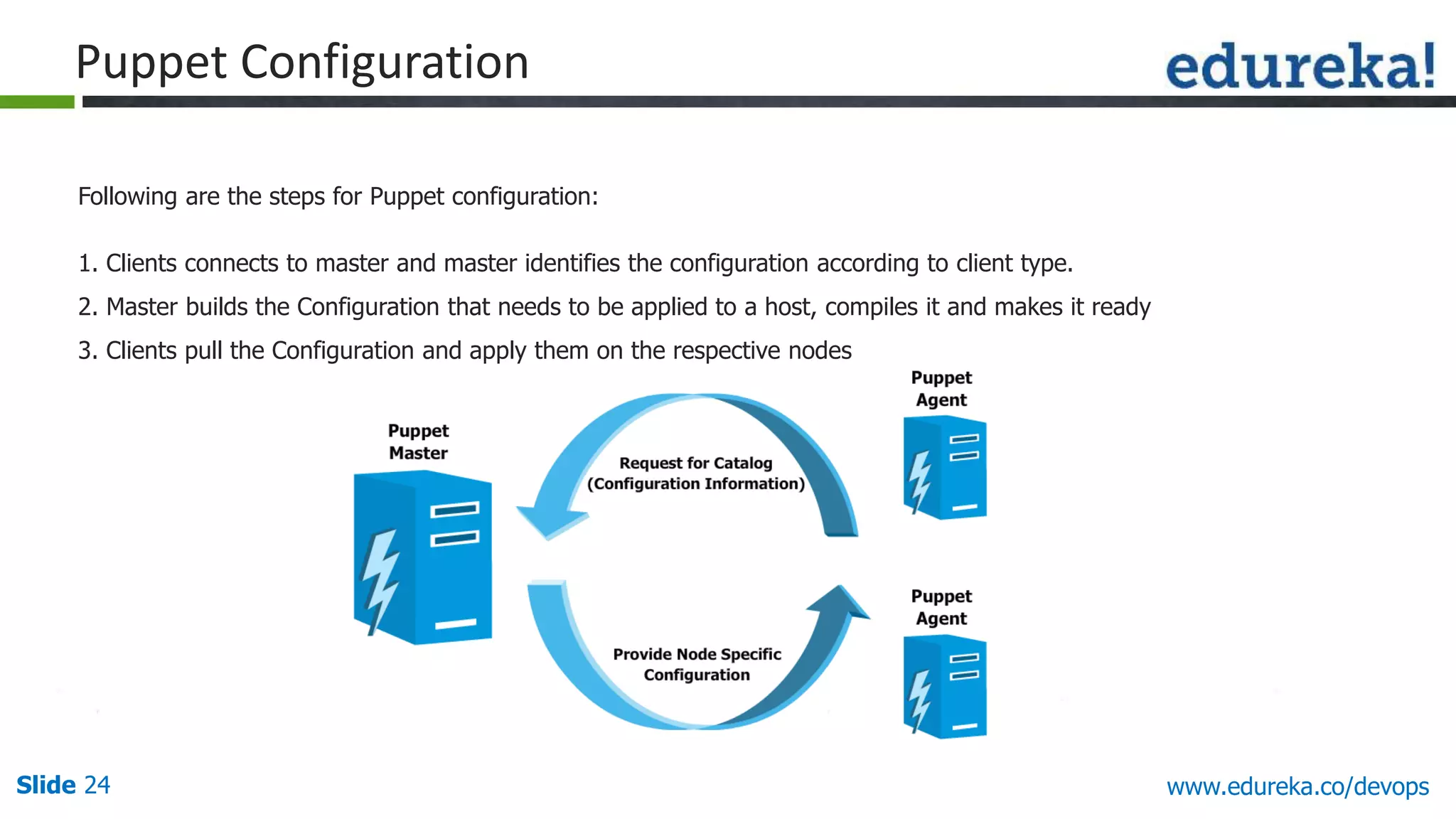
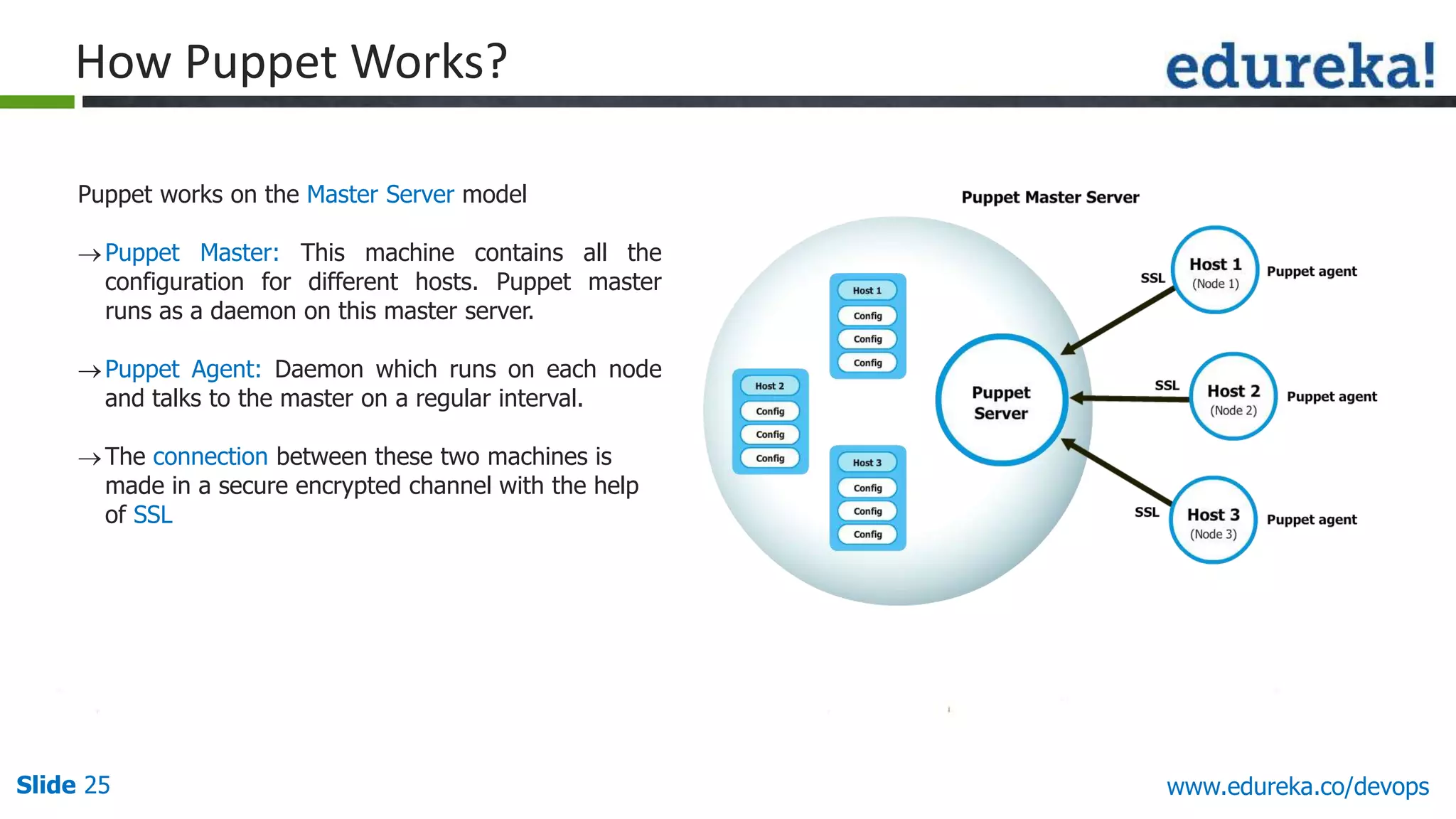
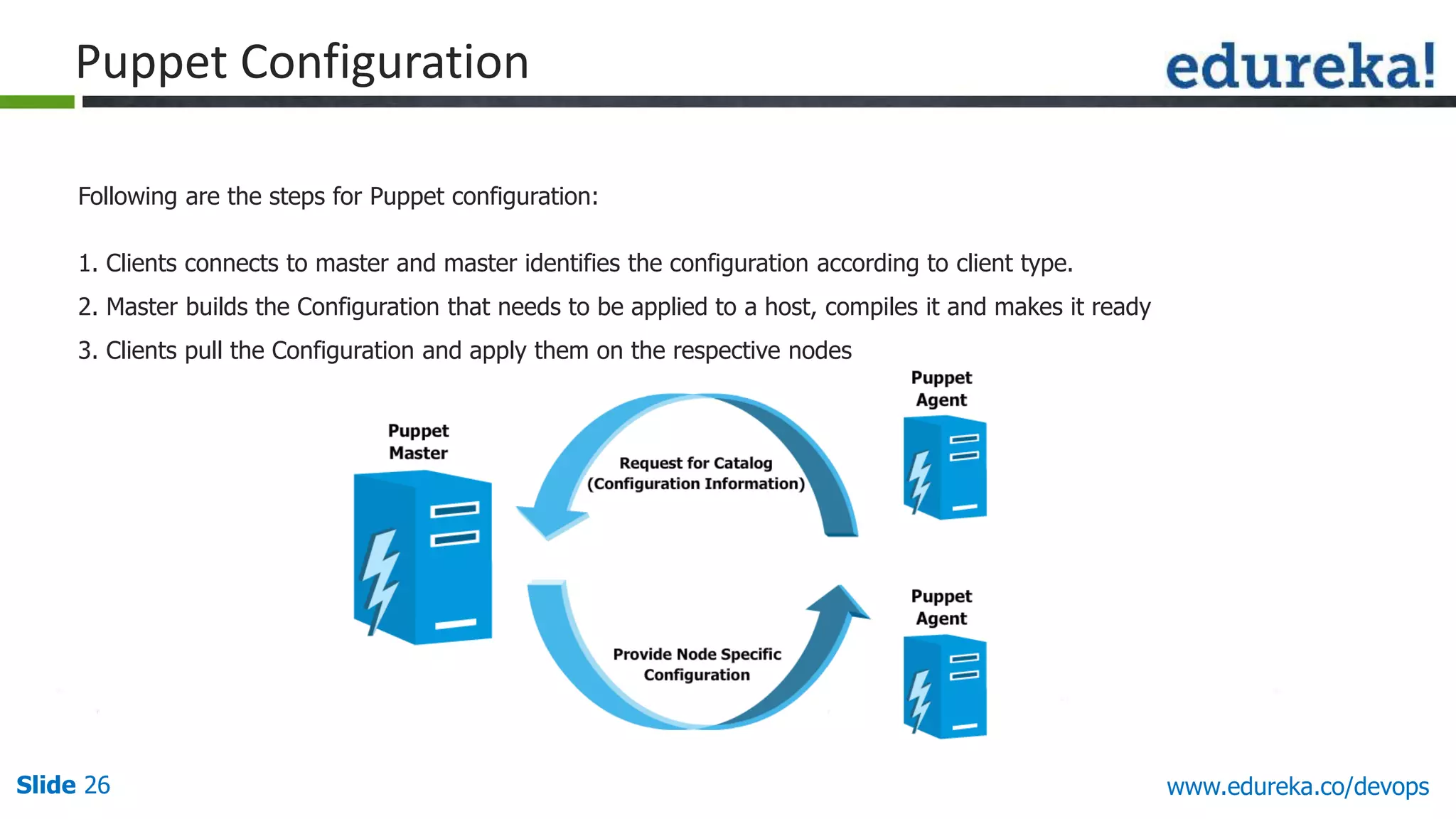
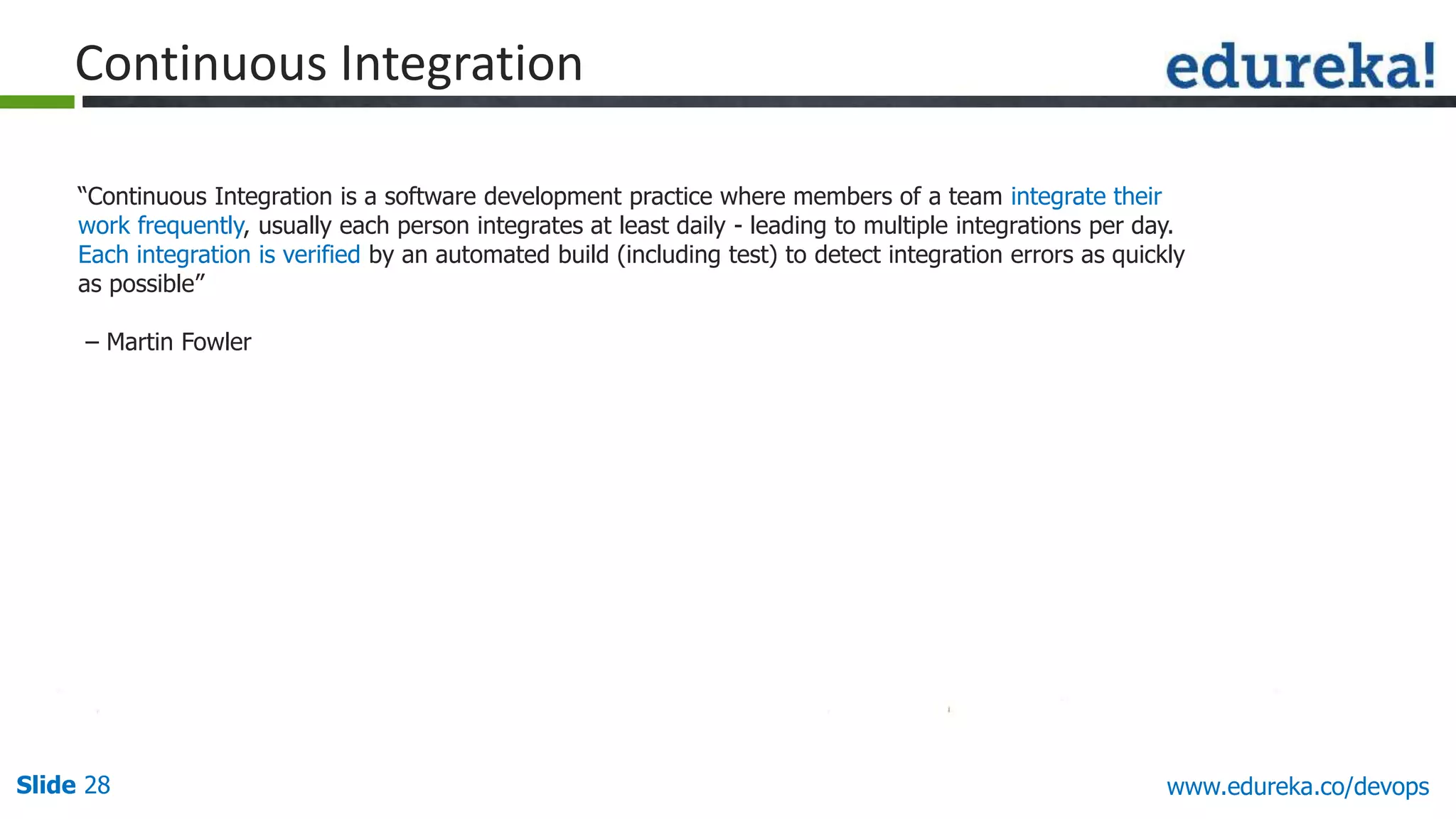
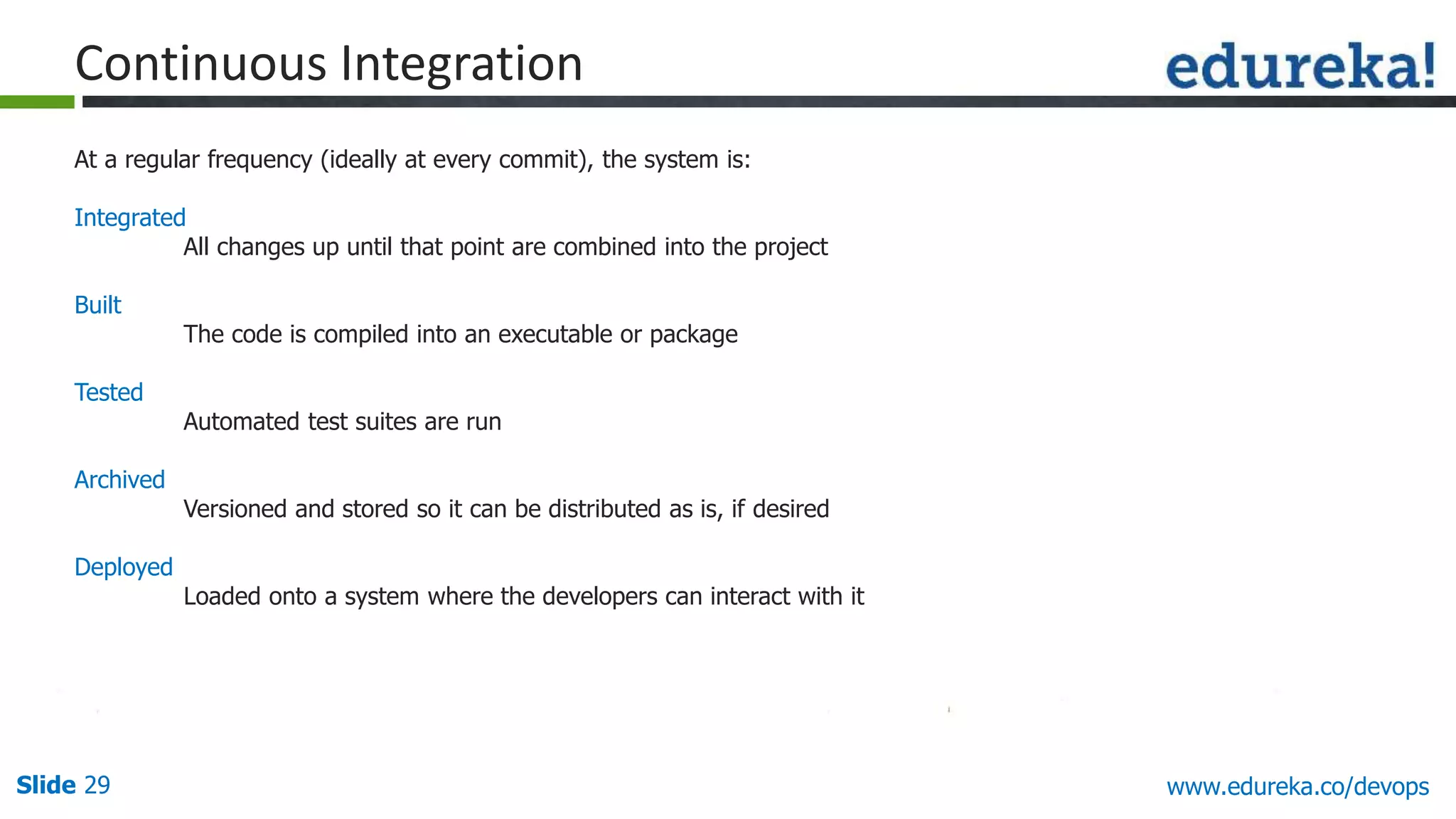
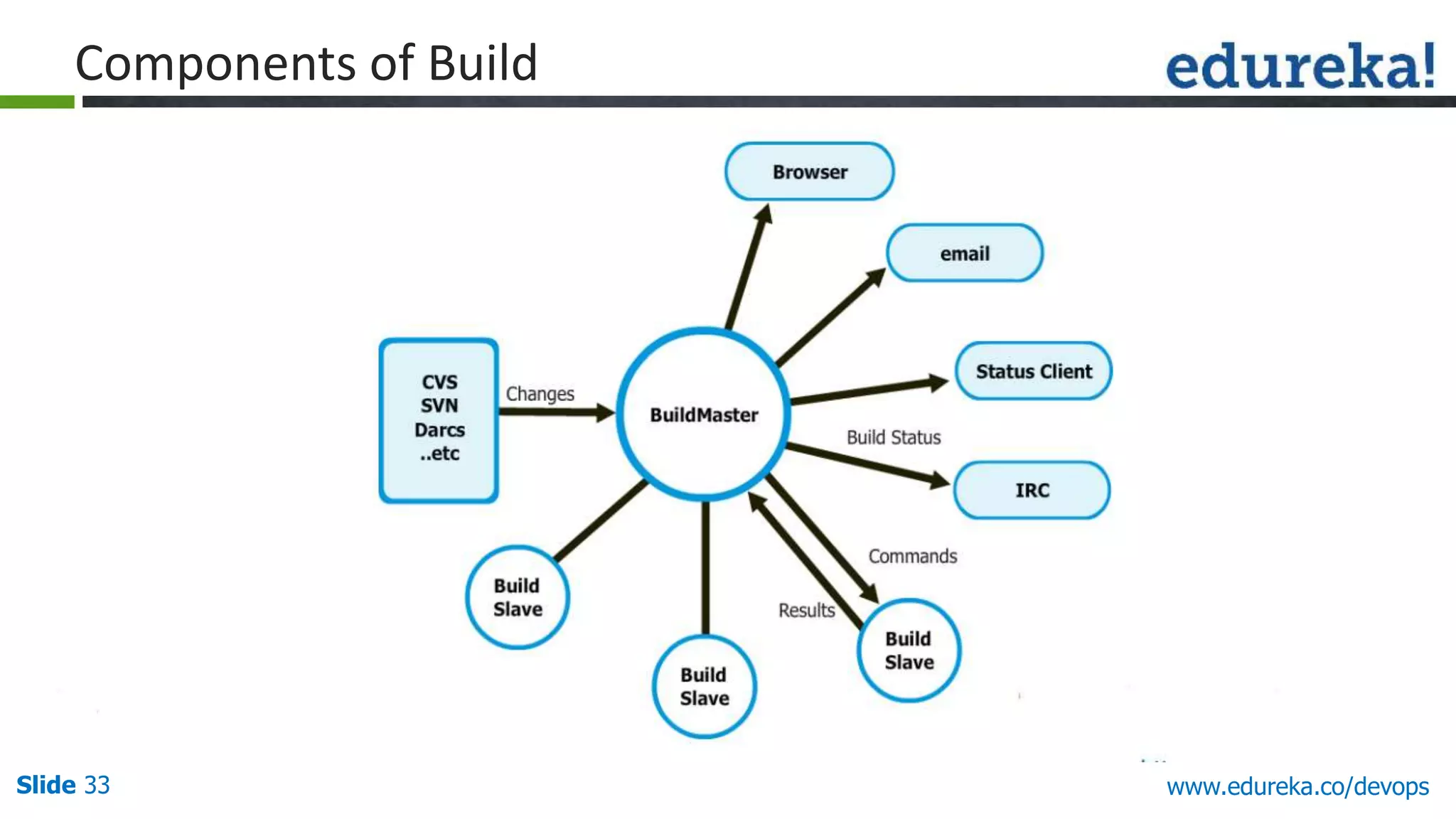
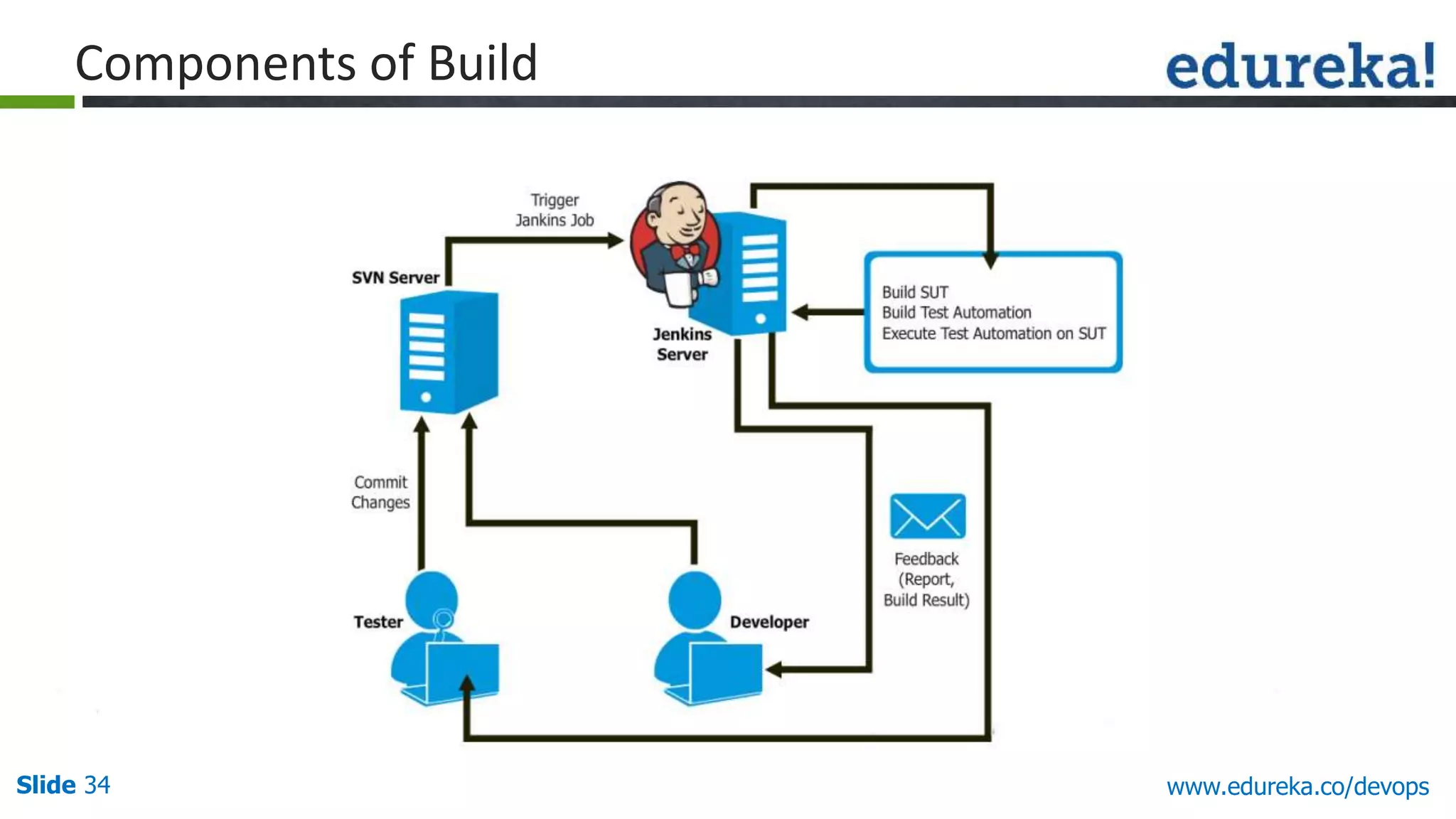
This document provides an overview of a DevOps course offered by Edureka. The course objectives are to understand DevOps and its importance, the DevOps lifecycle, configuration management using Puppet, continuous integration using Jenkins, and demos of Puppet and Jenkins. The document defines DevOps, explains the need for DevOps due to gaps between development and operations teams, and outlines tools and concepts covered in the course like Puppet, Jenkins, virtualization, and monitoring.