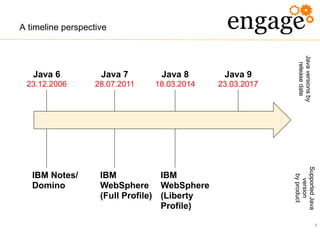
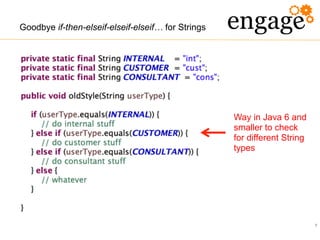
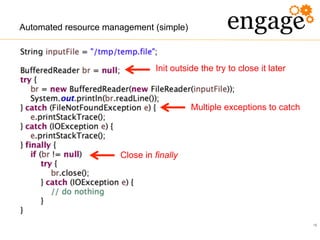
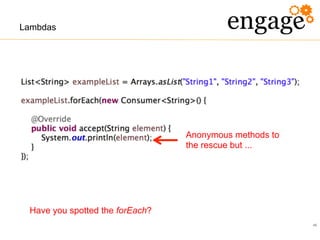
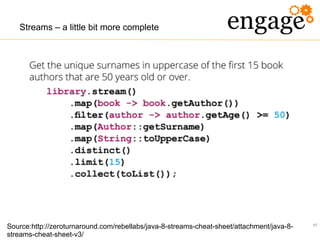
The document discusses the transition from Java 6 to Java 8, highlighting key improvements such as the introduction of switch statements for strings, the diamond operator for type inference, and enhanced automated resource management with the autocloseable interface. It further covers new features in Java 7 and 8, including lambda expressions, stream processing, and updates to date and time handling, aimed at improving code readability and reducing boilerplate. The presentation emphasizes the importance of adapting to these changes to leverage the benefits of newer Java versions.