Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times

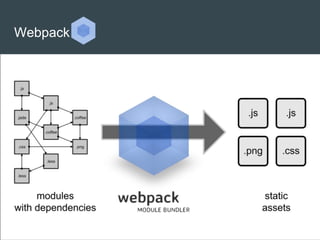



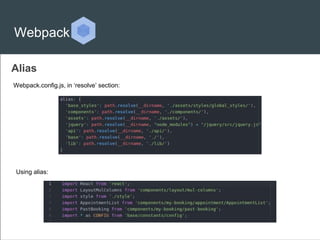
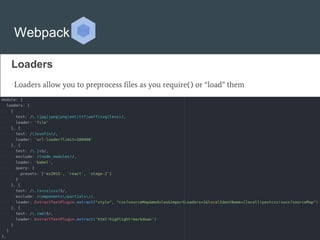









Webpack is a module bundler that can bundle JavaScript files and their associated modules and dependencies. It provides features like dependency graph, aliasing, loaders to preprocess files, plugins to customize functionality, and code splitting to optimize bundles. Webpack can also be used to polyfill features and fetch resources. While powerful, Webpack can be difficult for beginners due to its complexity. The document provides an overview of Webpack's key features but is poorly formatted and hard to follow, especially for newcomers.
















