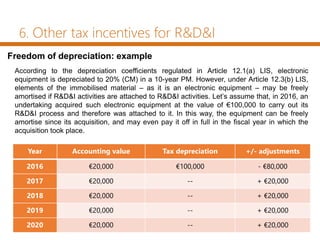
This document summarizes tax incentives for research and entrepreneurship in Spain. It discusses direct and indirect tax incentives for R&D, including a tax credit for R&D expenses up to 25% and the patent box regime which provides a 60% reduction in taxable income from certain intangible assets. The document also outlines other incentives like accelerated depreciation for R&D assets and a tax credit for entrepreneurs who invest in startups. Finally, it discusses an allowance for social security contributions for companies' research staff.