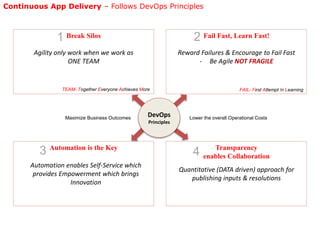
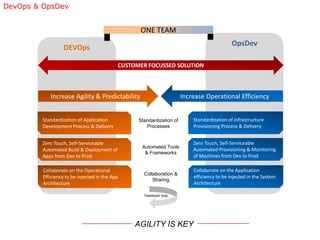
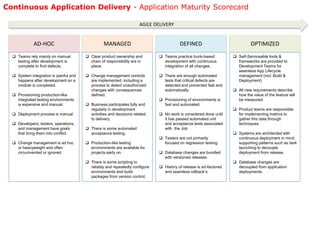
The document discusses continuous application delivery (CAD) and how DevOps principles enable it. It describes breaking down silos, automating processes, and collaborating as a unified team. The CAD maturity model scores organizations on agile delivery practices like continuous integration, automated testing, and self-service tools. Highly mature organizations implement patterns like trunk-based development, automated testing and deployment, and decoupling database changes.