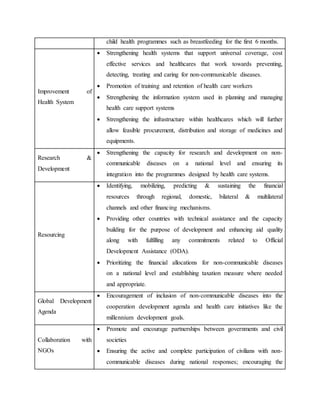
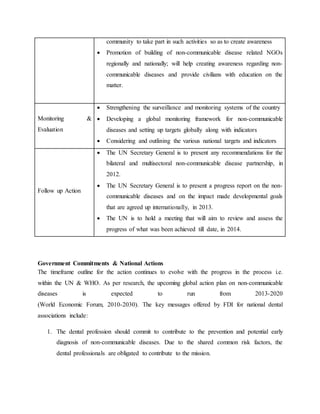
The UN Political Declaration on non-communicable diseases identified common risk factors between oral diseases and other non-communicable diseases. It defined a global response and contained commitments around national leadership, early diagnosis and treatment, prevention, health systems improvement, research and development, and resourcing. Key commitments included establishing national non-communicable disease policies by 2013, implementing cost-effective interventions to reduce risk factors, and mobilizing financial resources to strengthen health systems and address non-communicable diseases.
![Dental Public Health
[Type the document subtitle]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em2015oma0112wr-150210032100-conversion-gate02/85/Em2015-oma0112wr-1-320.jpg)



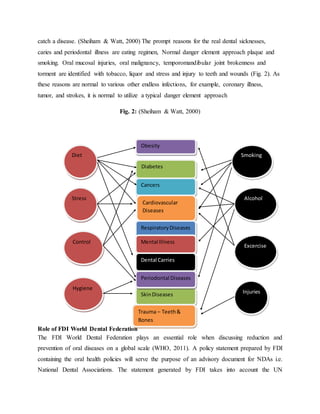







![established that these may benefit from the responses to non-communicable diseases. It is
evidence that several oral diseases share common risk factors with other non-communicable
diseases such as diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular diseases etc. For this reason, the prevention of
oral diseases needs to be integrated with prevention of other non-communicable diseases and
should be outline in the Common Risk Factor Approach (CRFA) which is known to address the
risk factors that are common to other chronic conditions.
The FDI World Dental Federation plays an essential role when discussing reduction and
prevention of oral diseases on a global scale (United Nations, 2011).. A policy statement
prepared by FDI containing the oral health policies will serve the purpose of an advisory
document for NDAs i.e. National Dental Associations. National dental associations and dentists
play a crucial role in combating non-communicable diseases and their primary principle role is of
an advocate; this refers to their role of advocating the integration and implementation of well-
developed interventions that may be within or outside the health sector. National Dental
Associations should combating oral diseases, as a part of the current non-communicable diseases
agenda, by using the common risk factor approach and the available evidence that will allow
prevention, when discussing the determinants of oral health. This approach will not benefit the
improvement of oral health along with the evidence based oral health care but will also result in
reduction of rates of non-communicable diseases.
References
1. Rio Political Declaration on Social Determinants of Health. Signed by WHO Member
States in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, on 21 October 2011.
2. The AOK Health Grant. The AOK-Health Grant 2003 Announcement.
3. The Hamburg Forum [homepage on the Internet]. Quality in Health Service. Available
from: http://www.quantforum.de/veranst/hh_forum_3/forum3_info.html (Accessed:
October 12, 2005).
4. The Jannsen-Cilag GmbH. Future Grant 2002. Broshure n.d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/em2015oma0112wr-150210032100-conversion-gate02/85/Em2015-oma0112wr-17-320.jpg)
