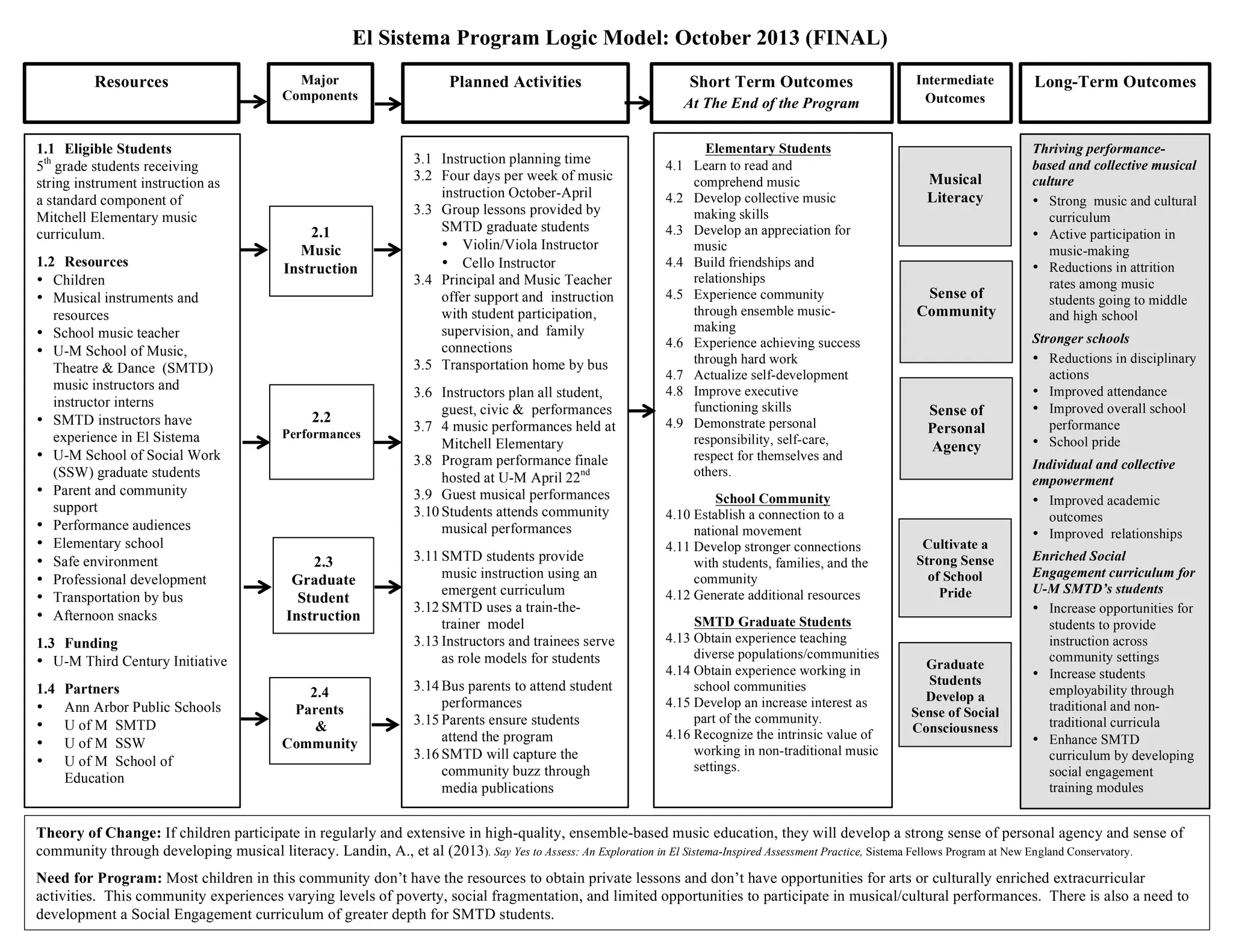
The document outlines the components and planned activities of a music program for 5th grade students. It involves weekly string instrument instruction provided by graduate students from the University of Michigan School of Music, Theatre & Dance. Over the course of the school year, students will participate in group lessons, performances, and attend other musical events to develop their musical skills and sense of community through ensemble-based learning. The goal is for students to learn musical literacy and self-development while also providing teaching experience for graduate students in non-traditional music settings.