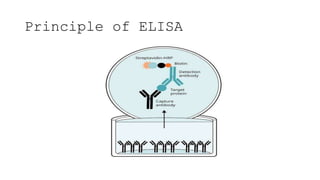
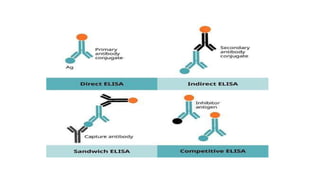
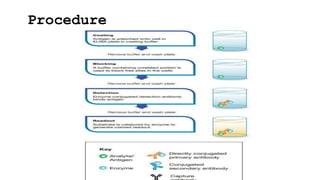
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a technique used to detect and quantify specific proteins, antibodies, or antigens using enzymes linked to antibodies or antigens. There are four main types of ELISA: direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive, each with distinct methodologies and applications in diagnostics, vaccine development, food and environmental safety. Despite its advantages, ELISA has limitations including specificity, sensitivity, time consumption, and dependency on operator and equipment.