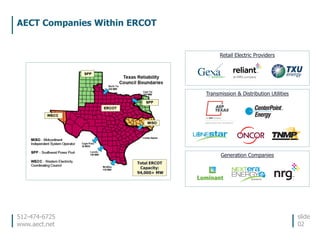
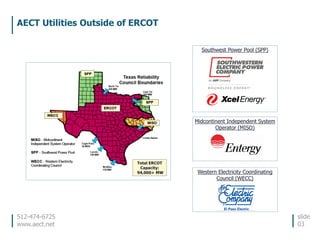
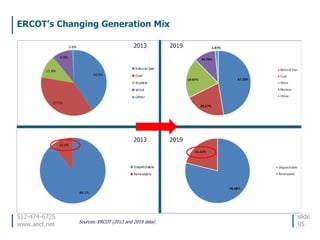
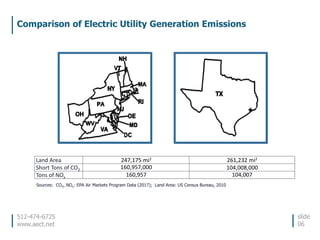
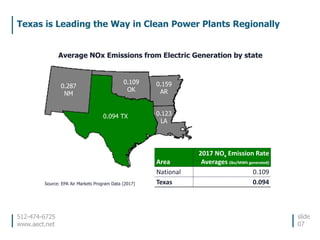
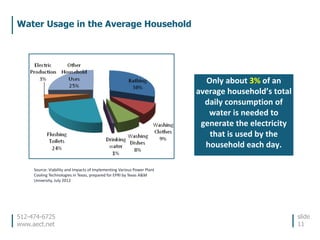
This document discusses the environmental performance and practices of electric companies in Texas. It summarizes that Texas electric generators have lower emissions rates than national averages and neighboring states. It also discusses the electric industry's reliance on water for cooling and how companies work to ensure reliable water access. The document provides information on generation sources, emissions comparisons, water usage, conservation efforts, and environmental programs.