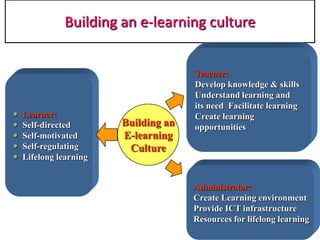
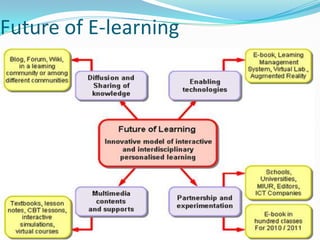
This document presents a seminar on e-learning given by Shikha Sharma to Dr. Hemant Lata Sharma. It defines e-learning as electronic learning and traces it back to 1963 when the first computer was installed for instruction. E-learning is described as exciting, energetic, and educational. It provides definitions of e-learning from various sources and discusses its features, advantages, disadvantages, types including synchronous and asynchronous, impacts on teaching and learning, building an e-learning culture, and the future of e-learning.