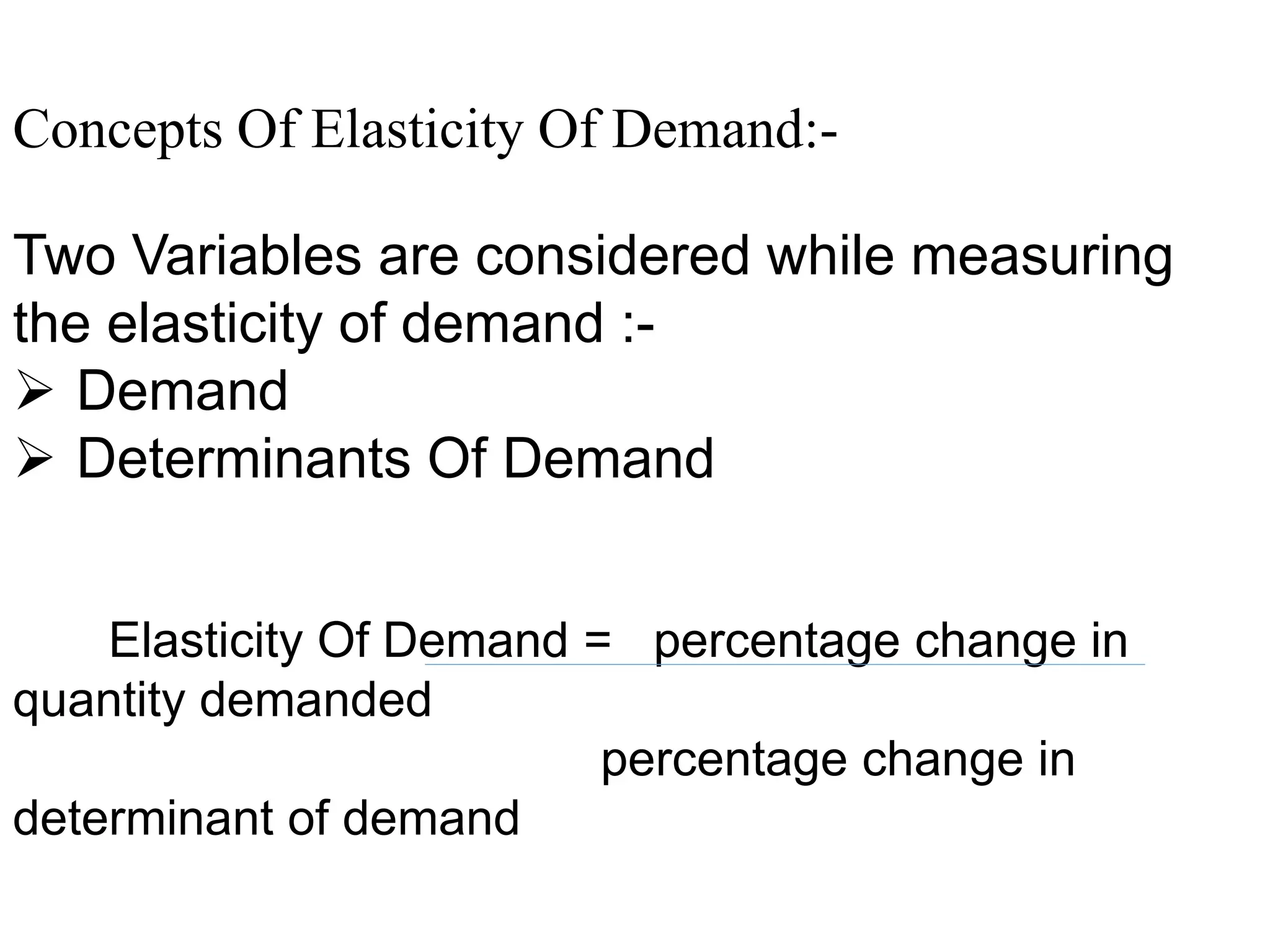
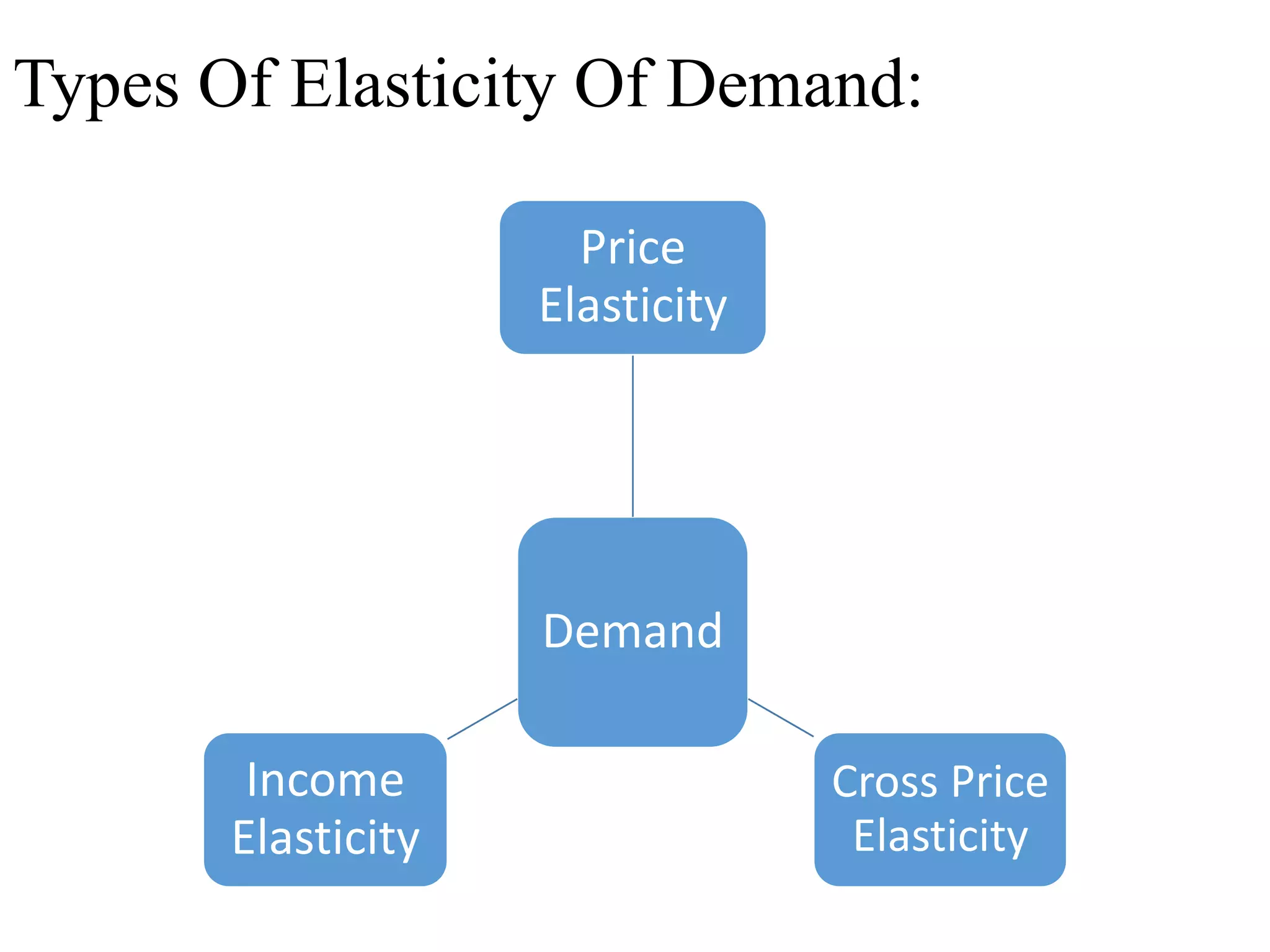
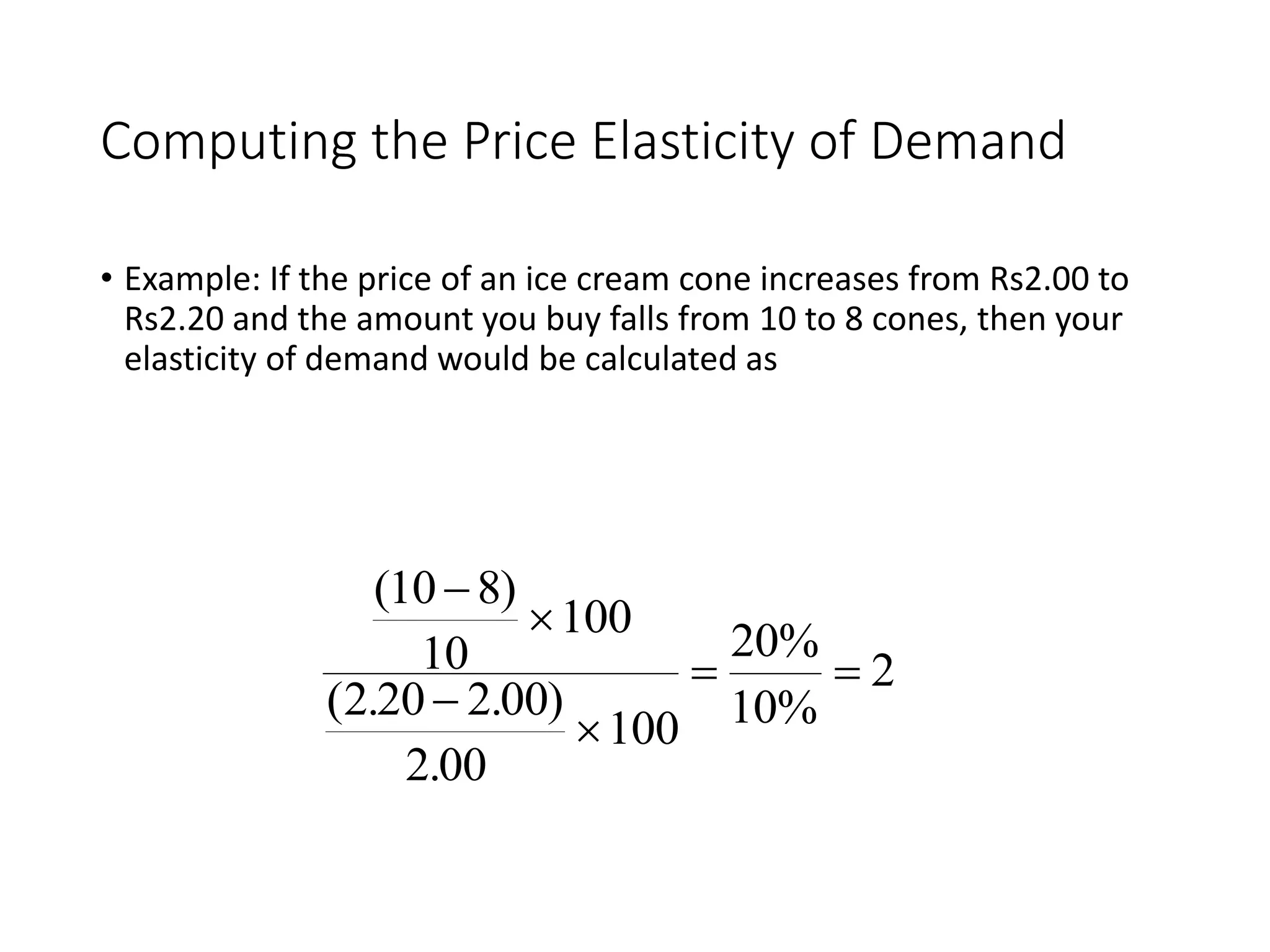
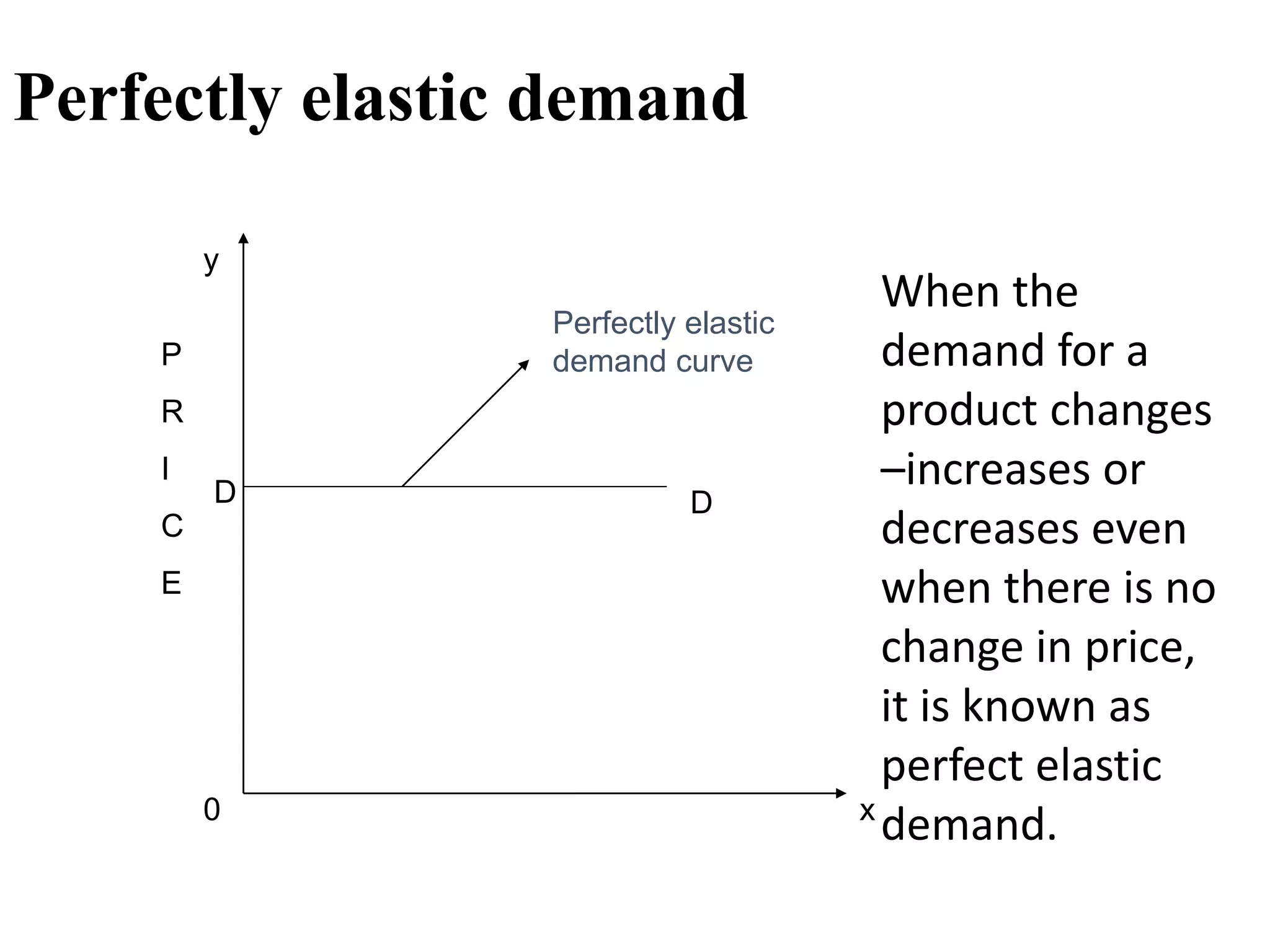
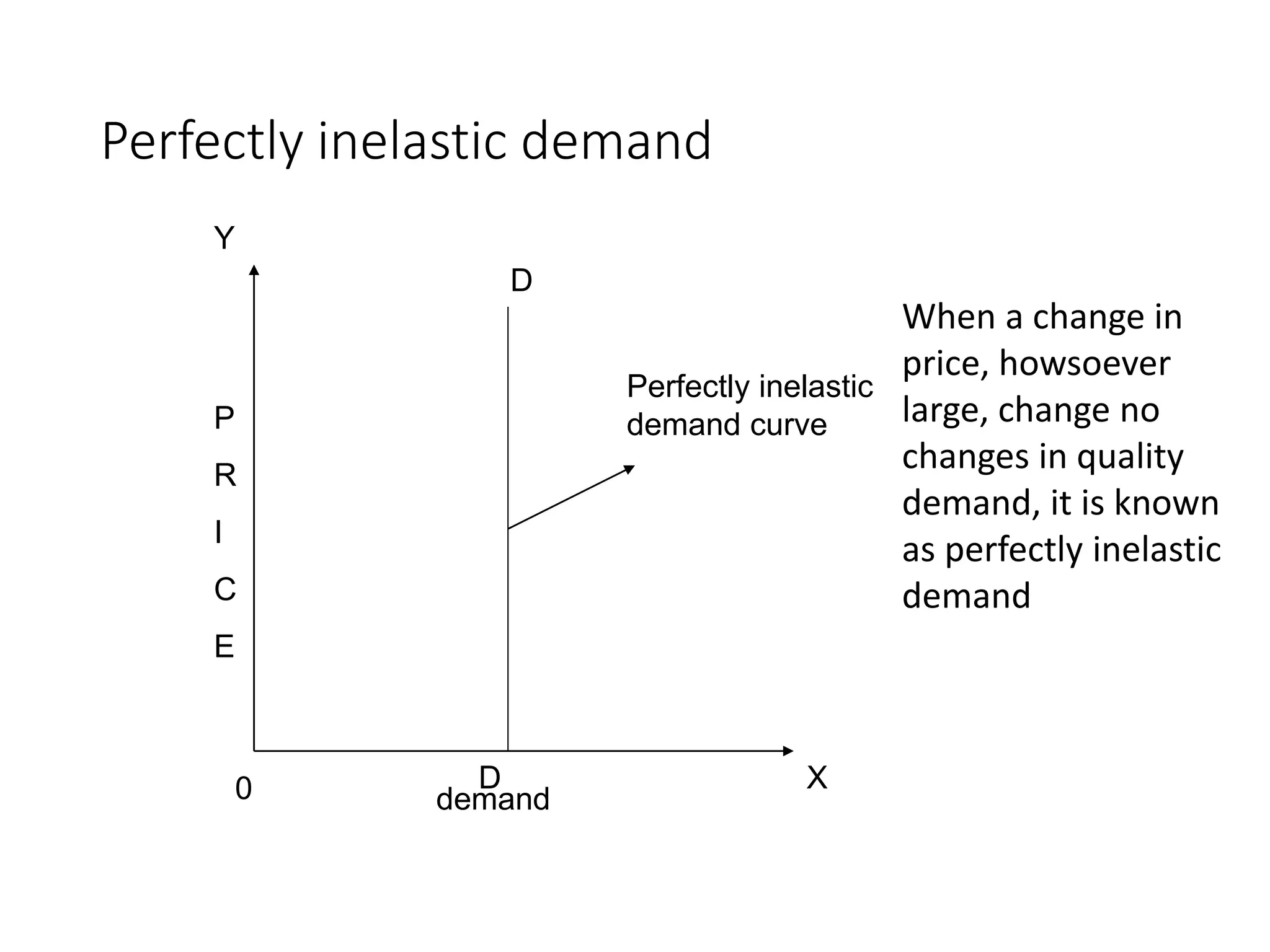
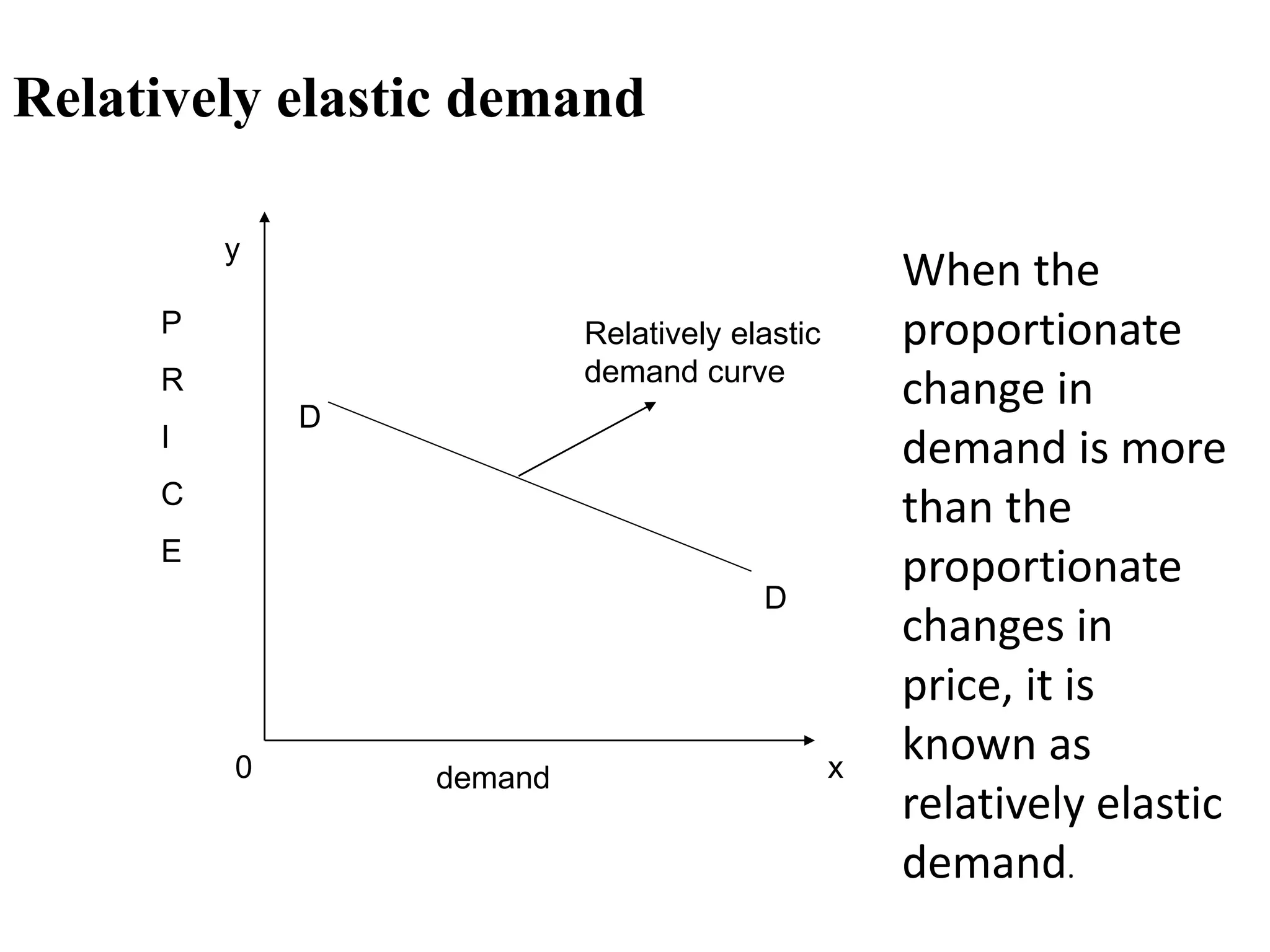
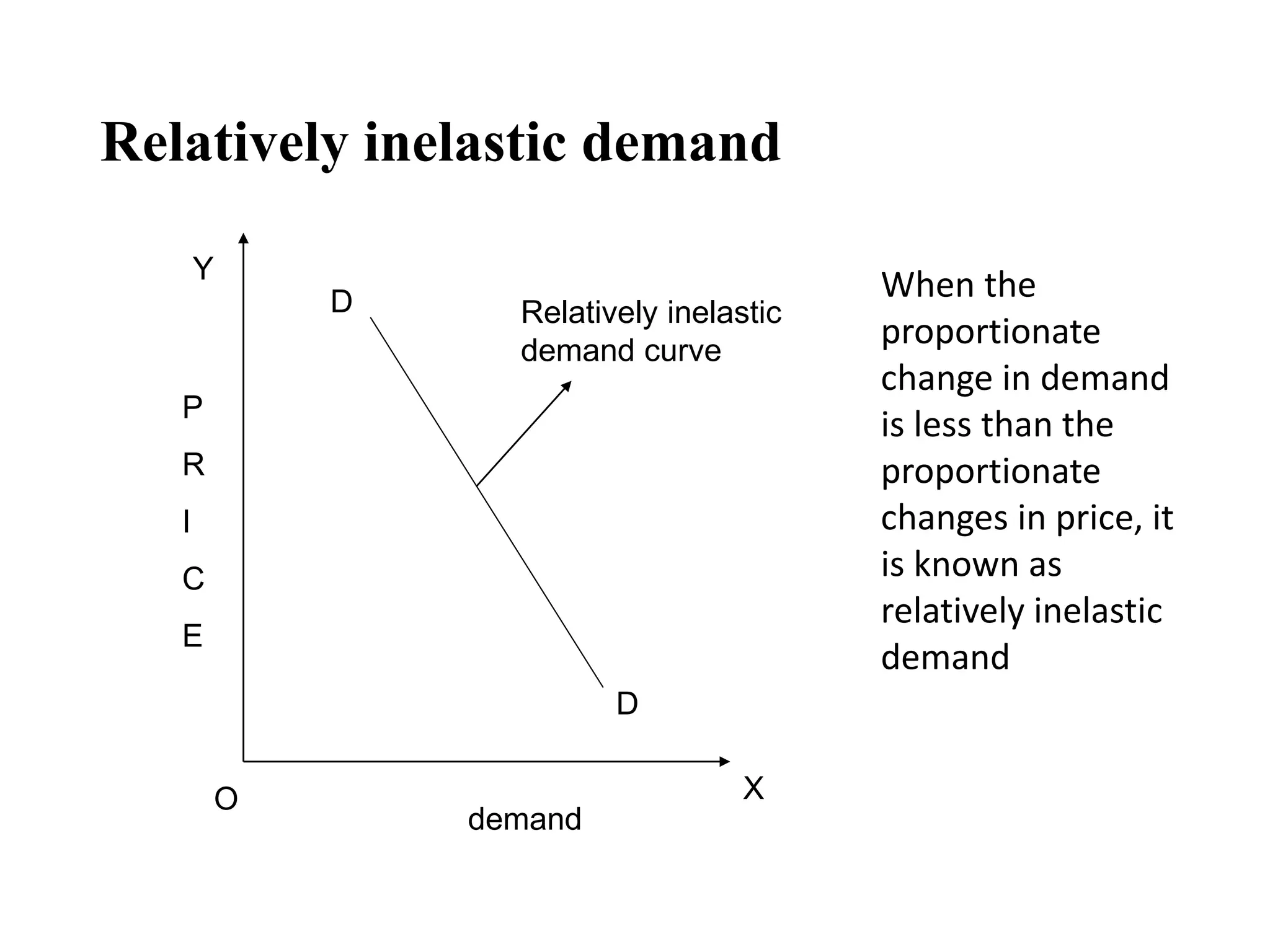
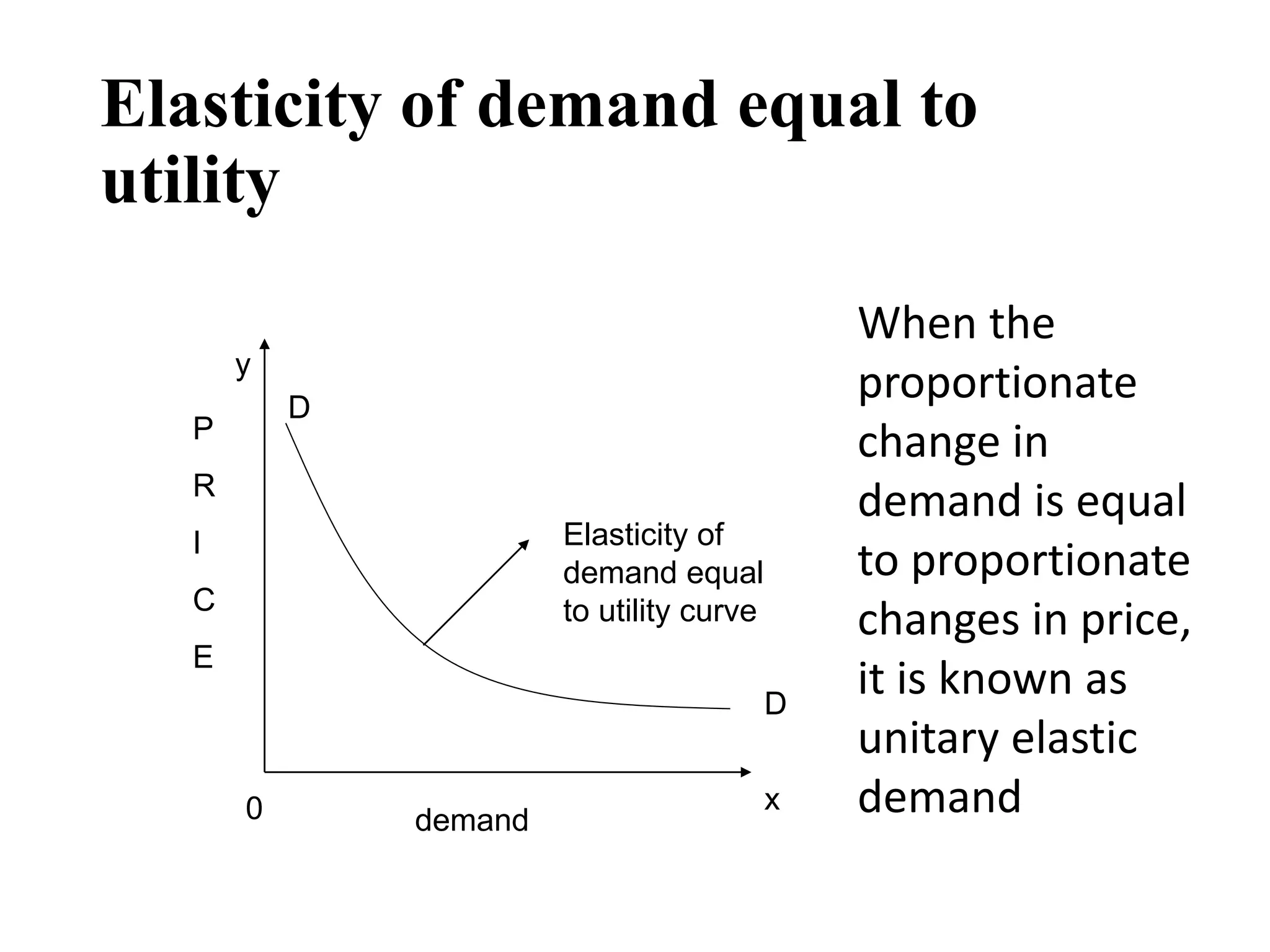
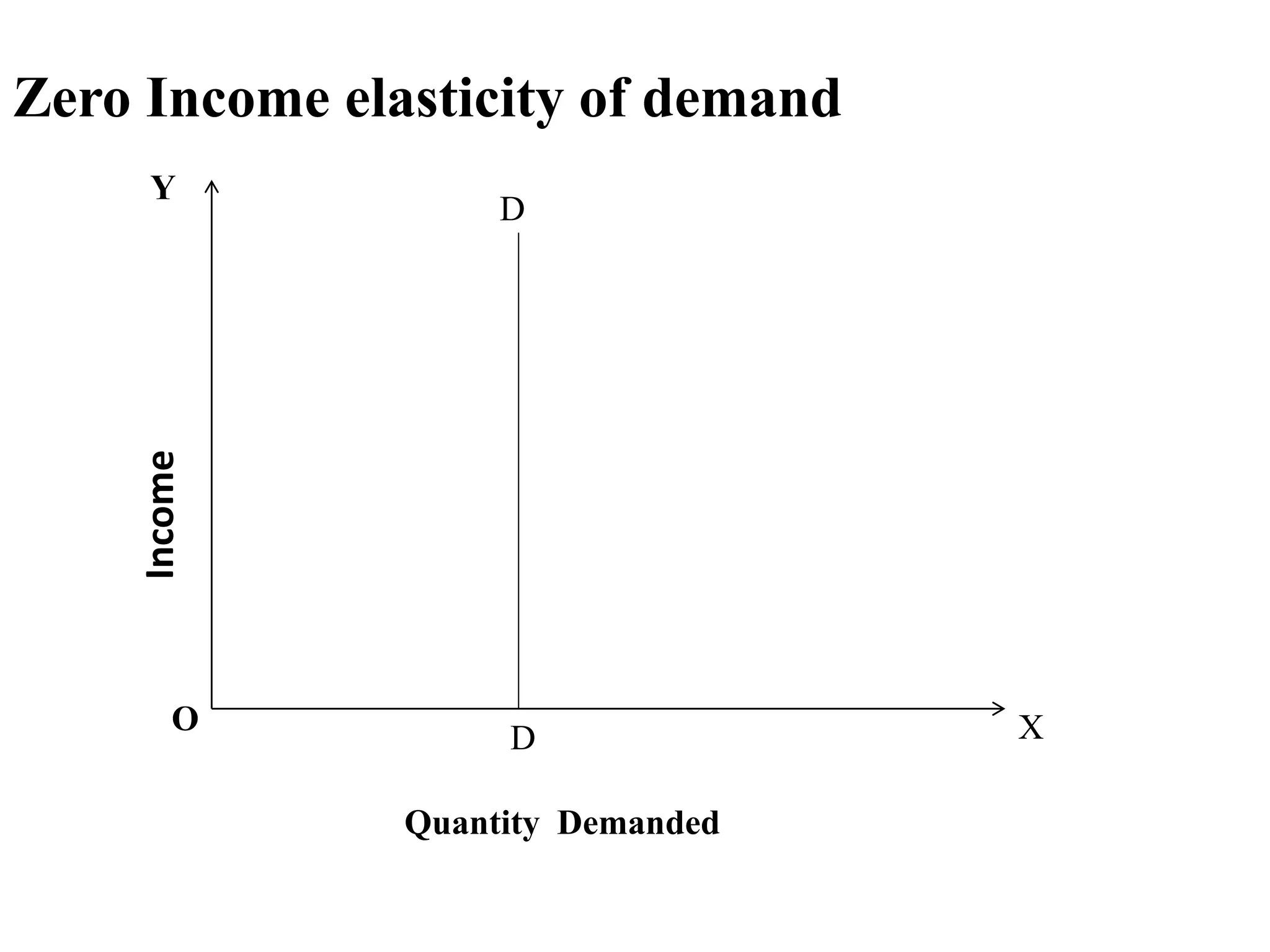
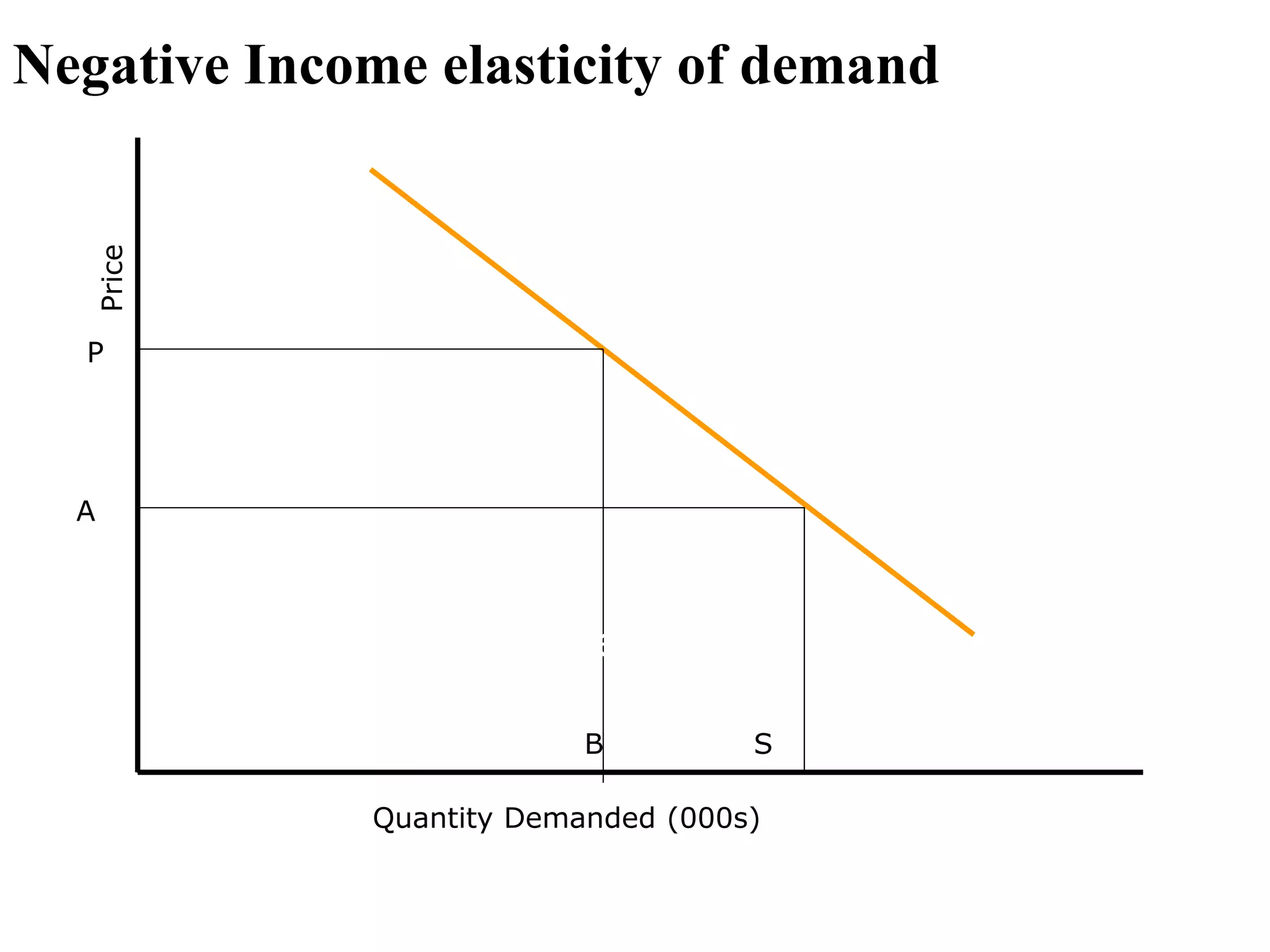
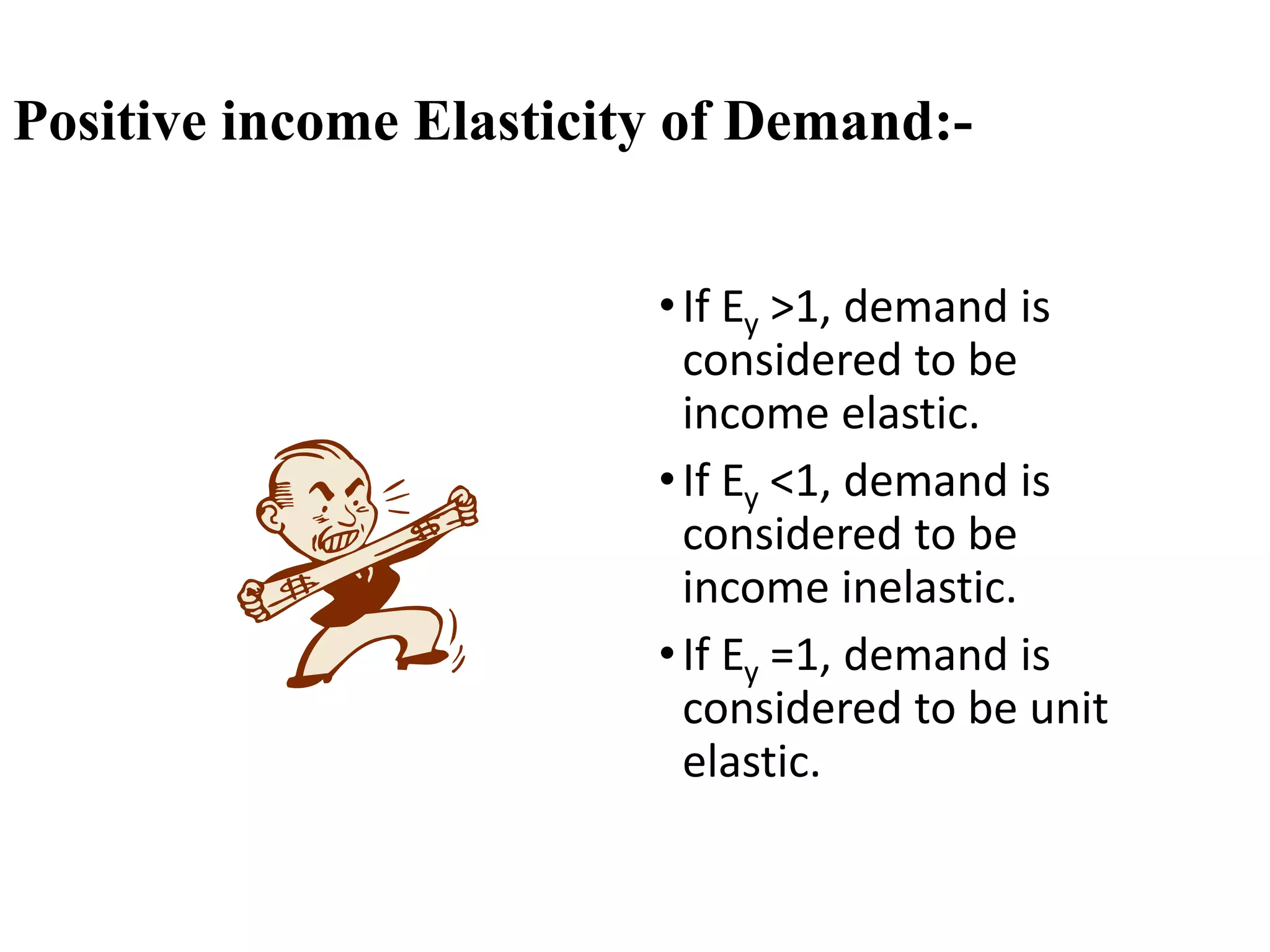
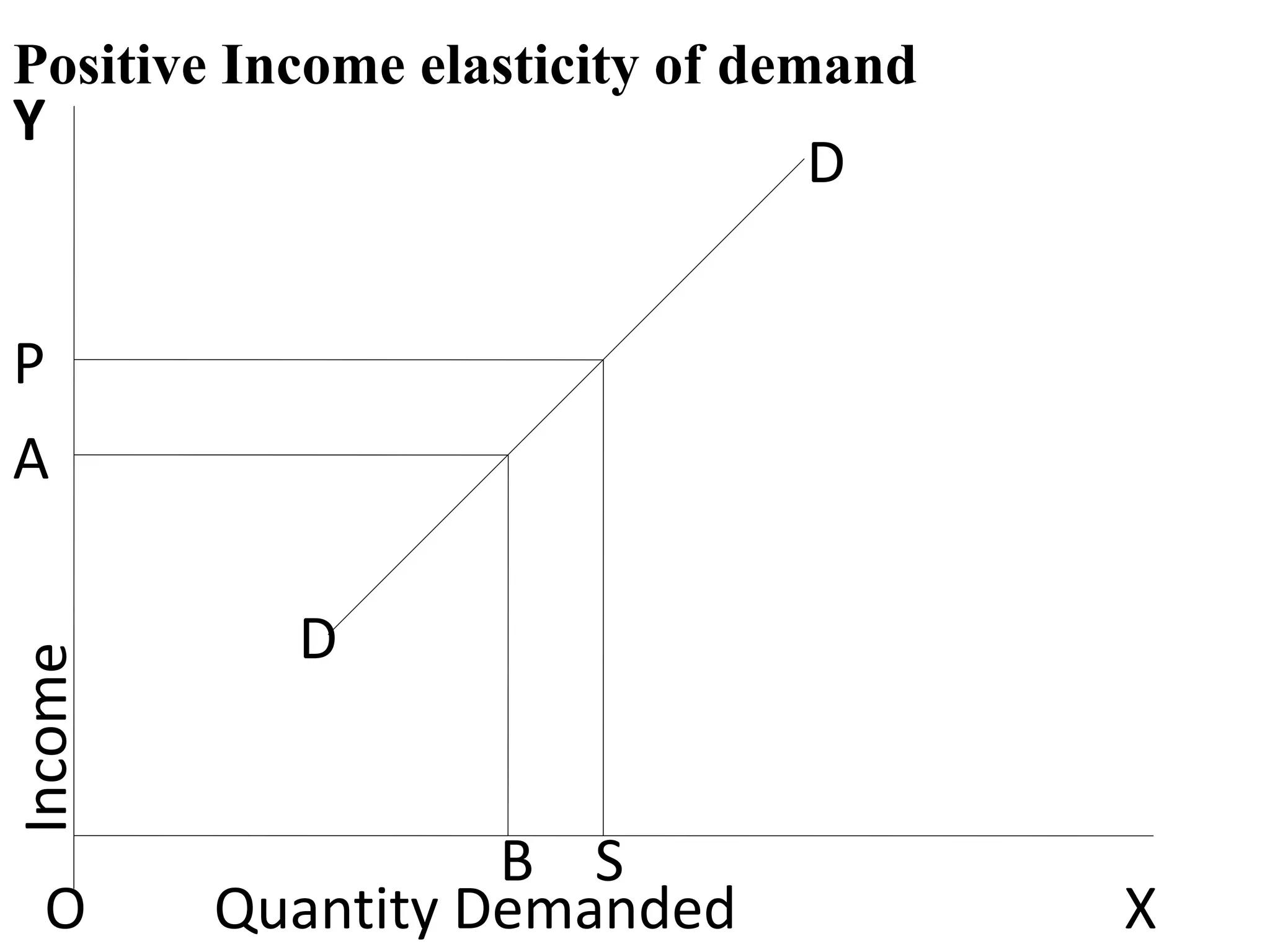
The document outlines concepts related to elasticity of demand, including price elasticity of demand and income elasticity of demand. It discusses the different types of price elasticity, such as perfectly elastic, perfectly inelastic, relatively elastic, and relatively inelastic demand. It also covers determinants that impact price elasticity, like the number of substitutes, and whether a good is a necessity or luxury. The document defines income elasticity of demand and describes the different types, including positive, negative, and zero income elasticity.