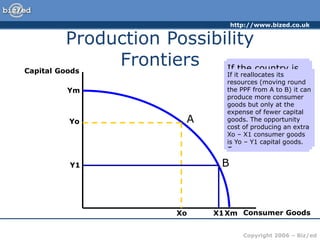
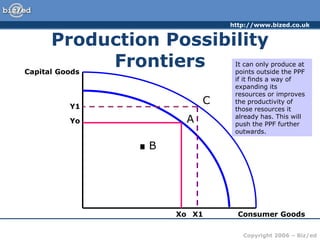
This document discusses key economic concepts including the economic problem, opportunity cost, and production possibility frontiers. It explains that economies have unlimited wants but scarce resources, so they must make choices about what and how to produce and who will consume goods and services. Opportunity cost is defined as the next best alternative sacrificed in a decision. Production possibility frontiers graphically show the combinations of goods an economy can produce and demonstrate that increasing one requires decreasing another due to scarce resources.