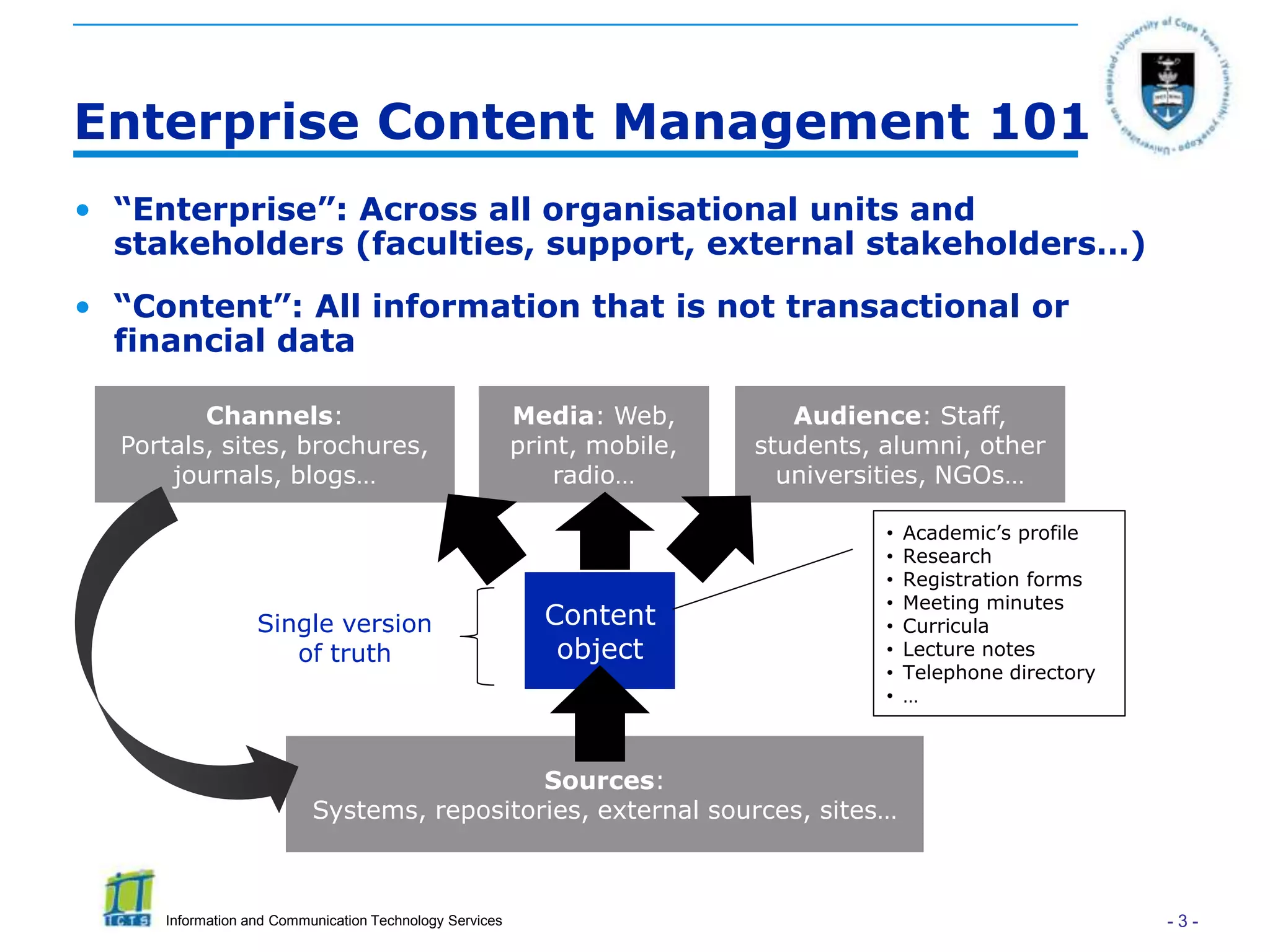
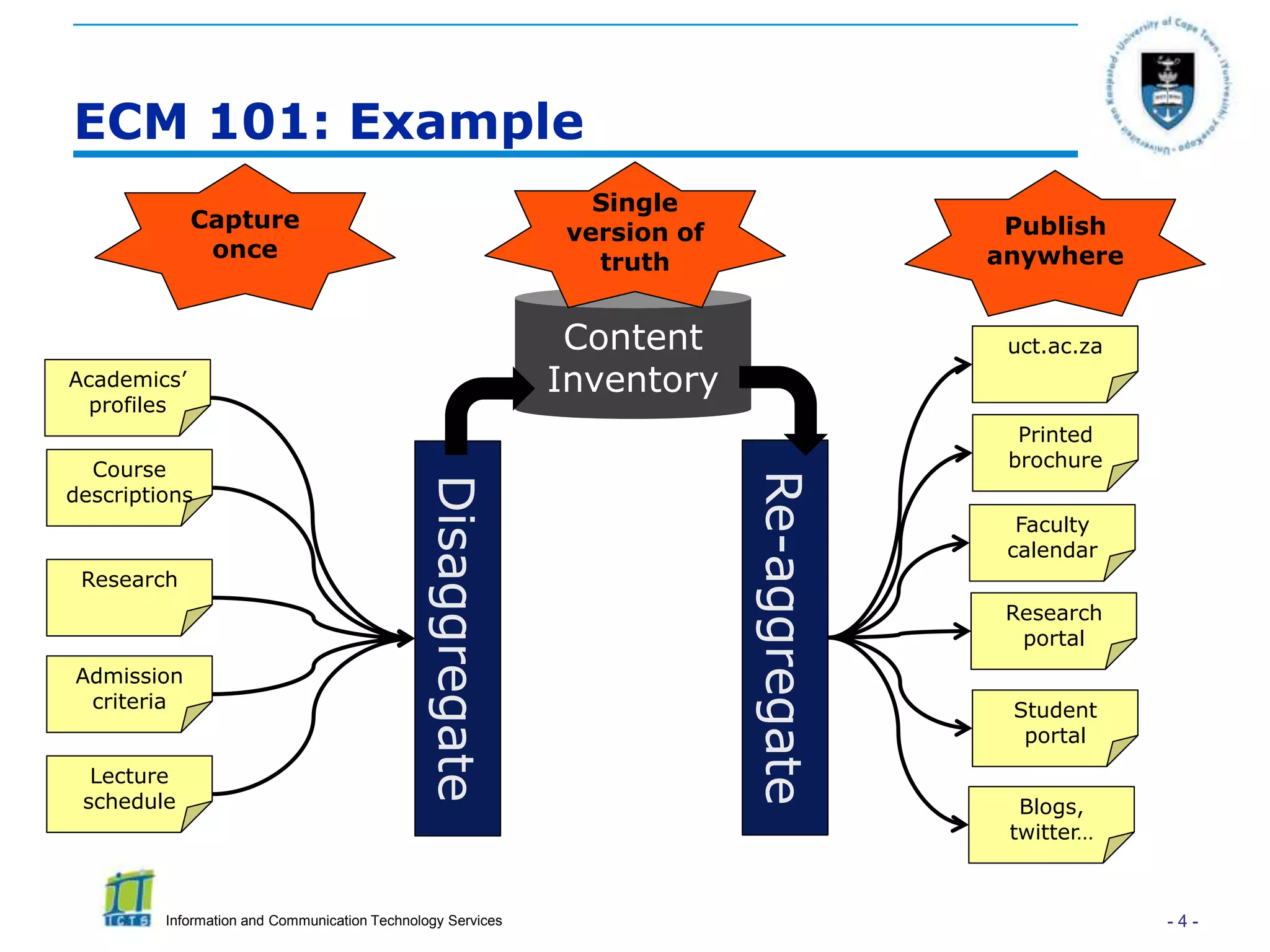
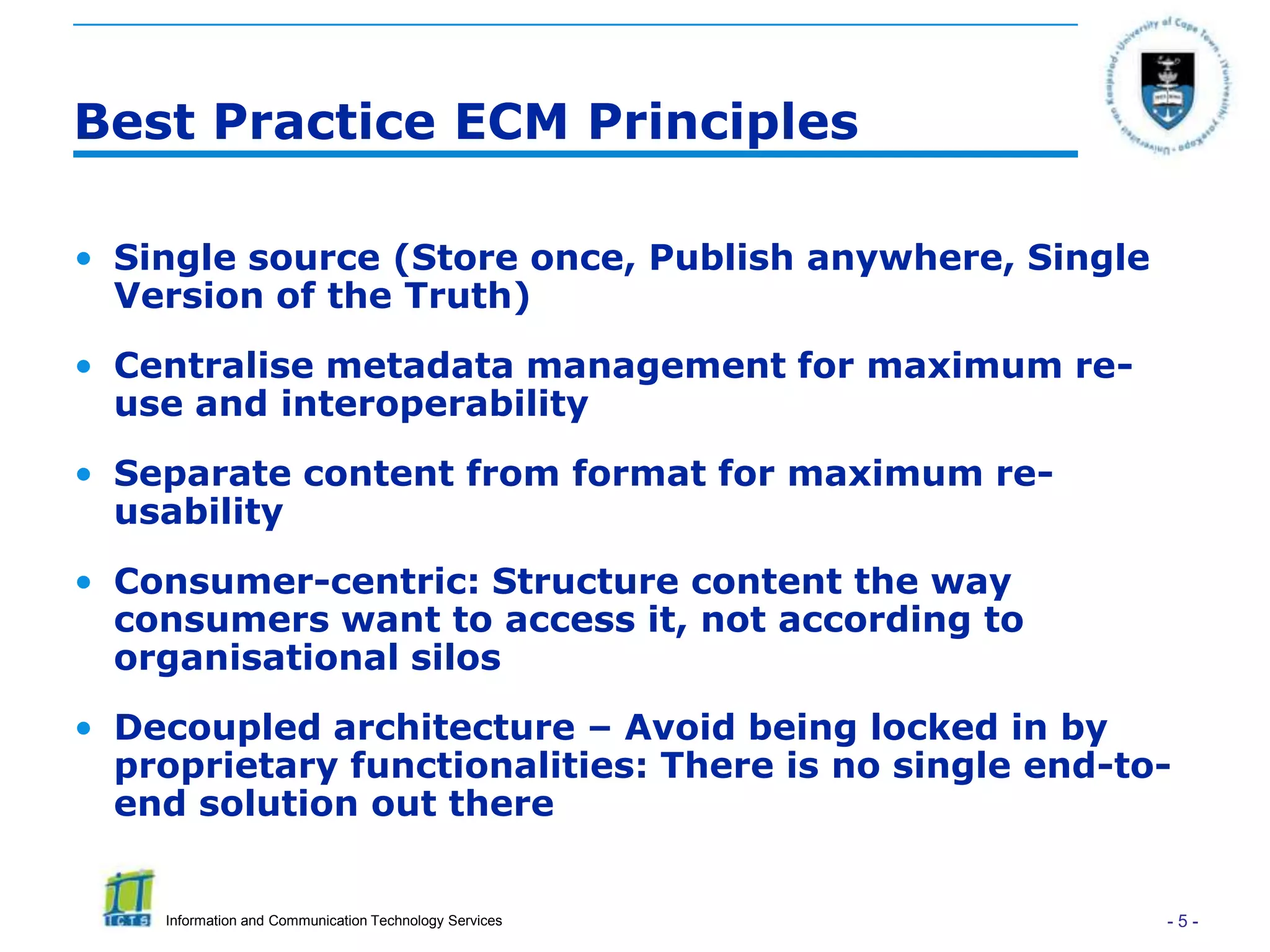
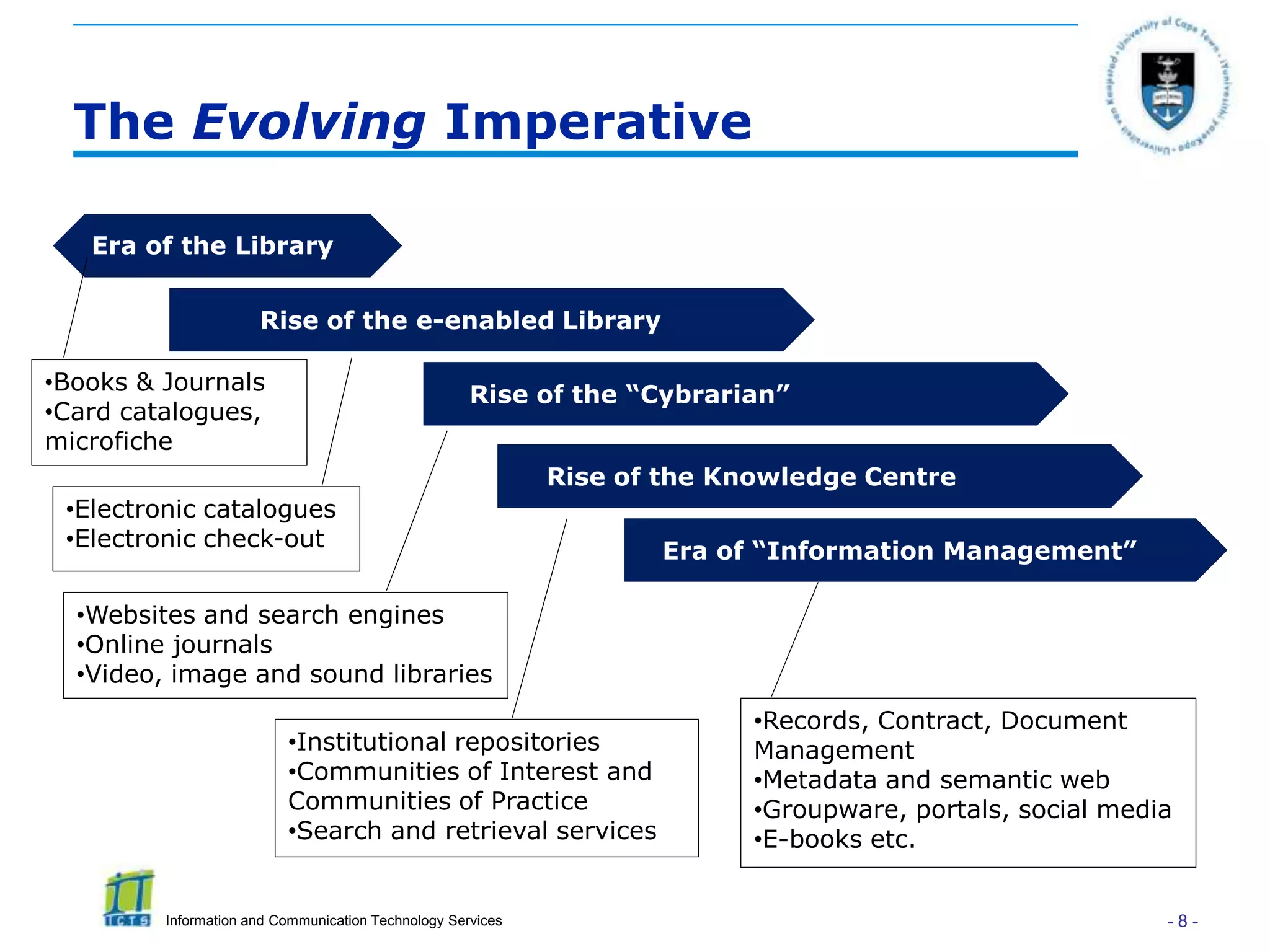
This document discusses enterprise content management (ECM) and the role of research librarians. It defines ECM as managing all organizational information across units and stakeholders through a centralized system. There are two approaches to ECM - taking a functionality/software-driven approach or an information/governance-driven one. The document argues that research librarians are well-positioned to play a key role in ECM initiatives due to their skills in areas like metadata, content curation and research support. It highlights how research portals can consolidate resources to better support researchers if driven by research needs rather than just technology.