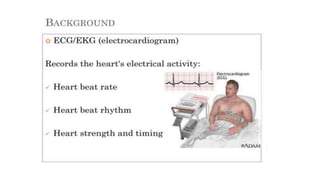
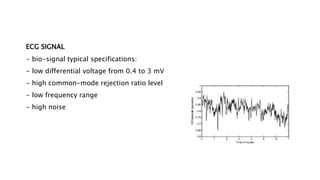
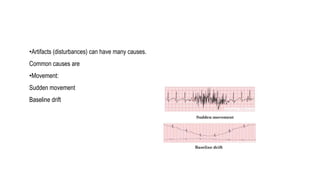
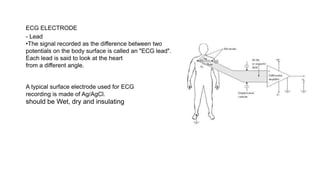
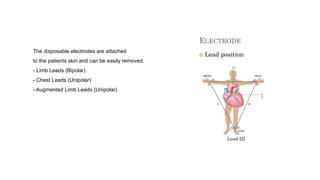
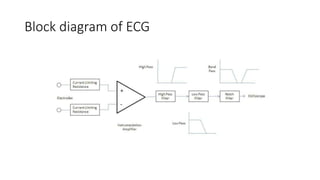
- The document describes the design of a low-cost ECG circuit to measure heart signals using discrete electronics. The system consists of 3 op-amp instrumentation amplifiers, high-pass and low-pass filters. The ECG circuit was tested using medical electrodes on volunteer subjects. The objectives are to practice designing low-cost medical devices and test an ECG system using discrete components.