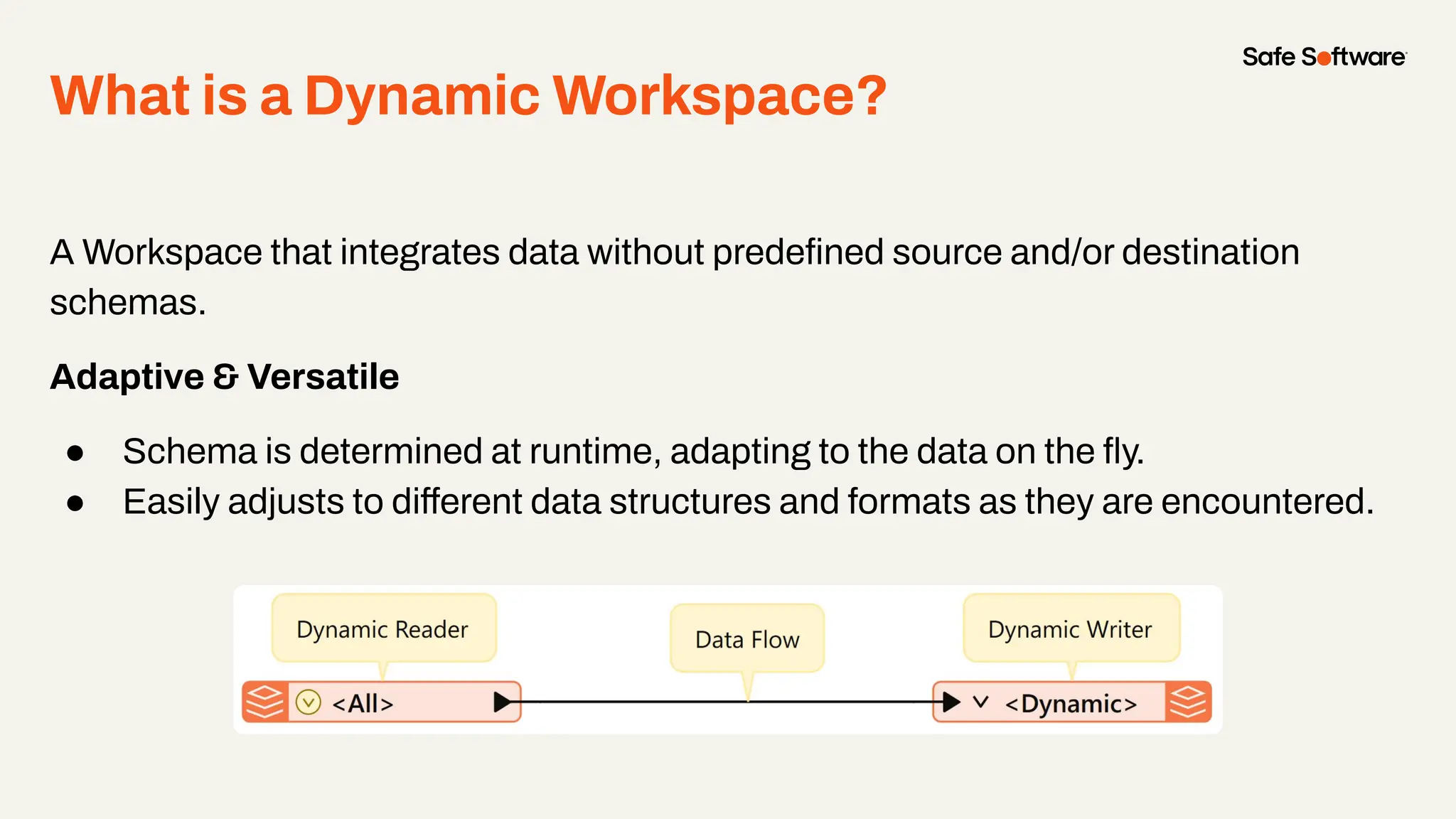
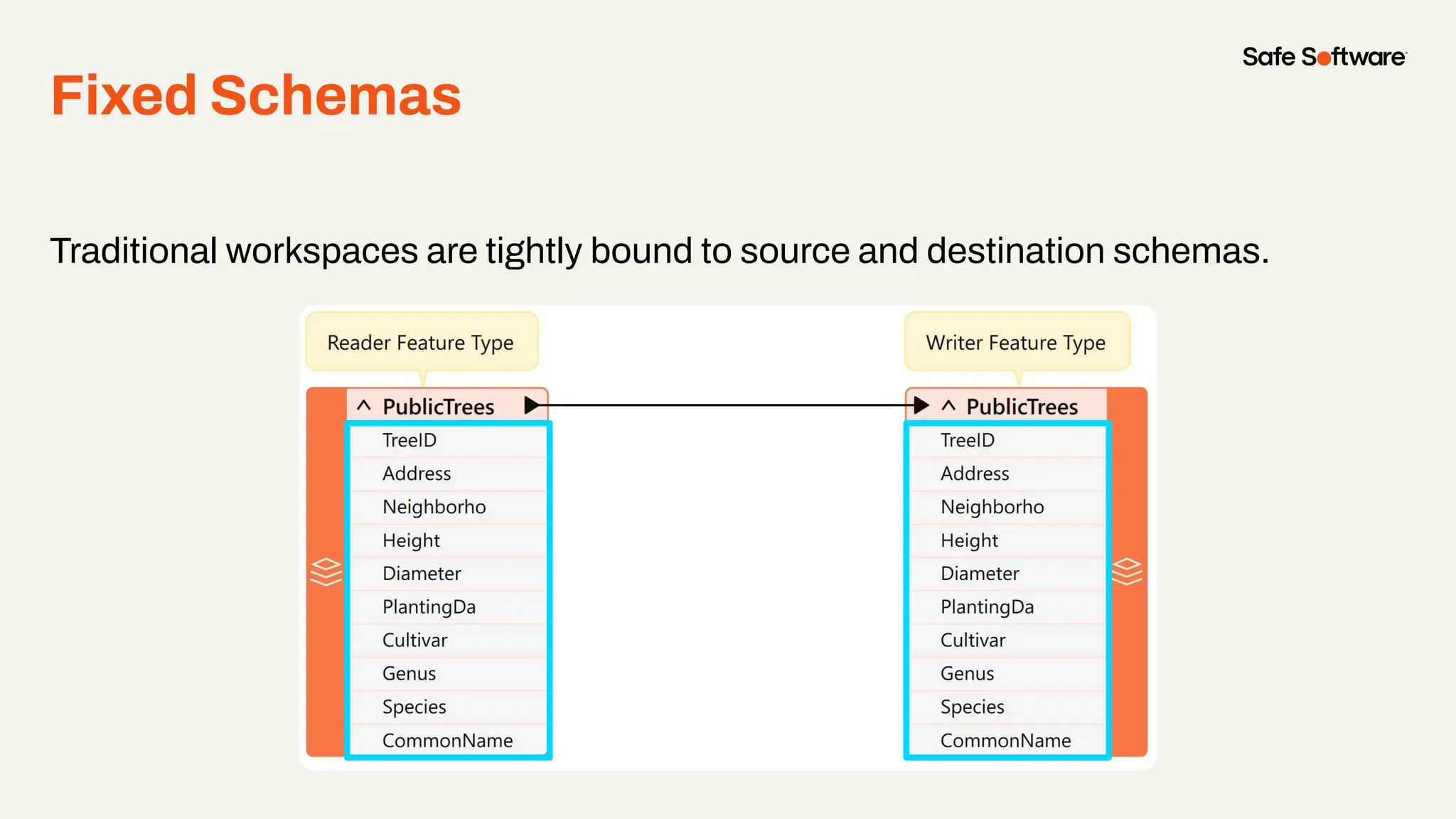
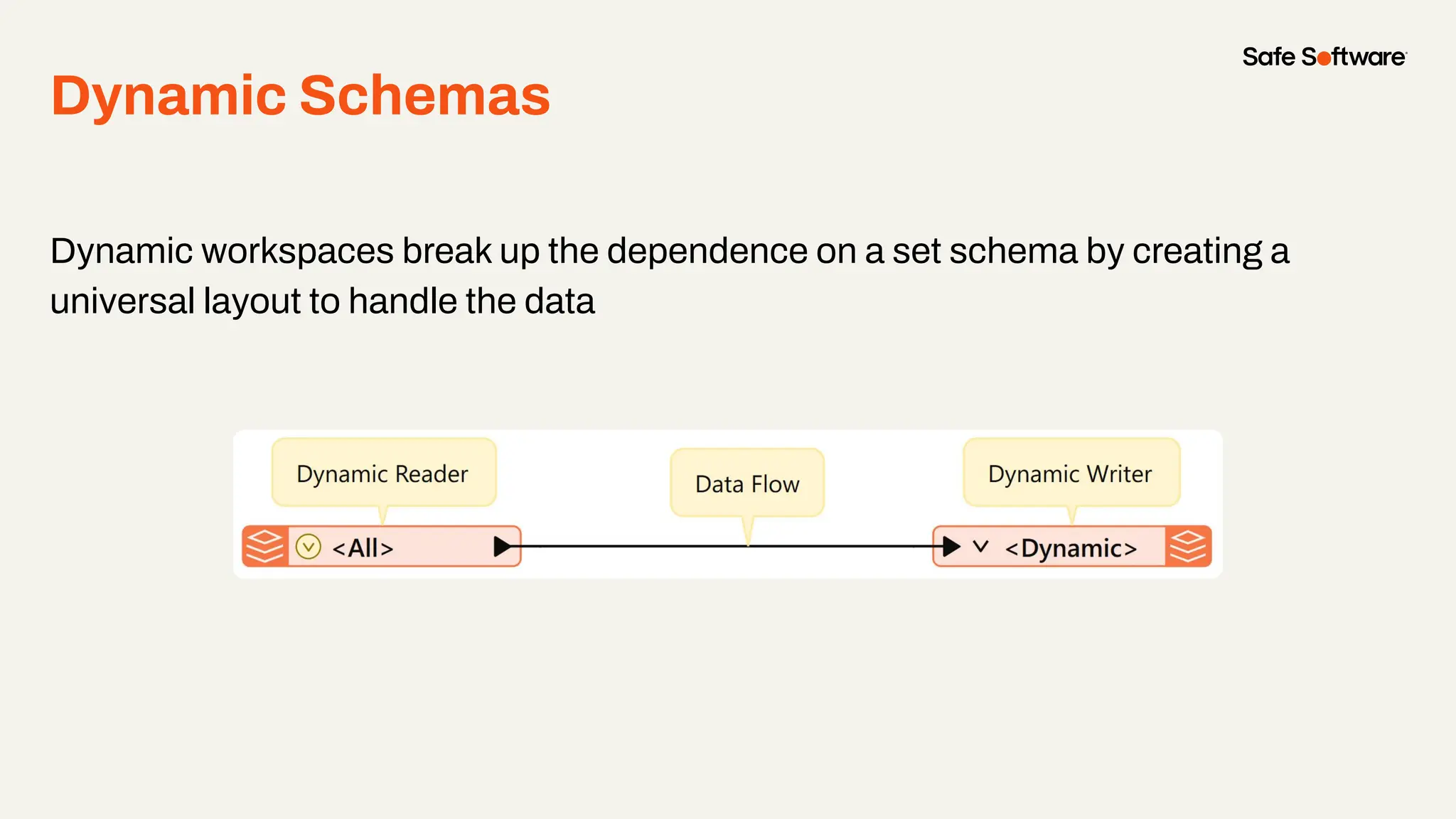
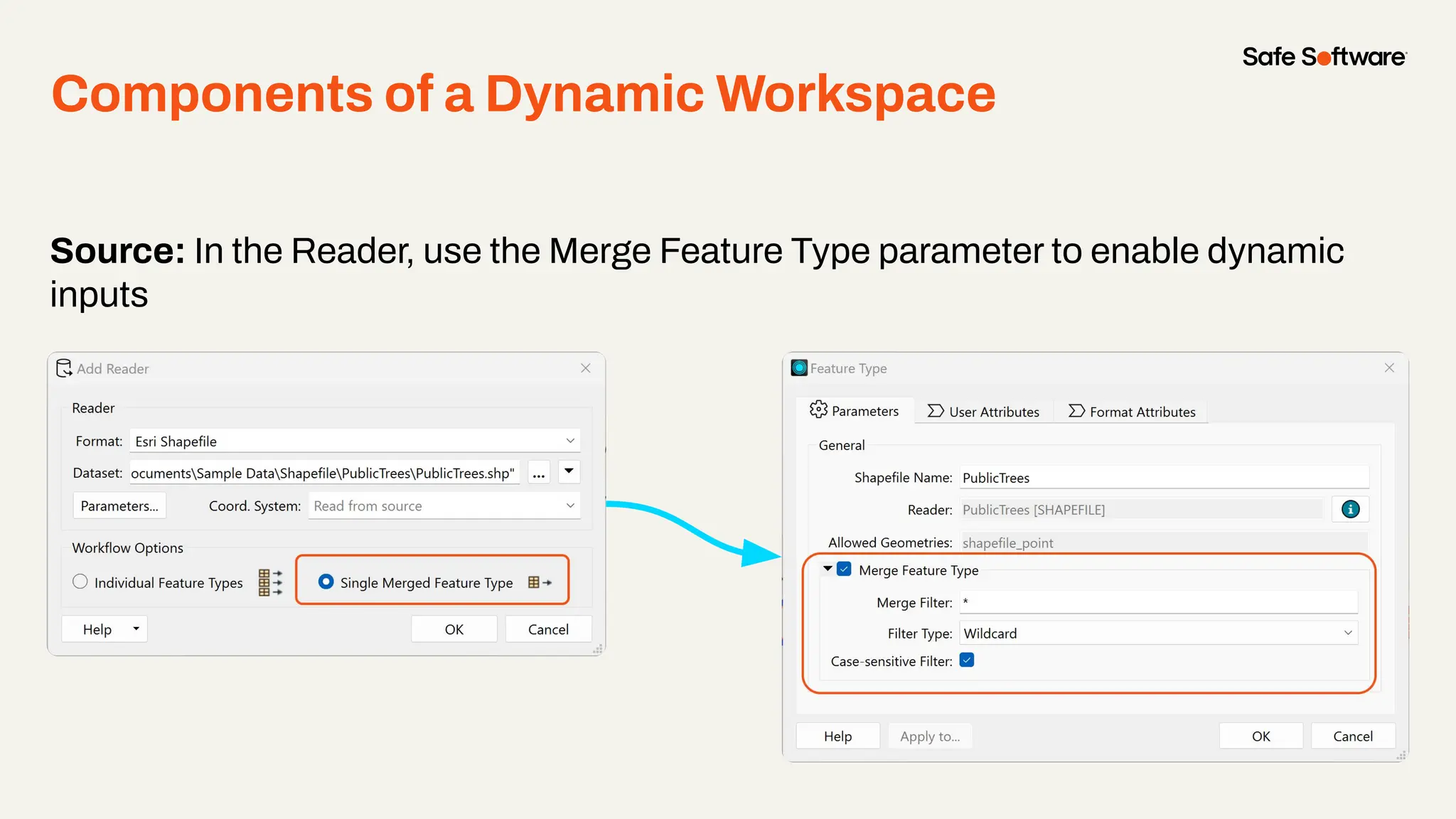
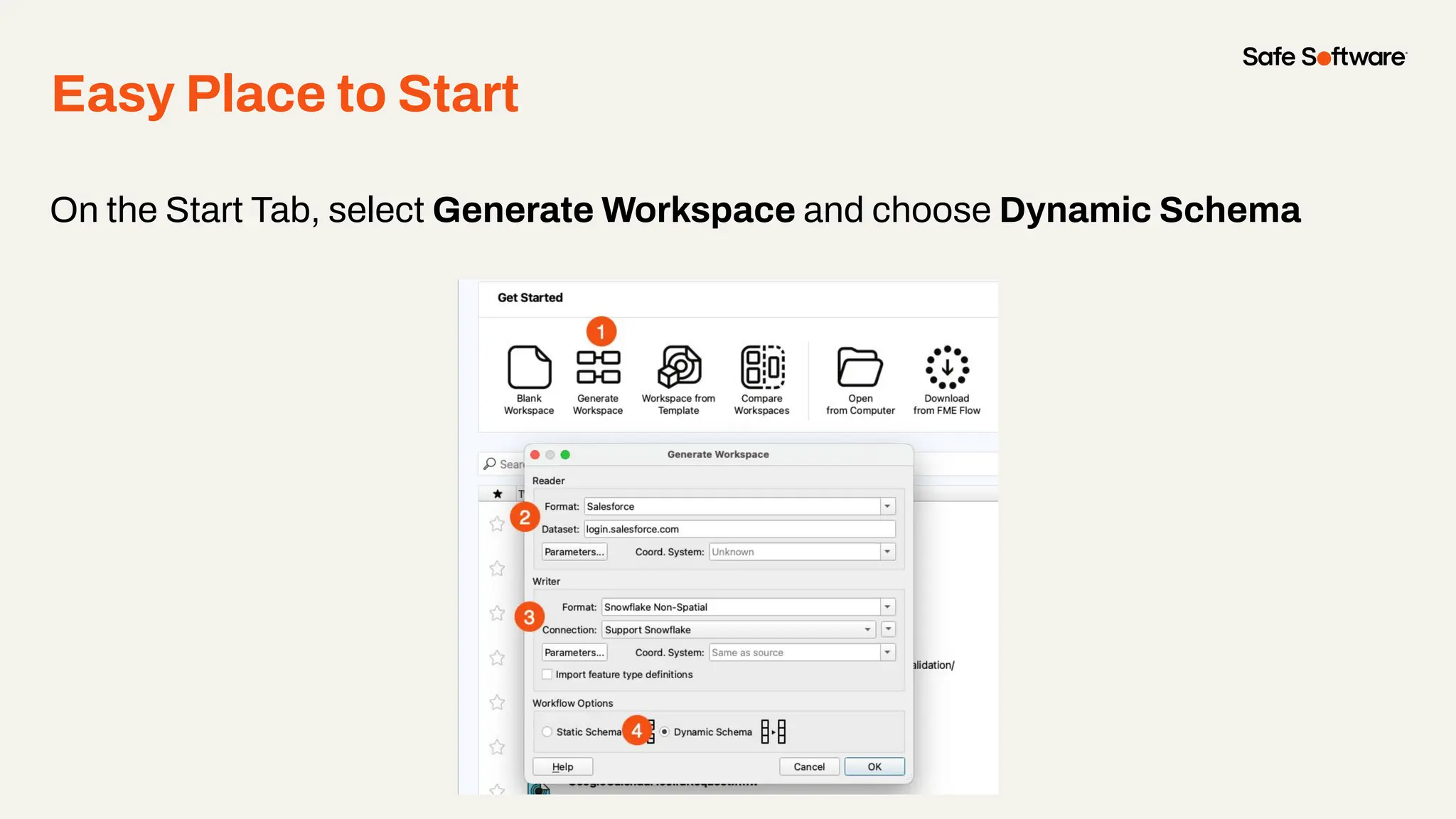
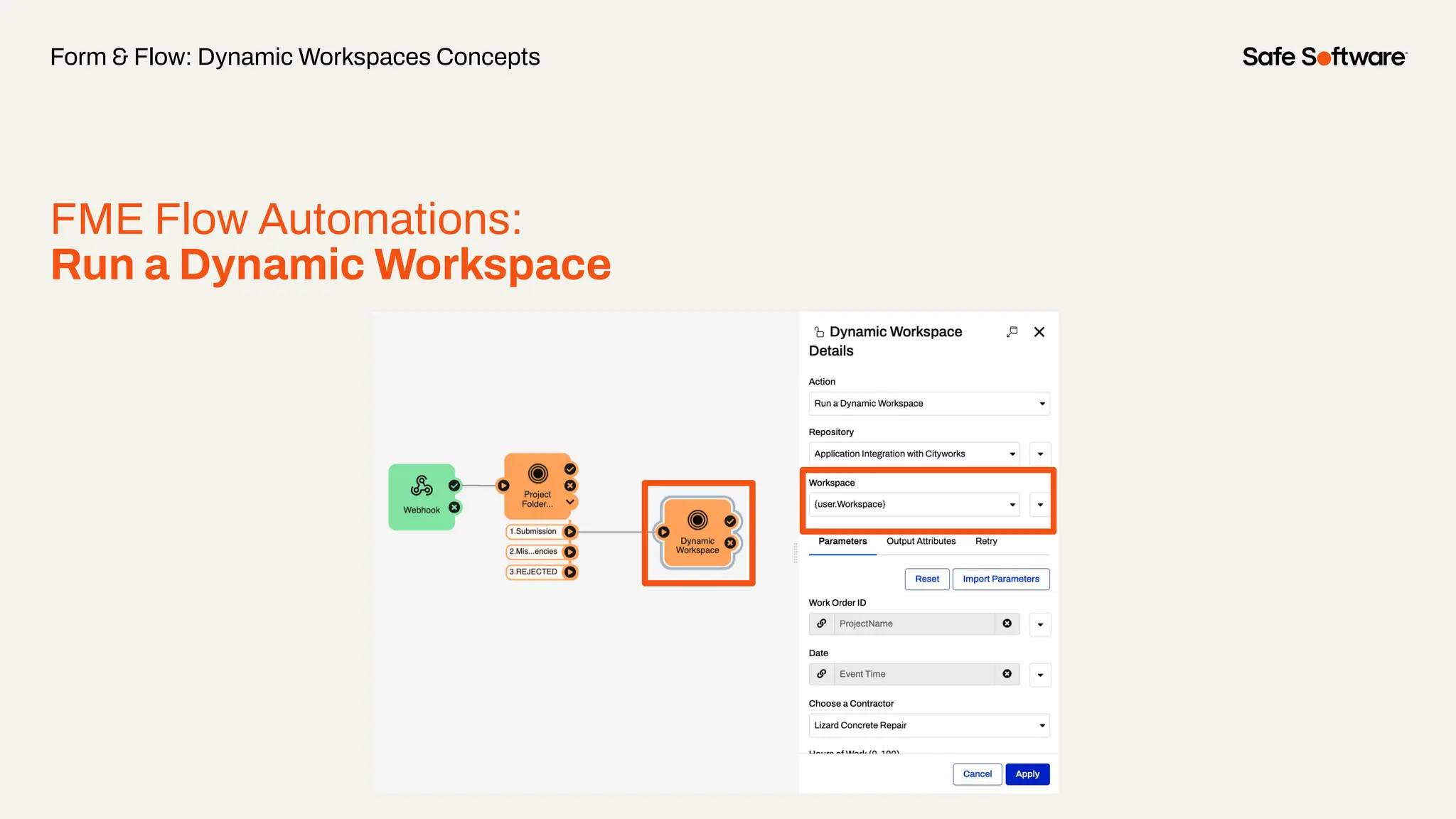
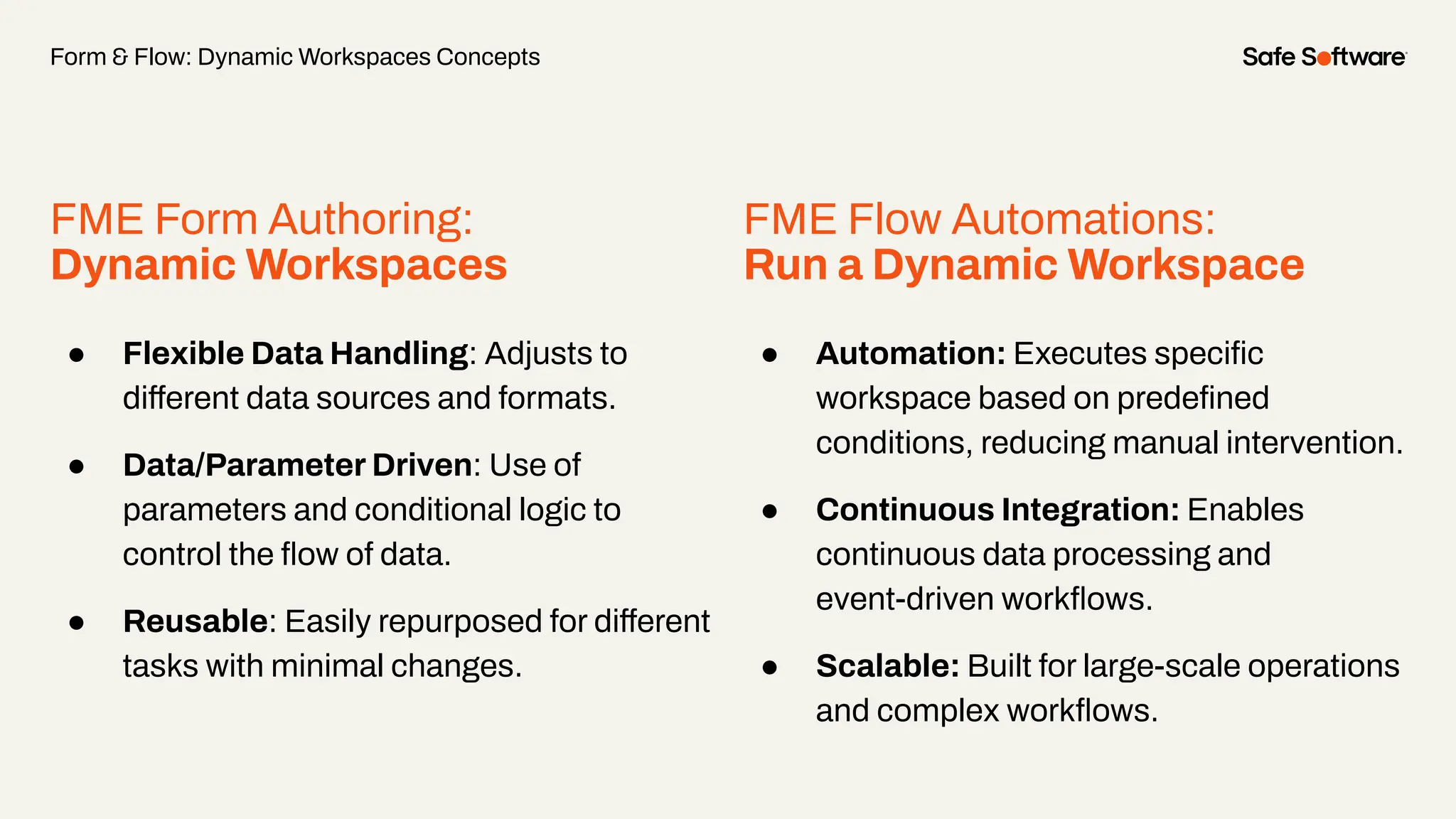
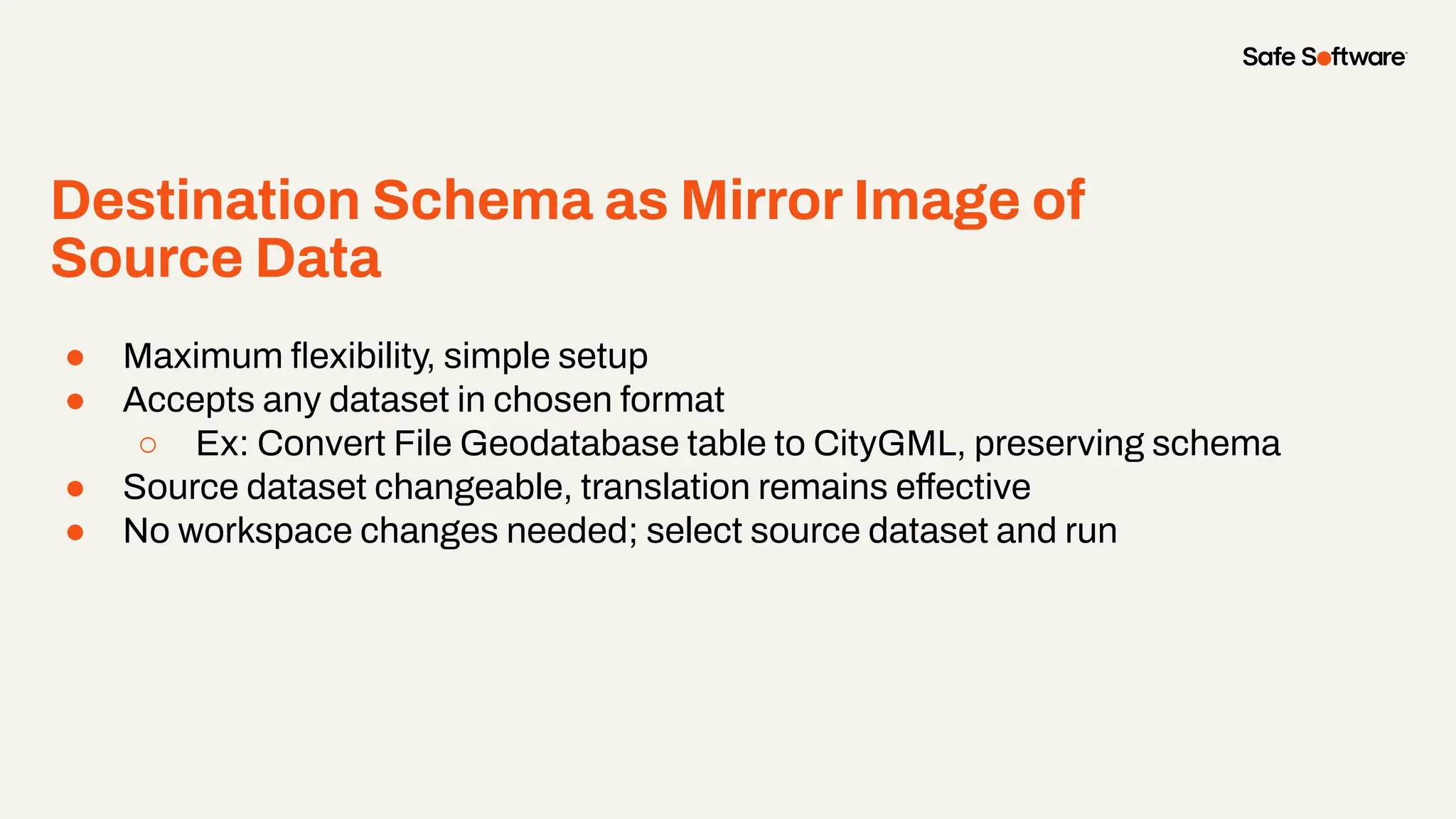
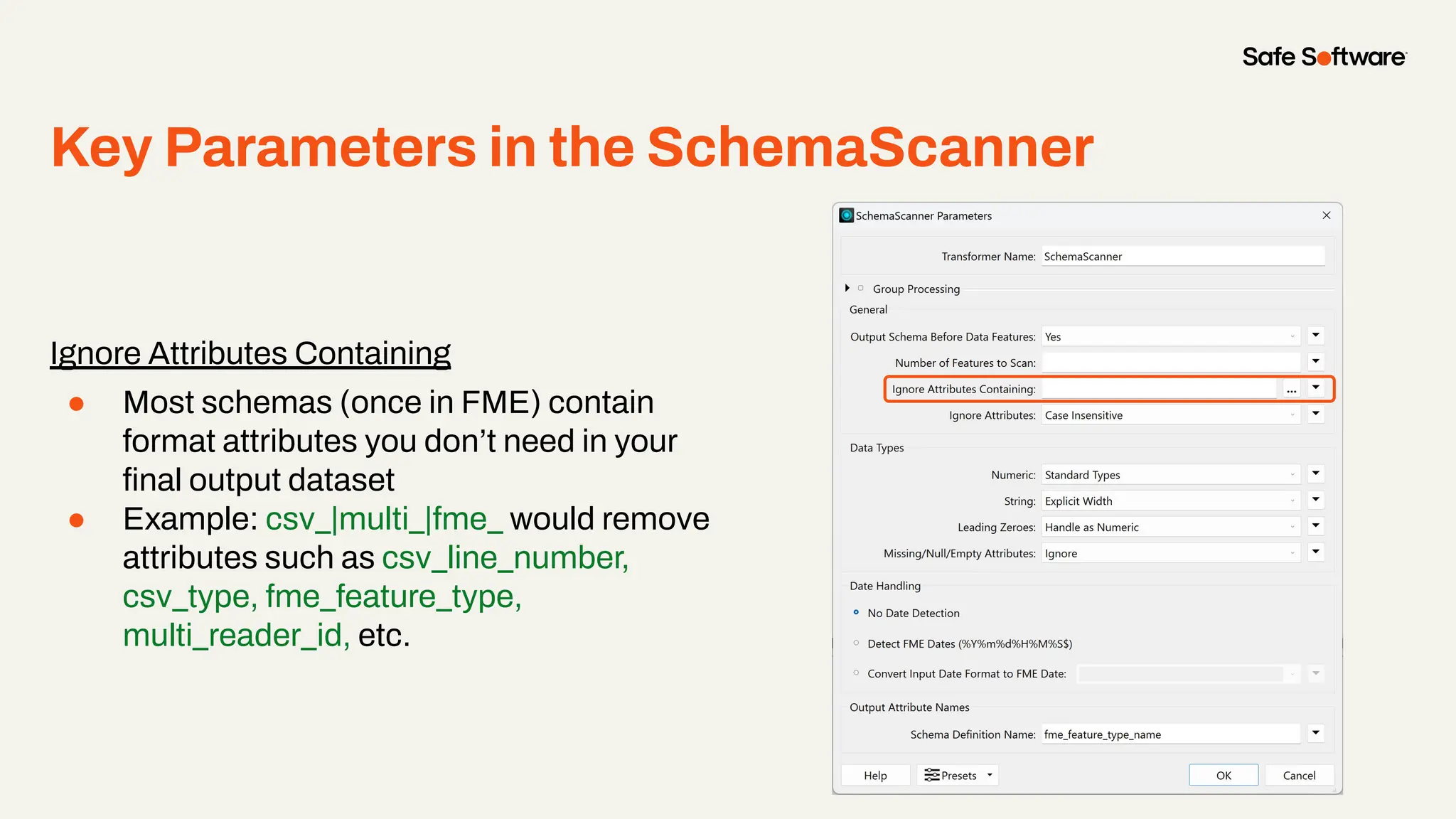
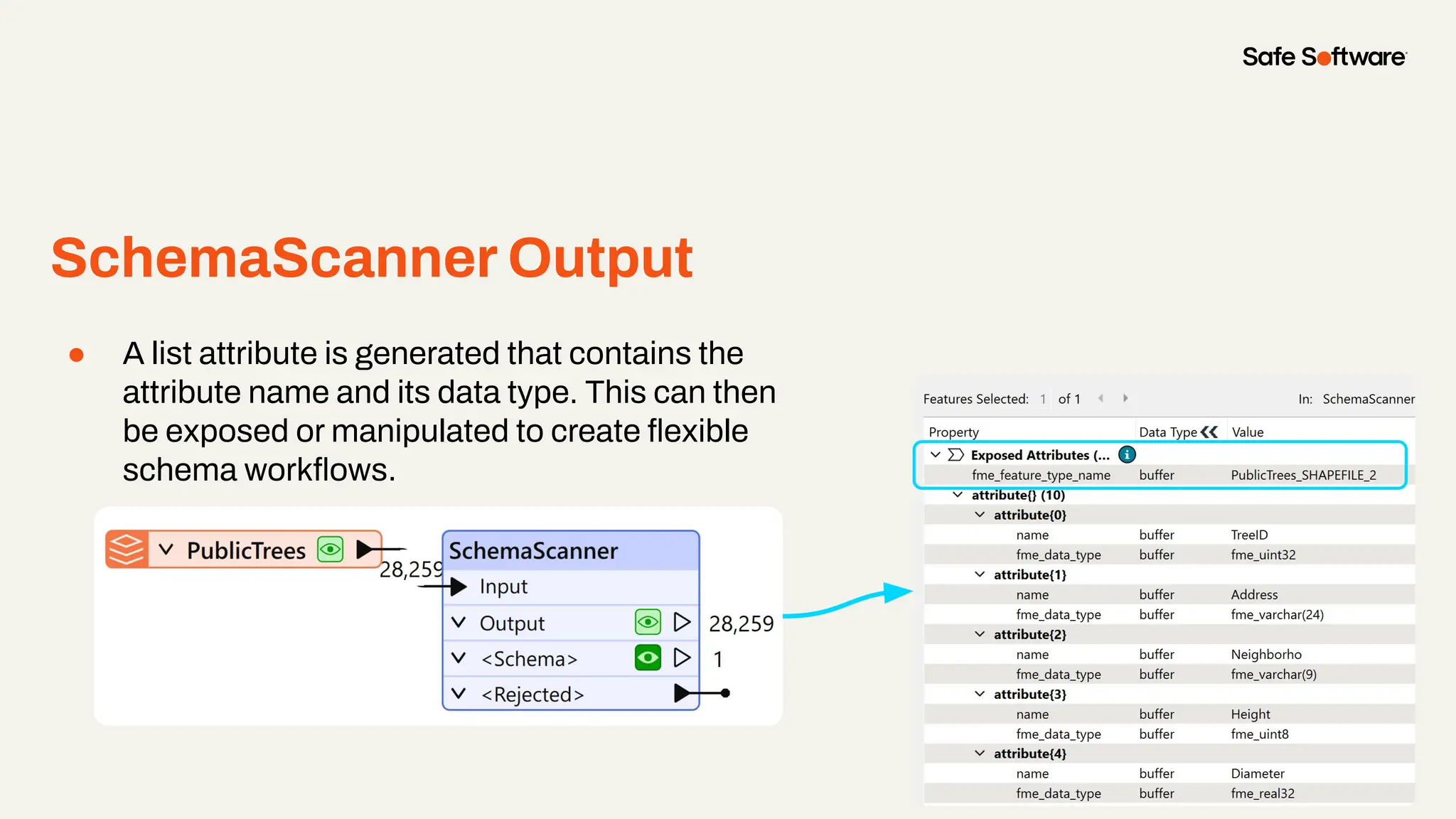
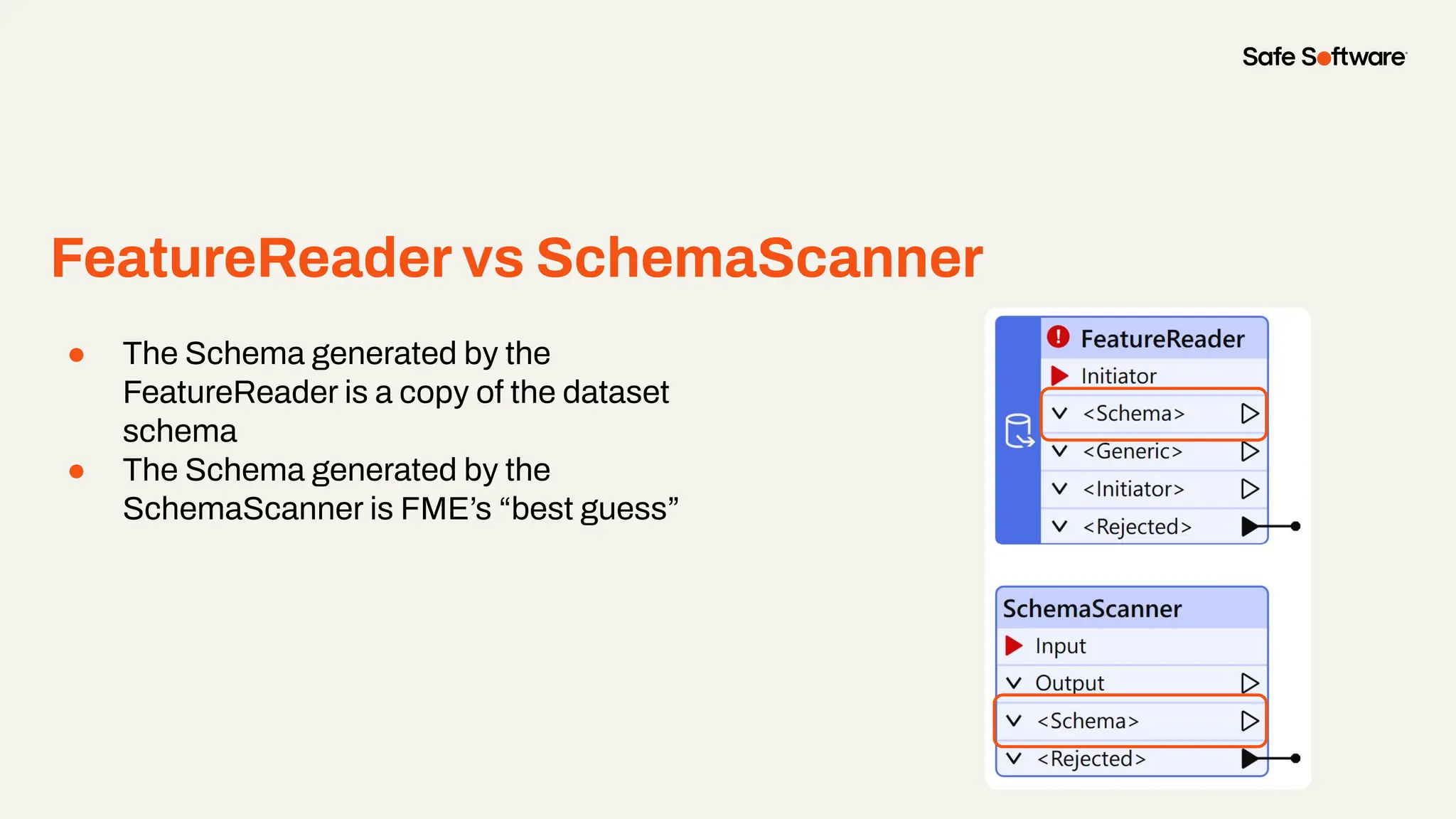
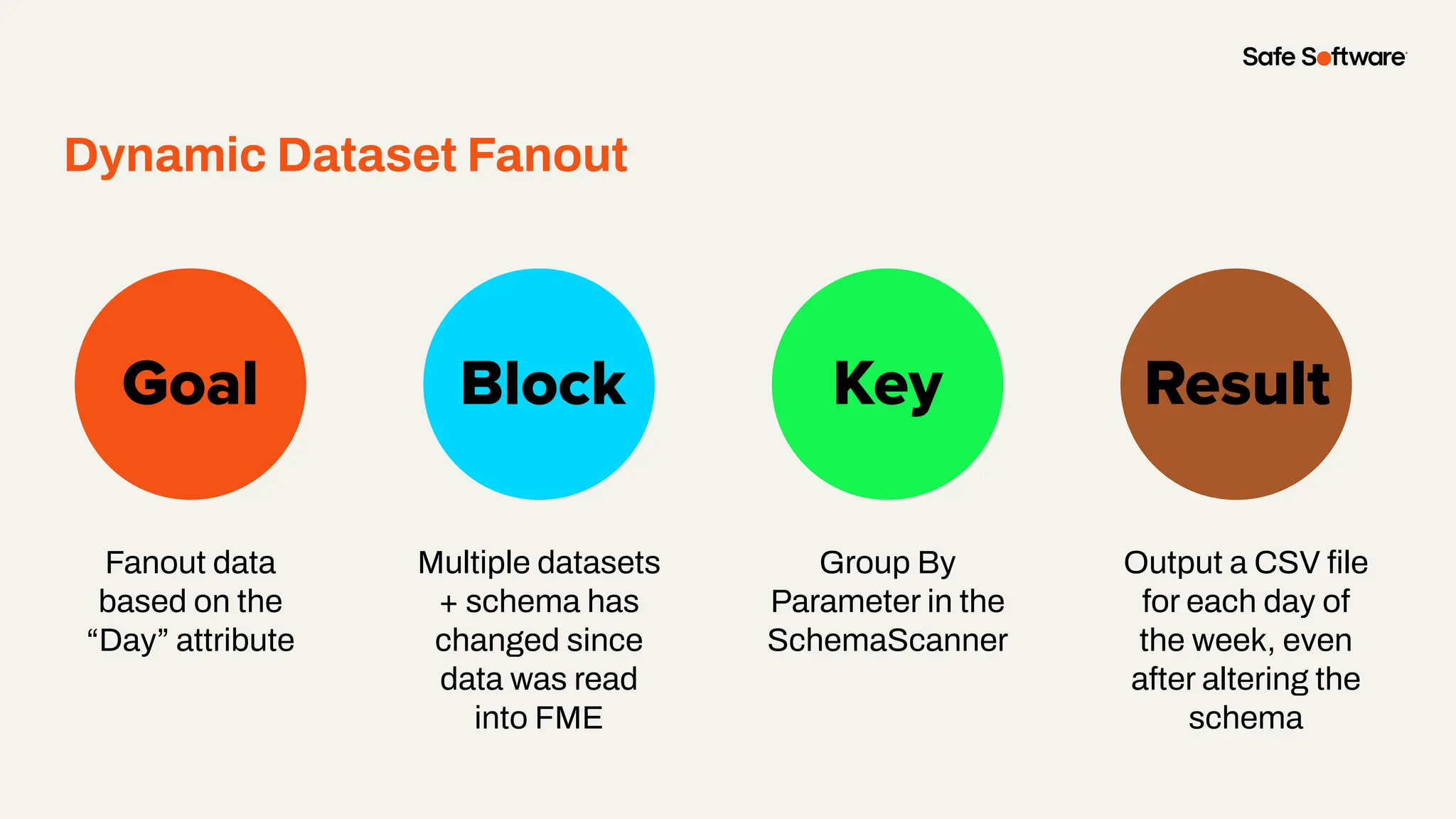
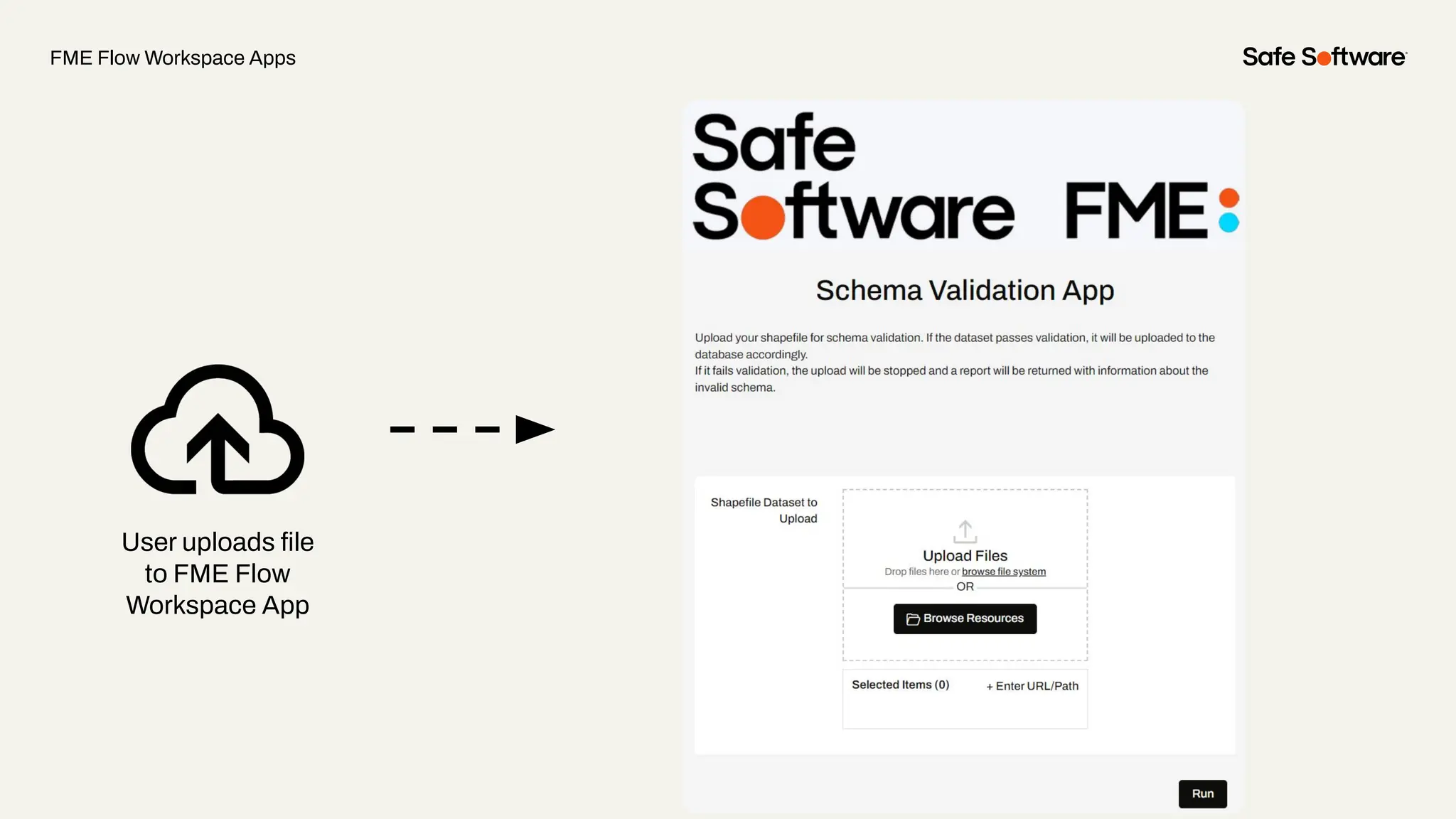
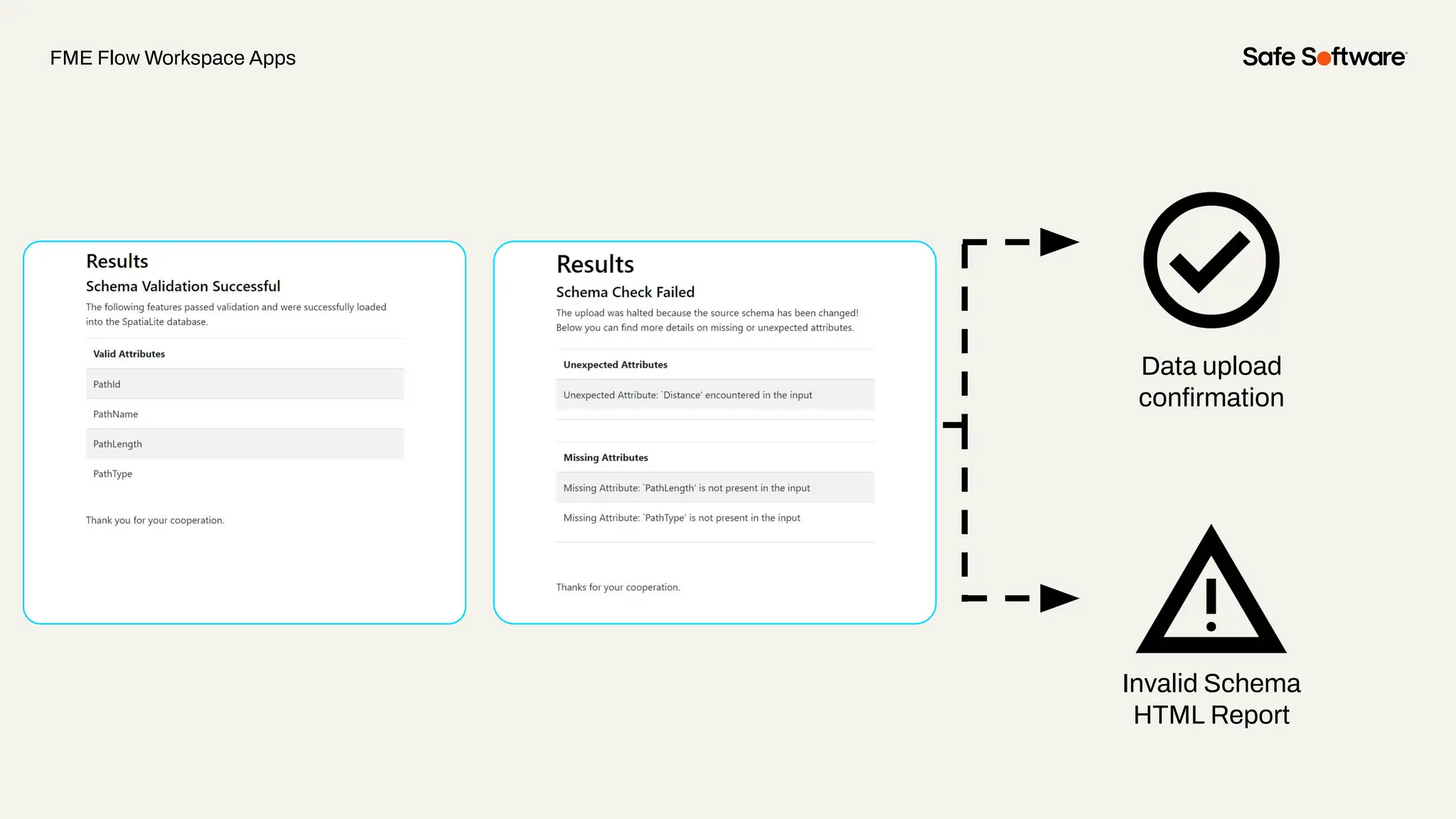
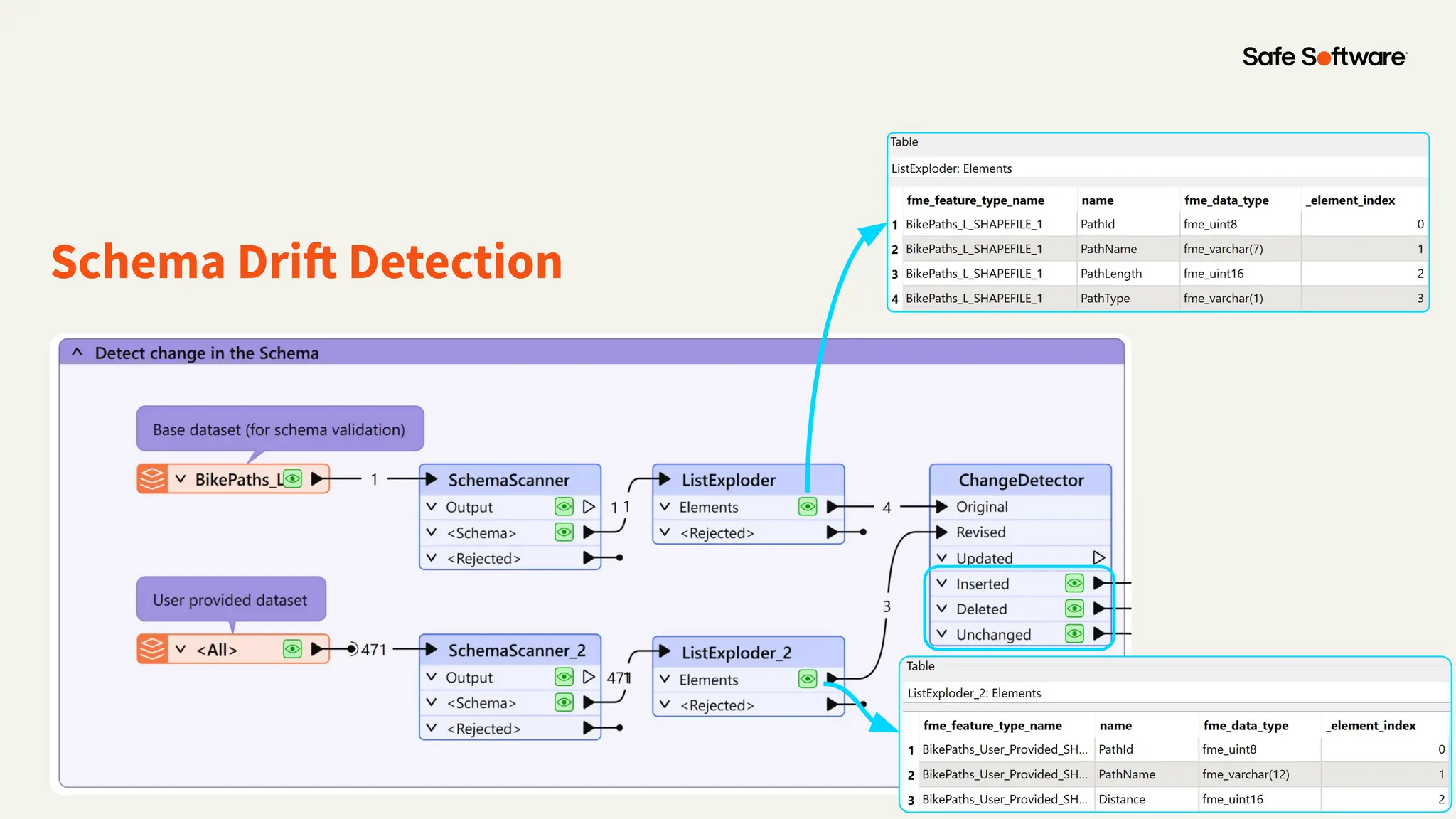
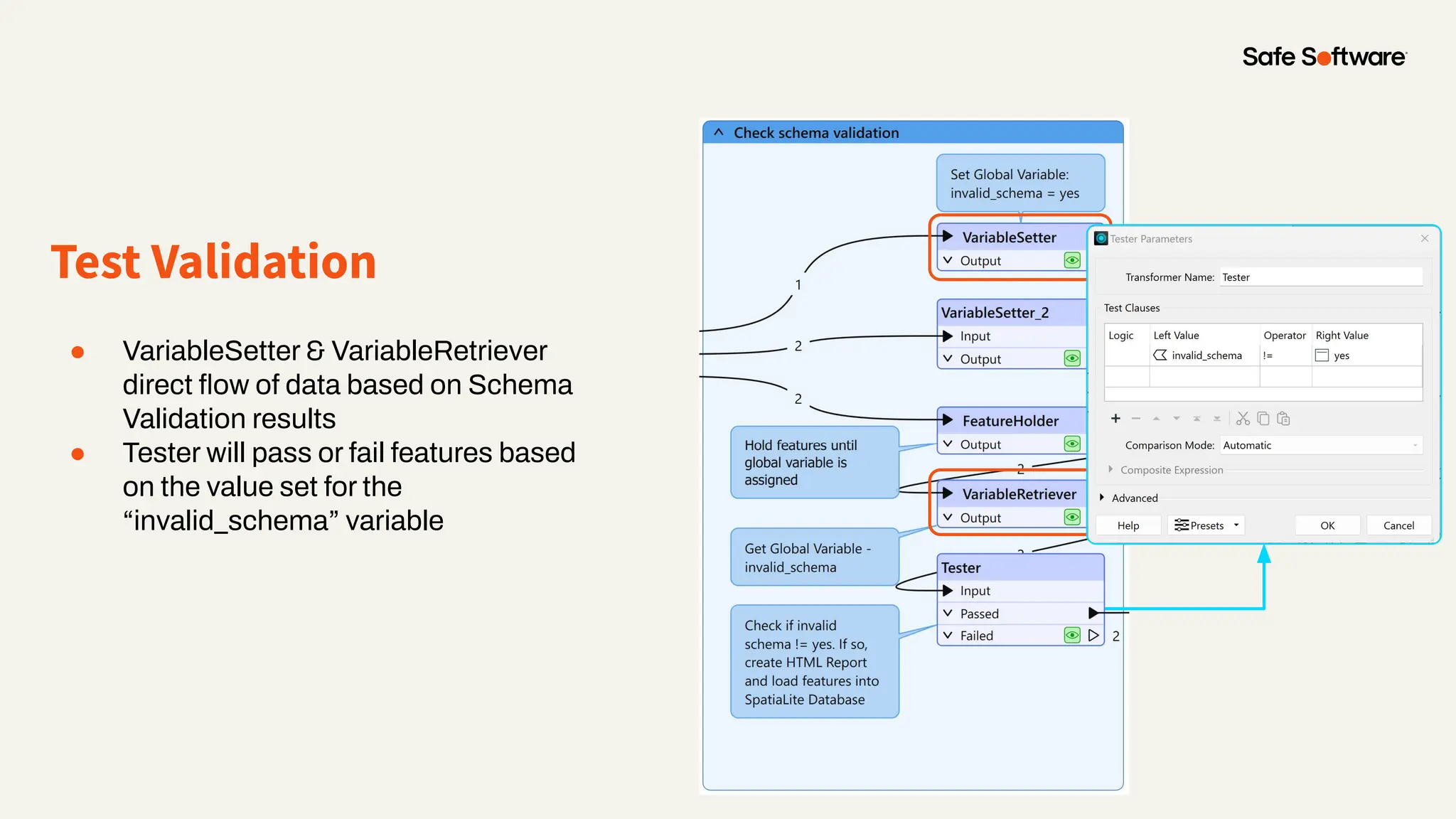
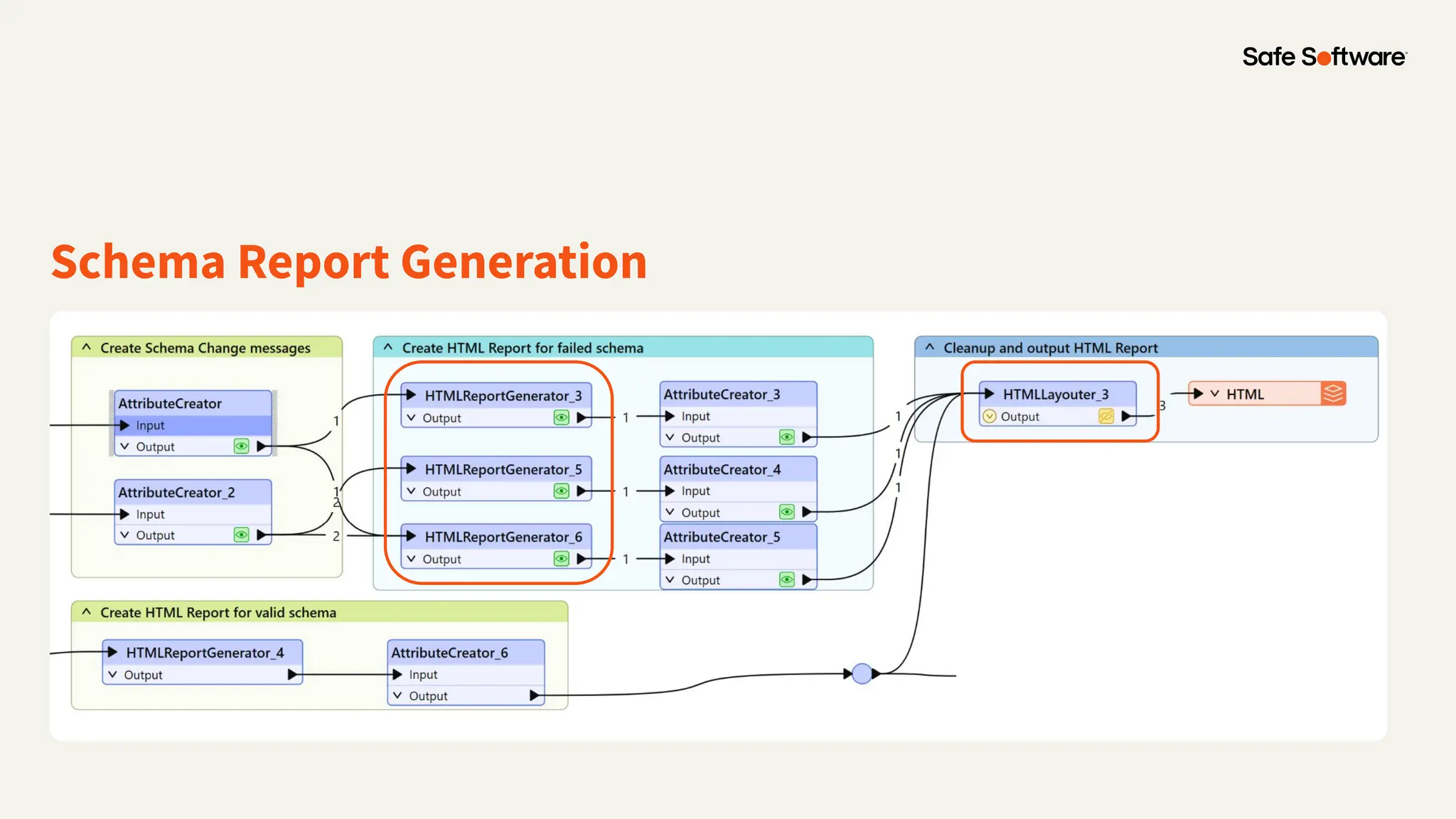
The document discusses dynamic workspaces in data management, emphasizing their adaptability to varying data types and structures without predefined schemas. It highlights use cases, components like the schema scanner transformer, and the benefits of automation in workflows. Additionally, resources and next steps for engaging with FME training and community are mentioned.