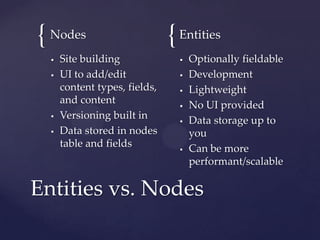
The document discusses Drupal 7's concept of entities, explaining how data is represented in a new way compared to Drupal 6. It highlights the differences between entities and nodes, the role of the Entity API, and includes a live example through the website textbookmadness.com, which utilizes these concepts for managing textbook listings. Additionally, it covers the definitions and functionalities of various entity types and their schema implementations.


![{ Drupal 6 { Drupal 7
{Custom DB table} {Custom DB table]
User Entity
Comment User
Comment
Taxonomy
Taxonomy
Node
Node
Page Page
Blog post Blog post
{Custom node type} {Custom node type}
{Custom entity type}
Drupal Data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal7entities-120227173103-phpapp01/85/Drupal-7-entities-TextbookMadness-com-3-320.jpg)











![School Schema Definition
/* Implements hook_schema(). */
function tbm_schema() {
$schema['tbm_school'] = array(
'fields' => array(
'school_id' => array('type' => 'serial', 'size' => 'small', 'unsigned' => TRUE, 'not null' => TRUE),
'machine_name' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 100, 'not null' => TRUE, 'description' => 'The machine name of the school.'),
'name' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 128, 'not null' => TRUE, 'description' => 'The name of the school.'),
'name_short' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 64, 'description' => 'The short name of the school.'),
'name_long' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 255, 'description' => 'The long name of the school.'),
'url' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 1024, 'not null' => TRUE, 'description' => 'The URL of the school's homepage.'),
'email_domains' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 1024, 'description' => 'The email domains (comma delimited) valid for the school.'),
'sponsor1_name' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 64, 'description' => 'The name of the first sponsor.'),
'sponsor1_name_short' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 32, 'description' => 'The short name of the first sponsor.'),
'sponsor1_name_long' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 128, 'description' => 'The long name of the first sponsor.'),
'sponsor1_url' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 1024, 'description' => 'The URL of the first sponsor's homepage.'),
'sponsor2_name' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 64, 'description' => 'The name of the second sponsor.'),
'sponsor2_name_short' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 32, 'description' => 'The short name of the second sponsor.'),
'sponsor2_name_long' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 128, 'description' => 'The long name of the second sponsor.'),
'sponsor2_url' => array('type' => 'varchar', 'length' => 1024, 'description' => 'The URL of the second sponsor's homepage.'),
'enabled' => array('type' => 'int', 'size' => 'tiny', 'unsigned' => TRUE, 'not null' => TRUE, 'description' => 'Whether the school is enabled.'),
'listed' => array('type' => 'int', 'size' => 'tiny', 'unsigned' => TRUE, 'not null' => TRUE, 'description' => 'Whether the school is listed.'),
),
'primary key' => array('school_id'),
'unique keys' => array(
'machine_name' => array('machine_name'),
),
);
return $schema;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal7entities-120227173103-phpapp01/85/Drupal-7-entities-TextbookMadness-com-16-320.jpg)
![School EntityFieldQuery
This function shows how to use an EntityFieldQuery
Users are necessarily associated with a school
I have a field, field_school, attached to the user entity type, which
stores this relationship data
The query finds active users (status == 1) at the given school
/**
* Load an array of uids of users at the school with the given ID.
* @param int $school_id The ID of the school to load users for
*/
function tbm_school_uids($school_id) {
$query = new EntityFieldQuery();
$result = $query
->entityCondition('entity_type', 'user')
->propertyCondition('status', 1)
->fieldCondition('field_school', 'school_id', $school_id)
->execute();
return array_key_exists('user', $result) ? array_keys($result['user']) : array();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal7entities-120227173103-phpapp01/85/Drupal-7-entities-TextbookMadness-com-17-320.jpg)
