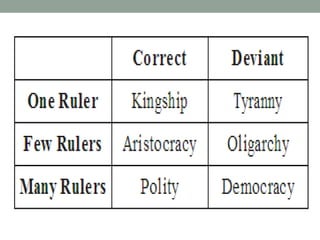
Aristotle, a Greek philosopher and student of Plato, made substantial contributions to various fields, particularly political science, where he classified states, discussed the role of the state, and emphasized the importance of justice and citizenship. He supported private property and offered controversial views on slavery and the roles of women in society, advocating for a hierarchical family structure. Aristotle believed that happiness (eudaimonia) was the ultimate goal of the state and introduced concepts like distributive justice, while critiquing previous philosophical views, particularly those of Plato.