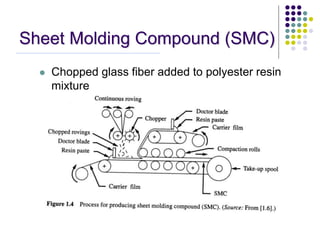
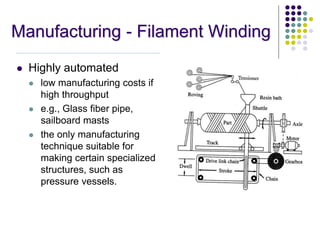
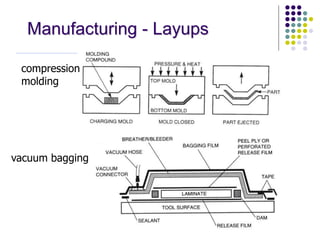
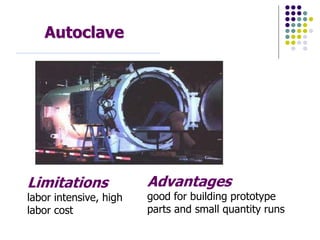
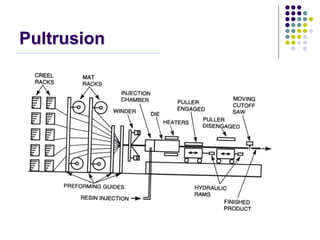
Composite materials are composed of two or more constituents, a reinforcement like fibers and a matrix like epoxy. Composites offer advantages like high strength and stiffness with low weight. They can be designed and manufactured to eliminate joints. Common applications include aerospace, sports, automotive, and construction. Composite manufacturing involves assembling fibers, impregnating resin, shaping the product, and curing the resin. Different manufacturing methods include sheet molding compound, filament winding, prepregs, layups, autoclaves, resin transfer molding, and pultrusion. Each has advantages and limitations depending on the application.