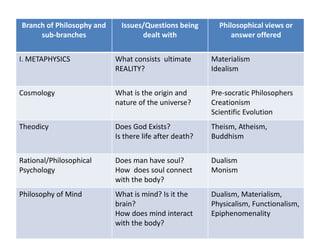
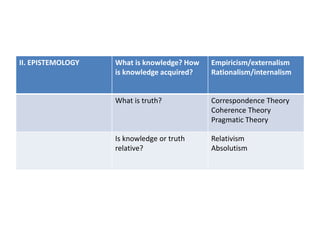
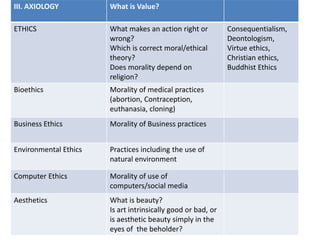
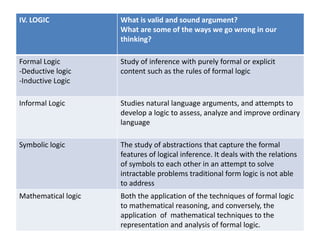
This document discusses doing philosophy. It begins by defining philosophy as the love of wisdom. It then discusses the origins of philosophy in ancient Greece with thinkers like Thales questioning the nature of reality. It outlines the main branches of philosophy like metaphysics, epistemology, ethics, and logic. It describes doing philosophy as asking questions, examining other philosophers' work, and reflecting critically. Key aspects of doing philosophy include wondering, doubting, seeking truth and simplicity, revising beliefs, and discussing ideas with others. Philosophical reading involves getting an overview, analyzing arguments, and relating ideas to one's own thinking.