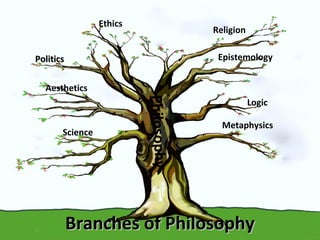
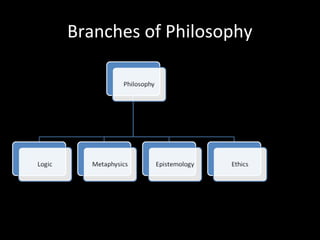
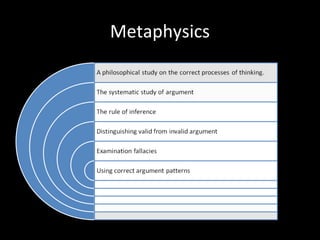
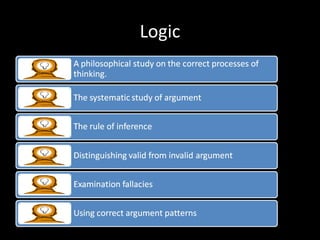
This document provides an overview of the field of philosophy by defining what philosophy is, exploring its origins and purposes, and outlining its major branches. It begins by explaining that philosophy arises from human curiosity and desire to understand fundamental questions. It then discusses the etymological roots of the word "philosophy" and defines it as the love of wisdom. The document concludes by listing and briefly describing the main branches of philosophy, including ethics, epistemology, metaphysics, politics, aesthetics, logic, religion, and the philosophy of science.