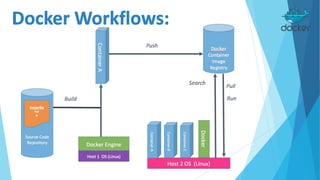
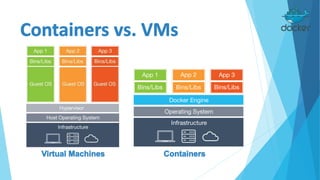
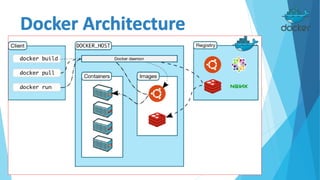
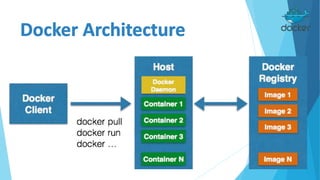
Docker is an open platform for building, shipping and running distributed applications. It allows developers to package applications into containers that have everything needed to run, including libraries and other dependencies, and ship them to any Docker-enabled infrastructure. Containers are more portable and provide better isolation than virtual machines, and allow applications to be deployed with minimal overhead or conflict. Docker uses containers, images and a Dockerfile to deploy and run applications reliably across any infrastructure.
















![FROM ubuntu:14.04
MAINTAINER Jirayut Nimsaeng <w [at] winginfotech.net>
ADD build-files /build-files
RUN apt-get update
RUN apt-get install -y openssh-server vim tmux rsync byobu
RUN mkdir /var/run/sshd
RUN sed -i 's/required pam_loginuid.so/optional
pam_loginuid.so/g' /etc/pam.d/sshd
CMD /start.sh
EXPOSE 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerpresentation-160429061125/85/Docker-Workshop-20-320.jpg)