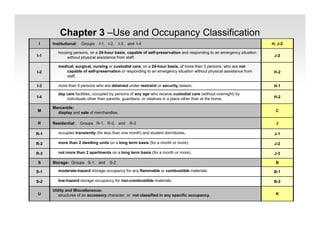
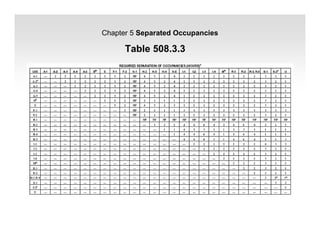
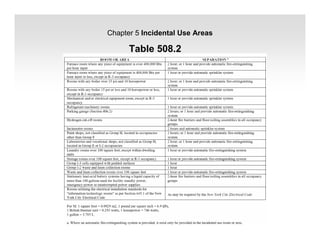
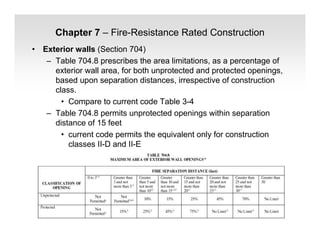
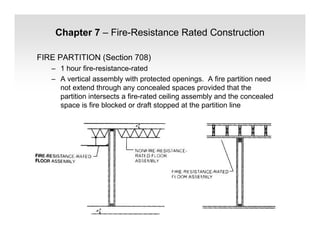
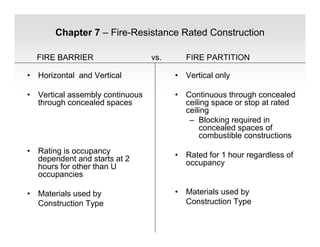
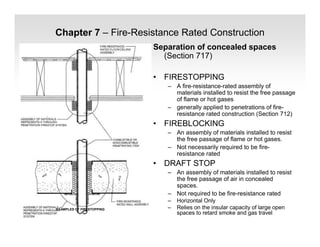
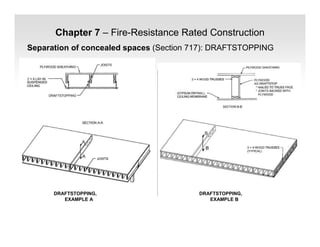
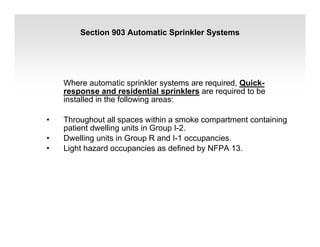
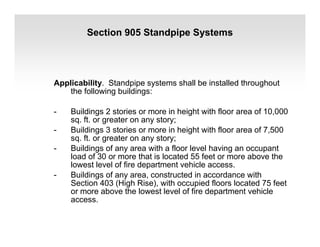
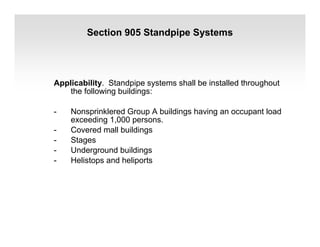
The document discusses fire protection requirements in the 2008 New York City Building Code. It covers various types of fire-resistance rated construction required by the code, including fire walls, fire barriers, fire partitions, and shaft enclosures. It describes the materials, fire ratings, and purposes of each type of construction. It also discusses exterior wall requirements and allowances for protected and unprotected openings based on construction type and fire separation distance.

























































![A manual and automatic fire alarm system shall be
installed in:
• Group A with occupant load of 300 or more
• Group B and M with an occupant load of 500 or more
persons, or more than 100 persons above or below lowest
level of exit discharge
• Group E occupancies
• Group F occupancies that are 2 or more stories in height and
have an occupant load of [500] 100 or more, or when 25
persons or more are above or below lowest level of exit
discharge
Section 907 Fire Alarm and Detection Systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dobtechforumnewcodechapter78-230301193103-d916cf77/85/DOBTechForumNewCodechapter78-pdf-75-320.jpg)