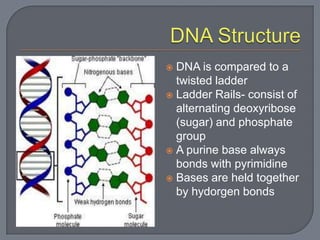
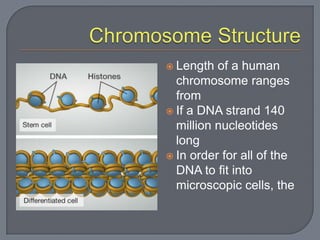
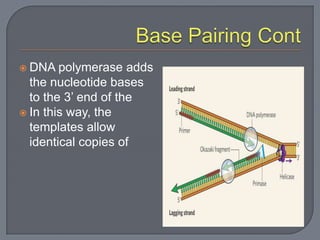
Nucleotides consist of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are made of nucleotides. DNA contains deoxyribose and thymine, while RNA contains ribose and uracil instead of thymine. DNA replication involves unwinding the DNA double helix, synthesizing new strands based on the existing strands, and rewinding the DNA.