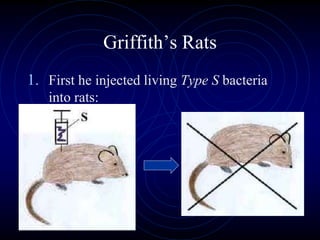
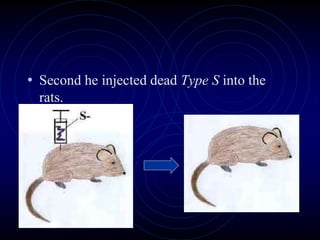
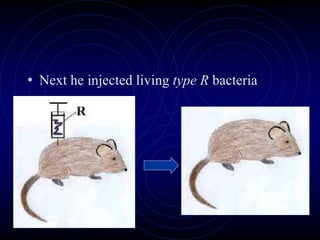
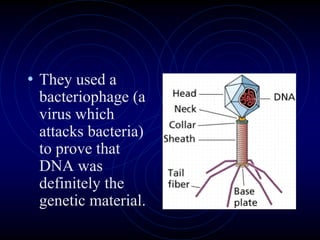
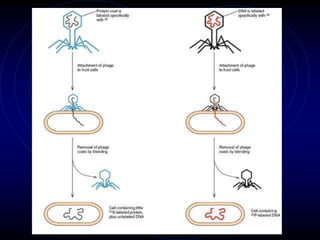
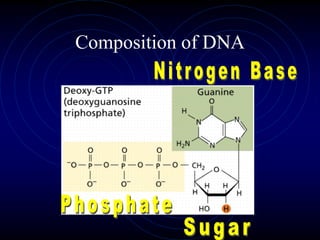
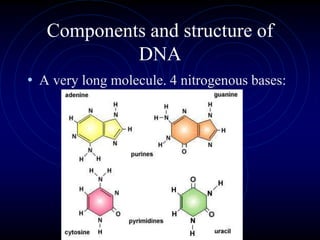
Frederick Griffith conducted an experiment in 1928 using two strains of bacteria that cause pneumonia - a severe type (S) and a relatively harmless type (R). He found that injecting a mixture of live R bacteria and dead S bacteria into rats resulted in the rats contracting the lethal S infection, showing that some "transforming principle" from the dead S bacteria allowed the R bacteria to take on the S phenotype. This transforming principle was later identified as DNA.