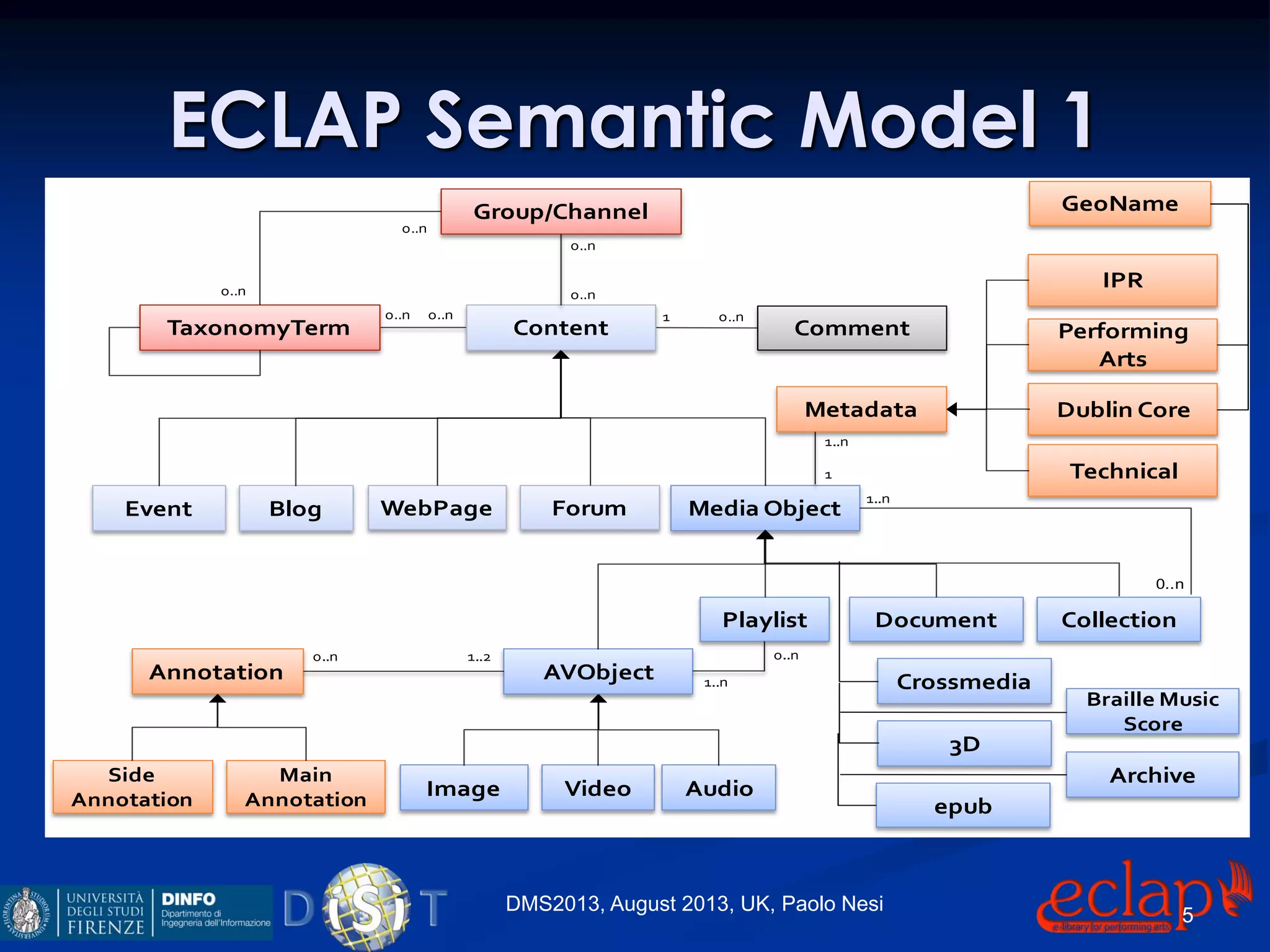
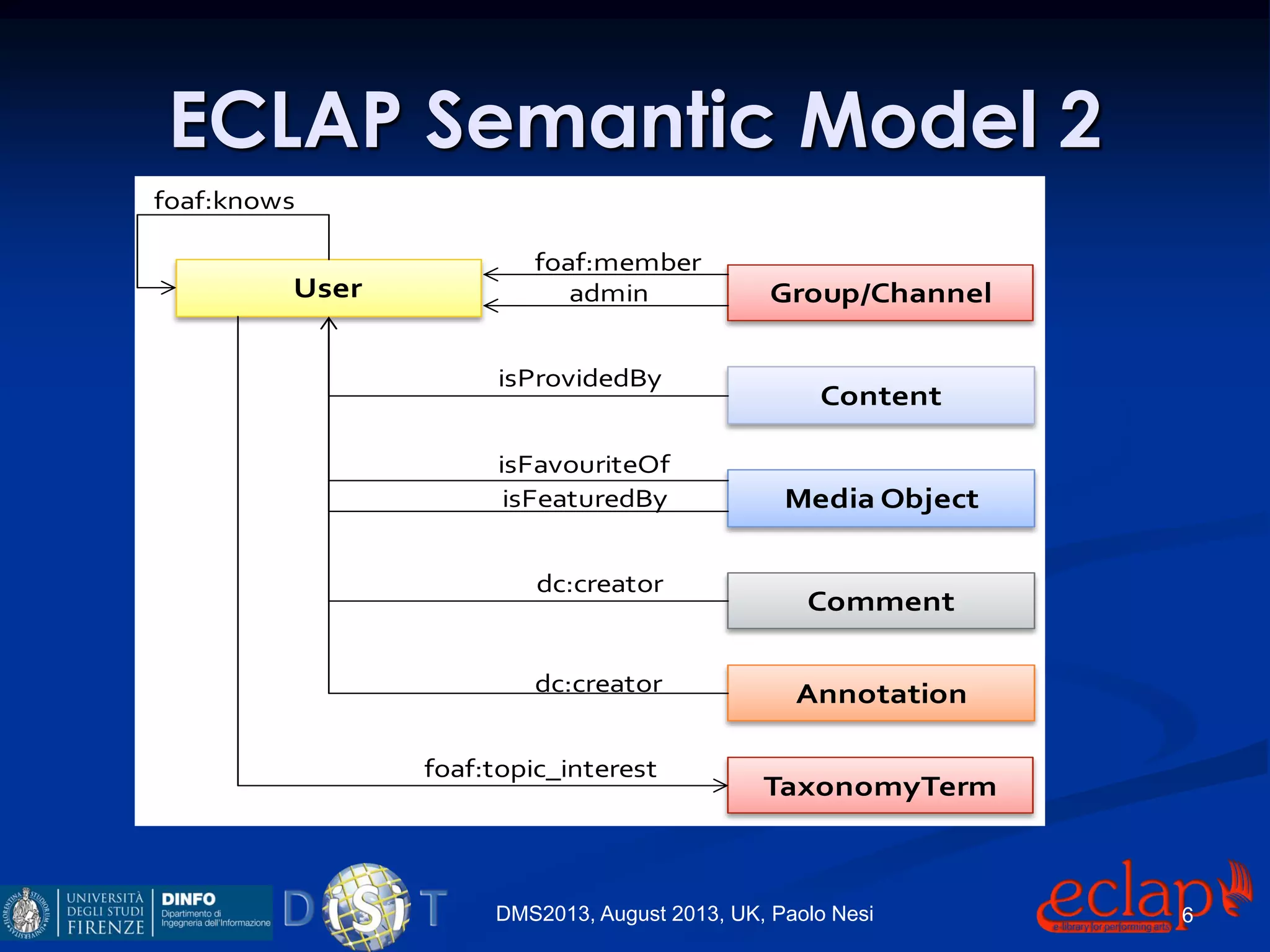
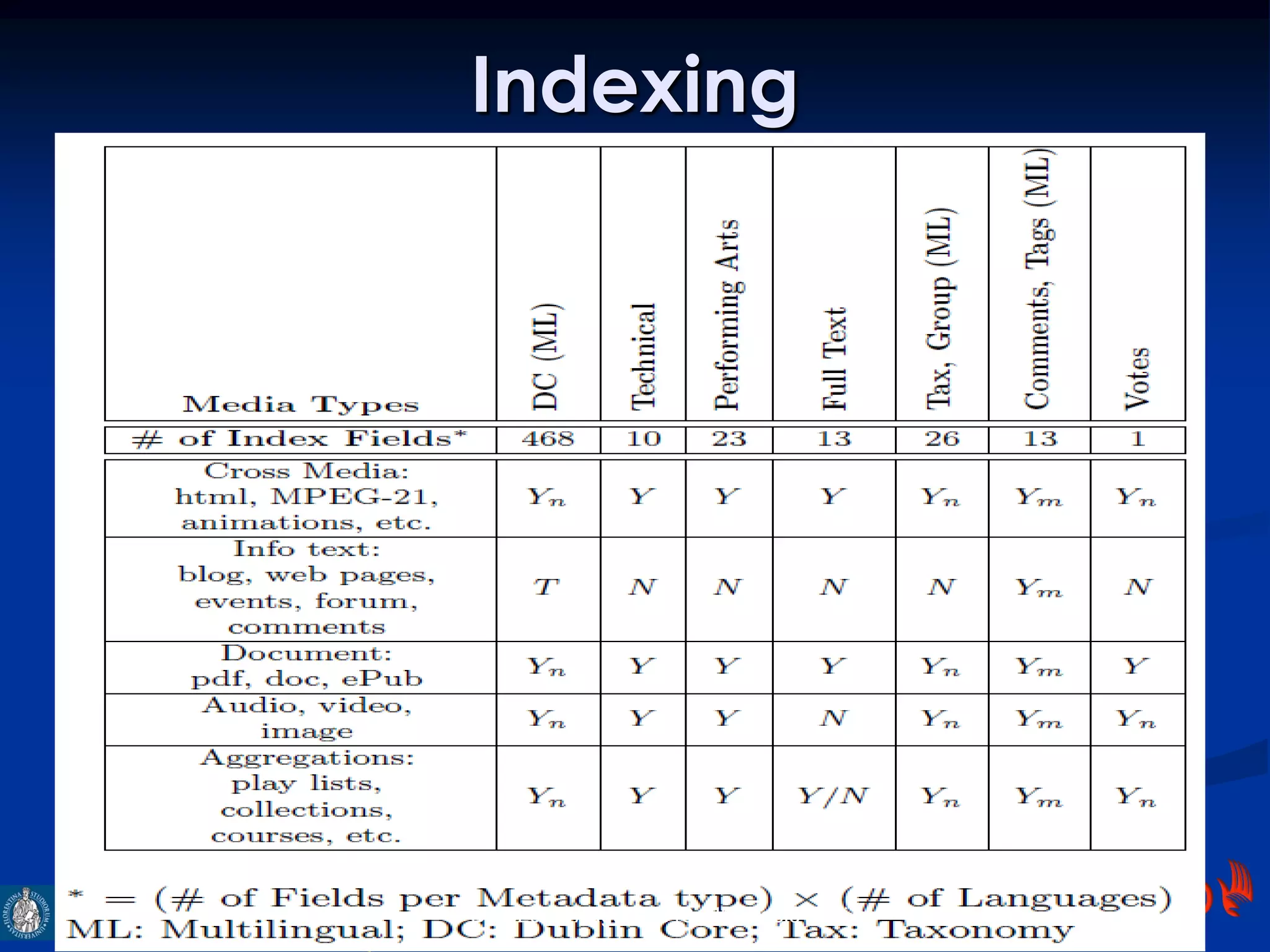
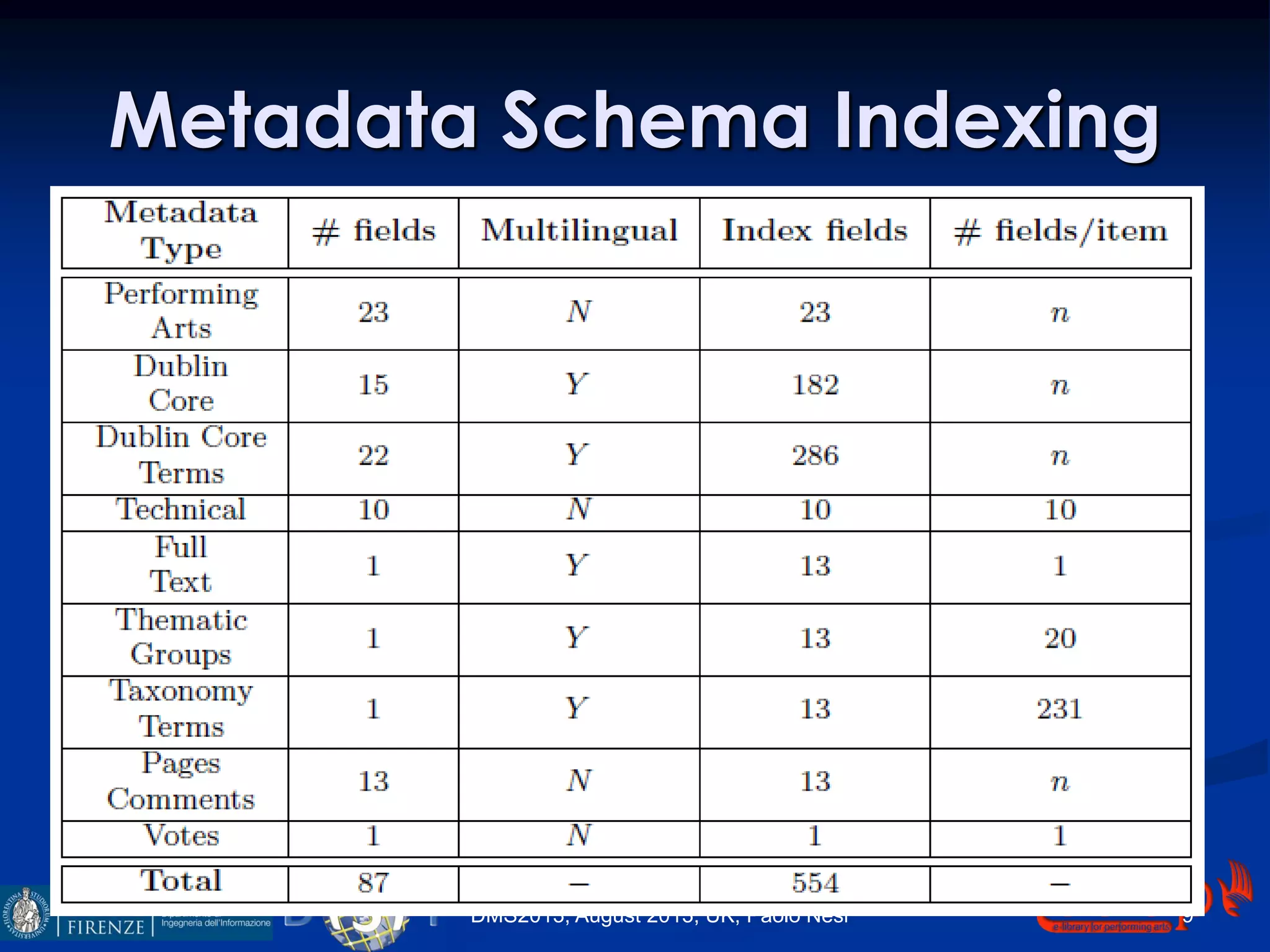
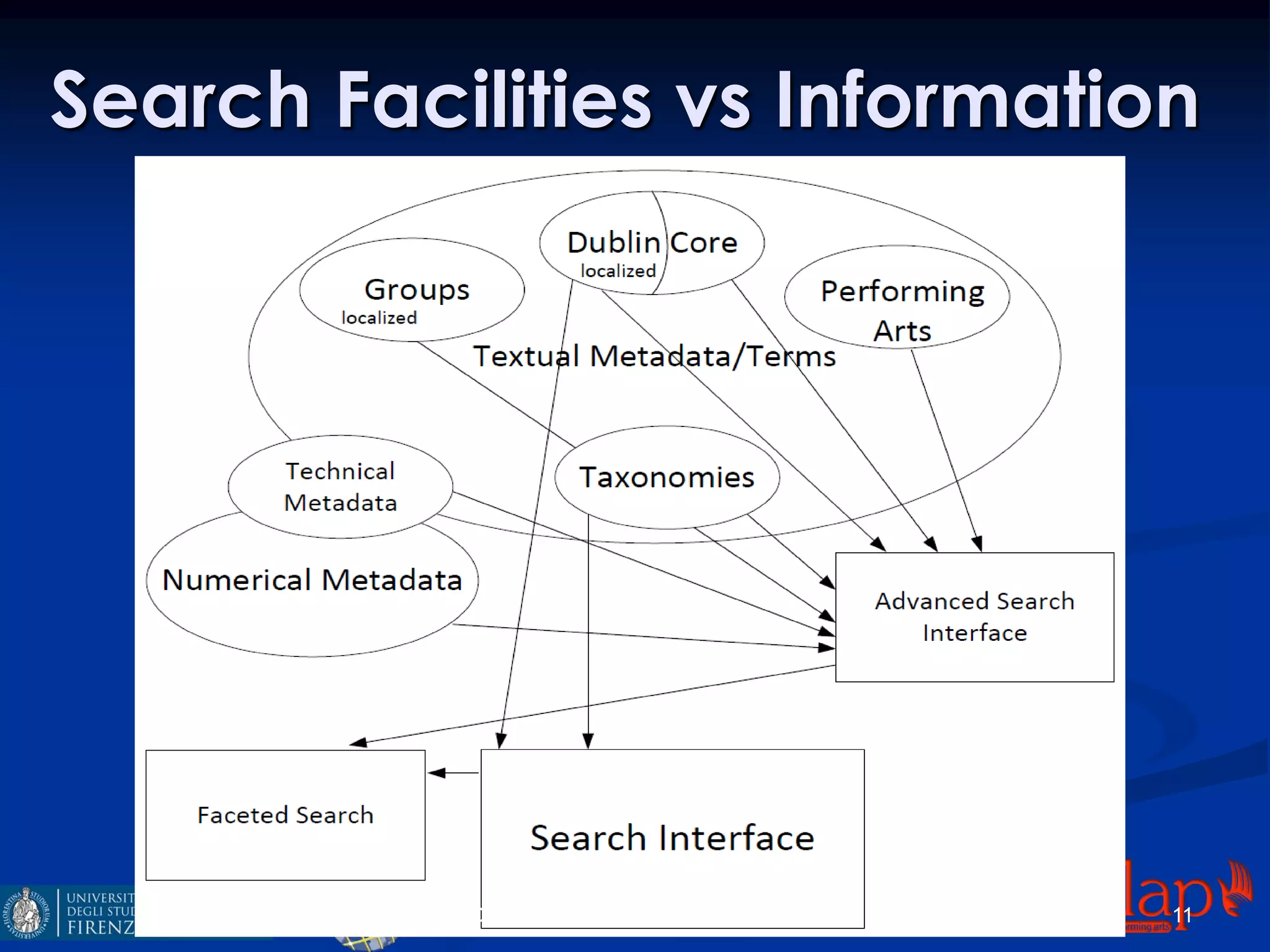
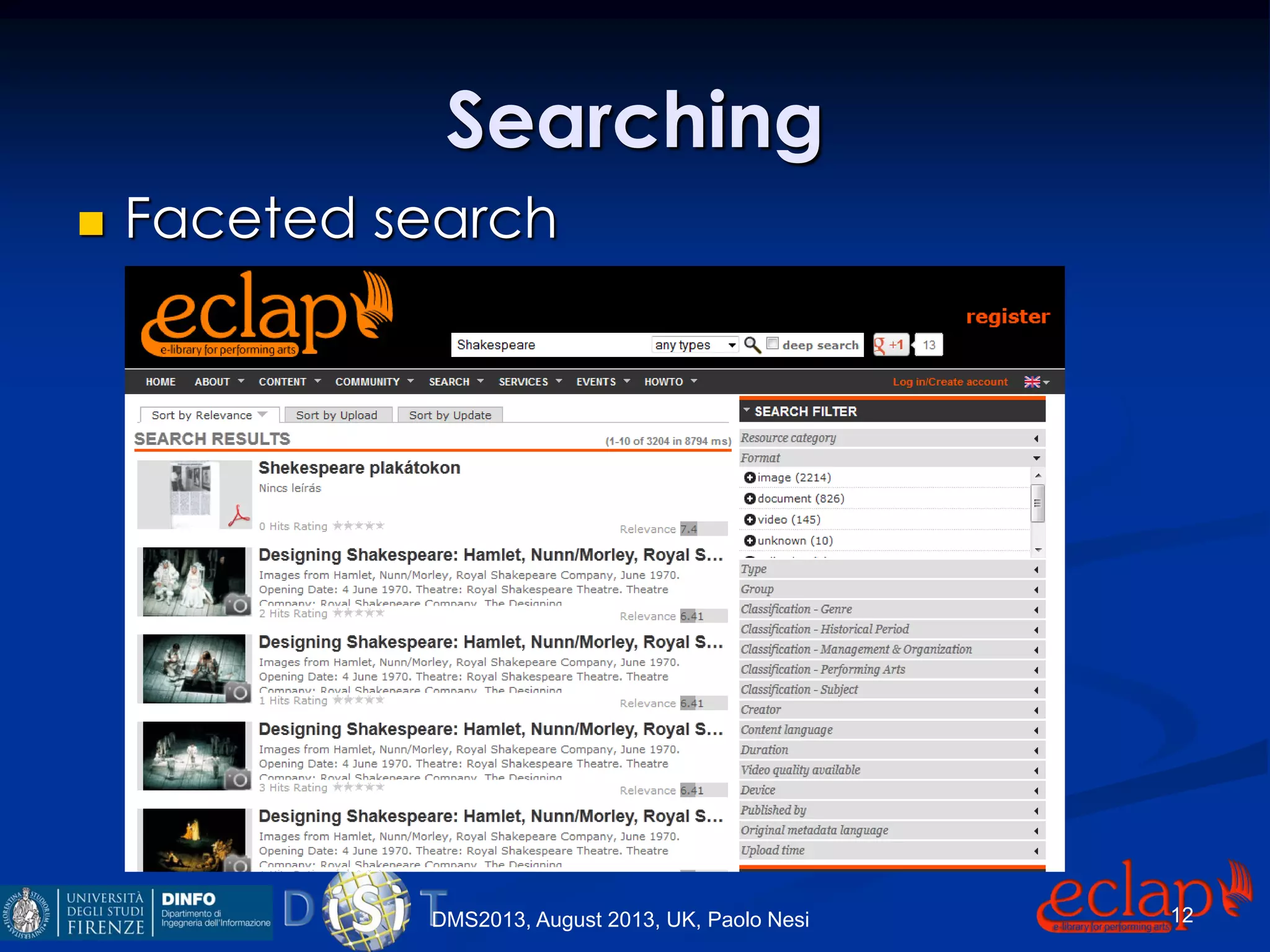
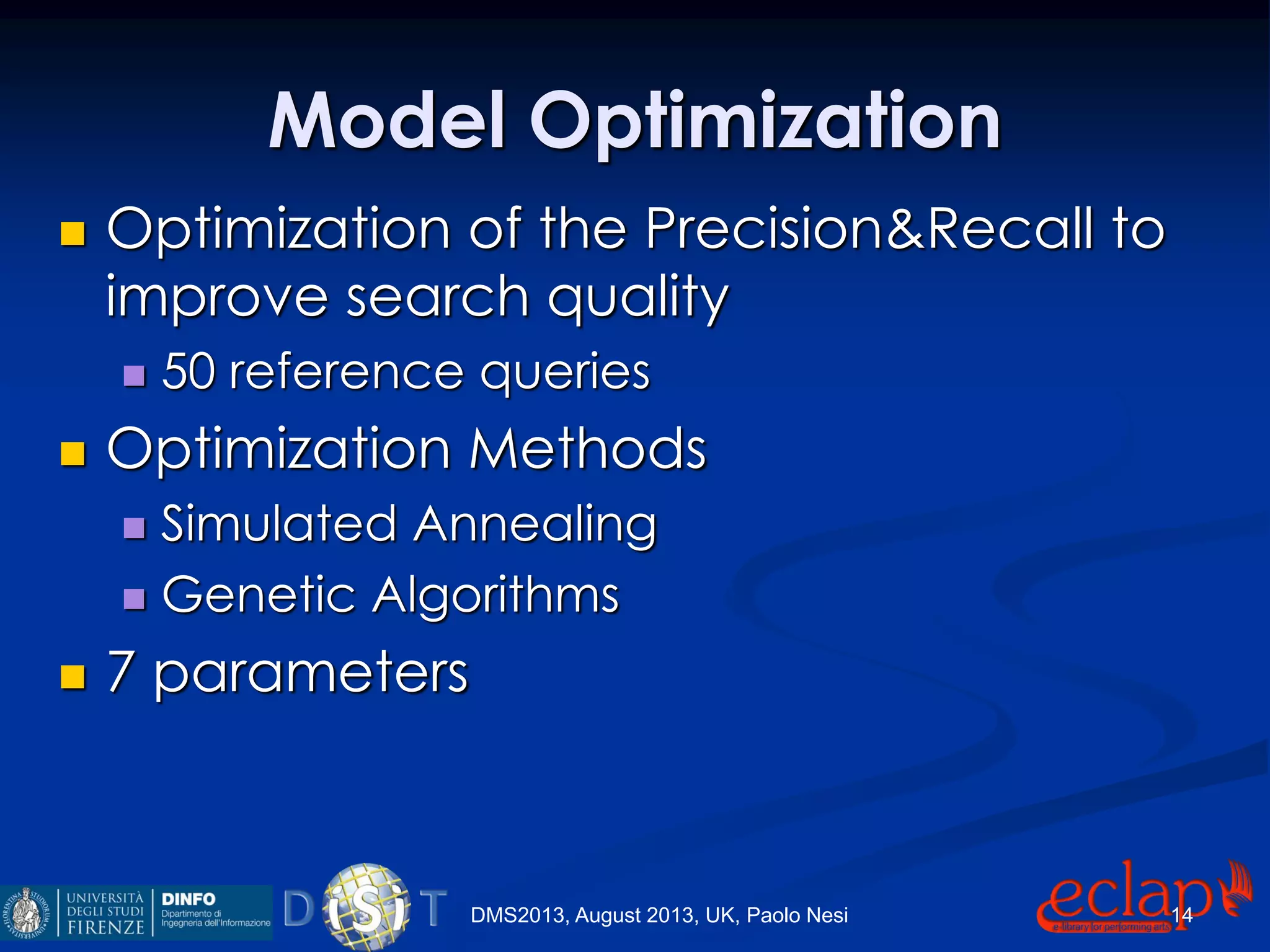
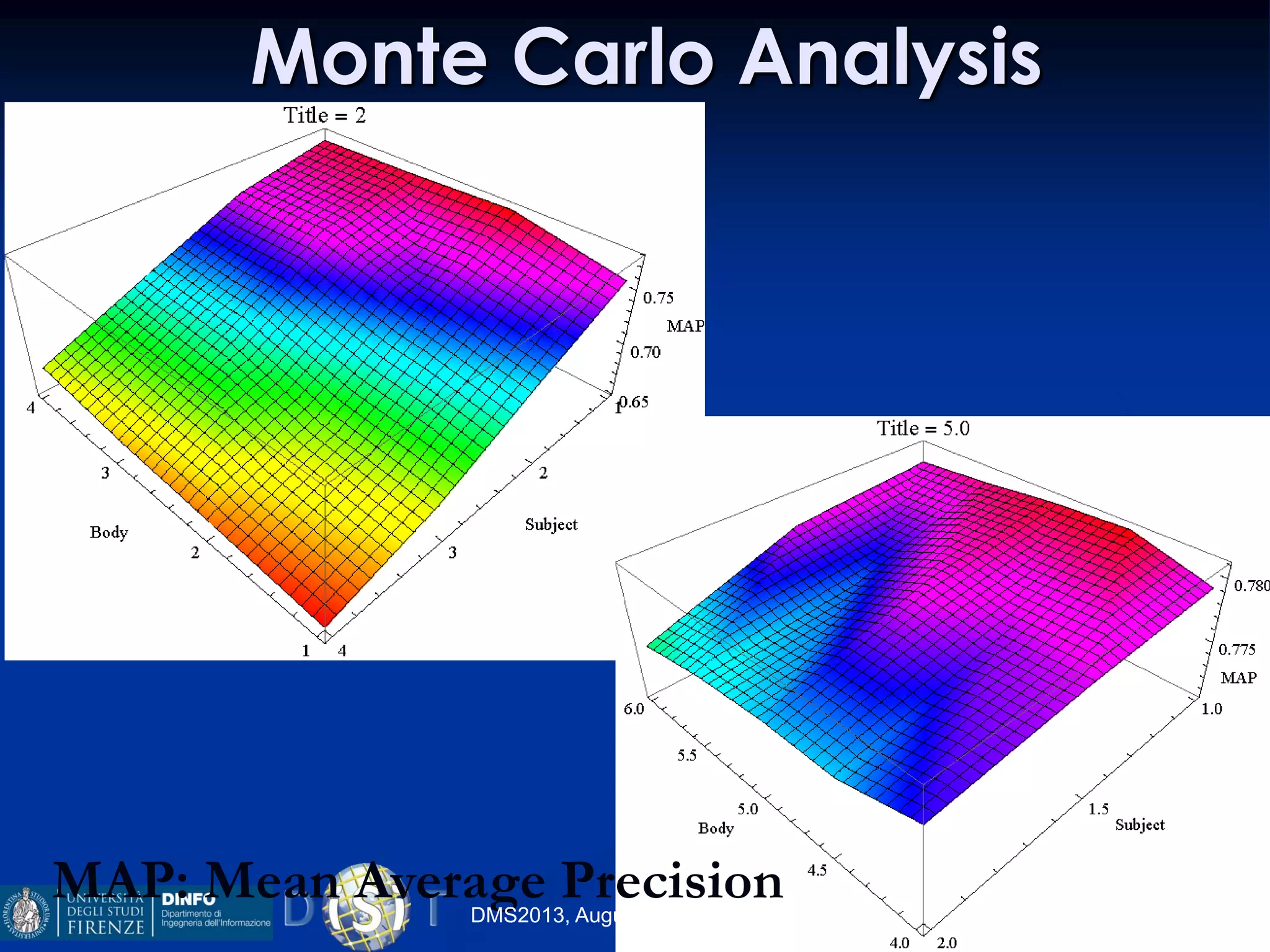
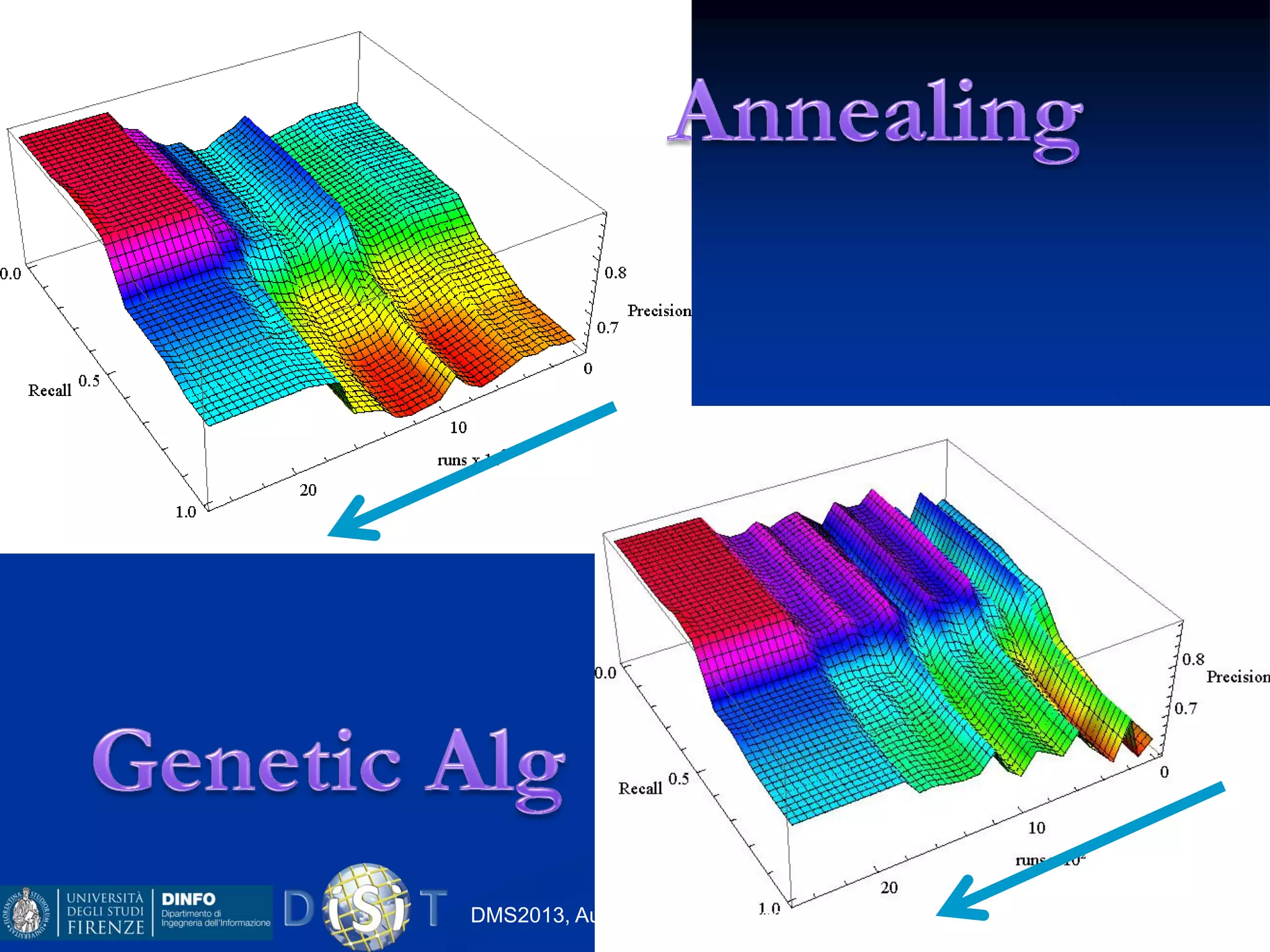
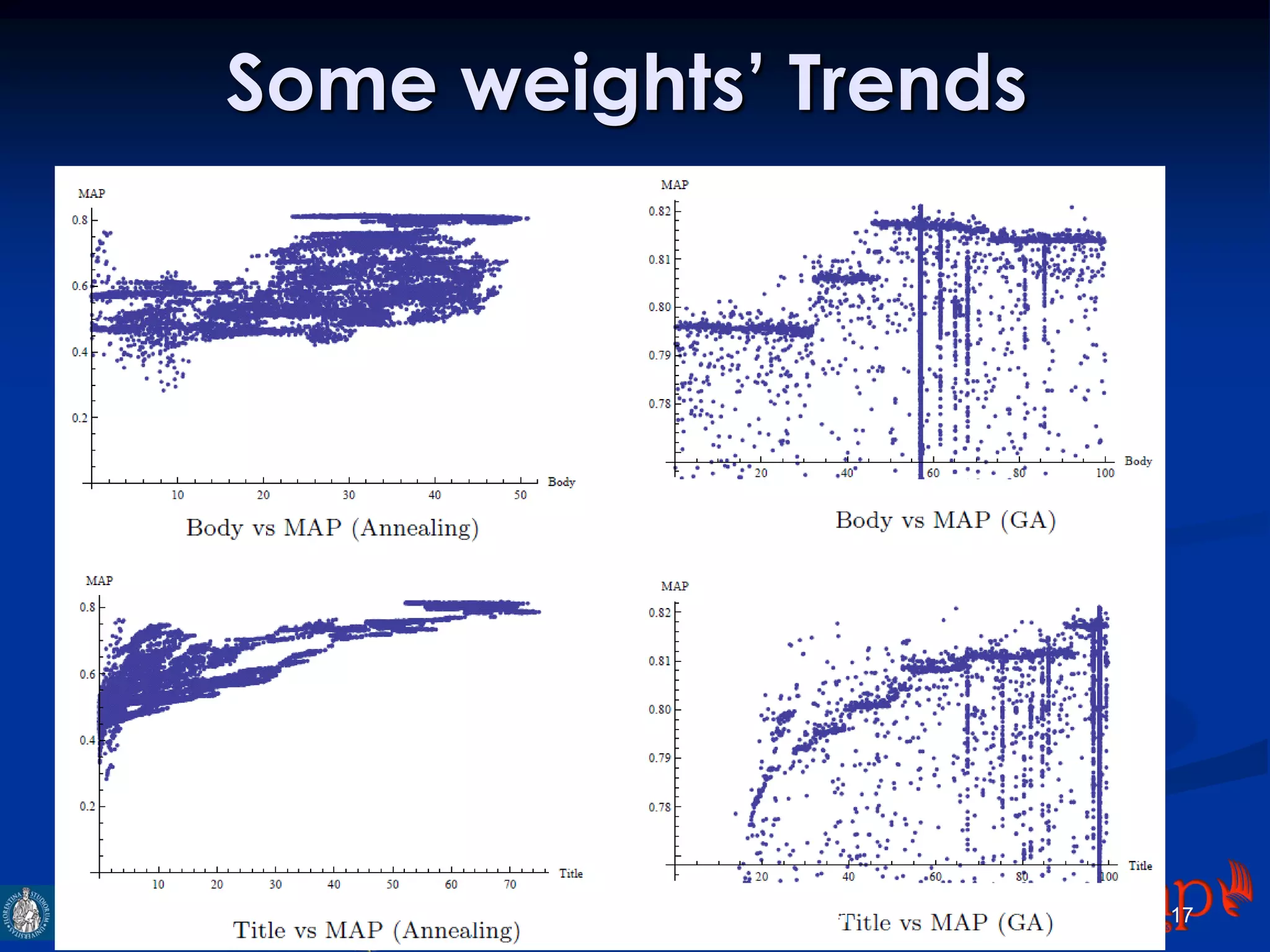
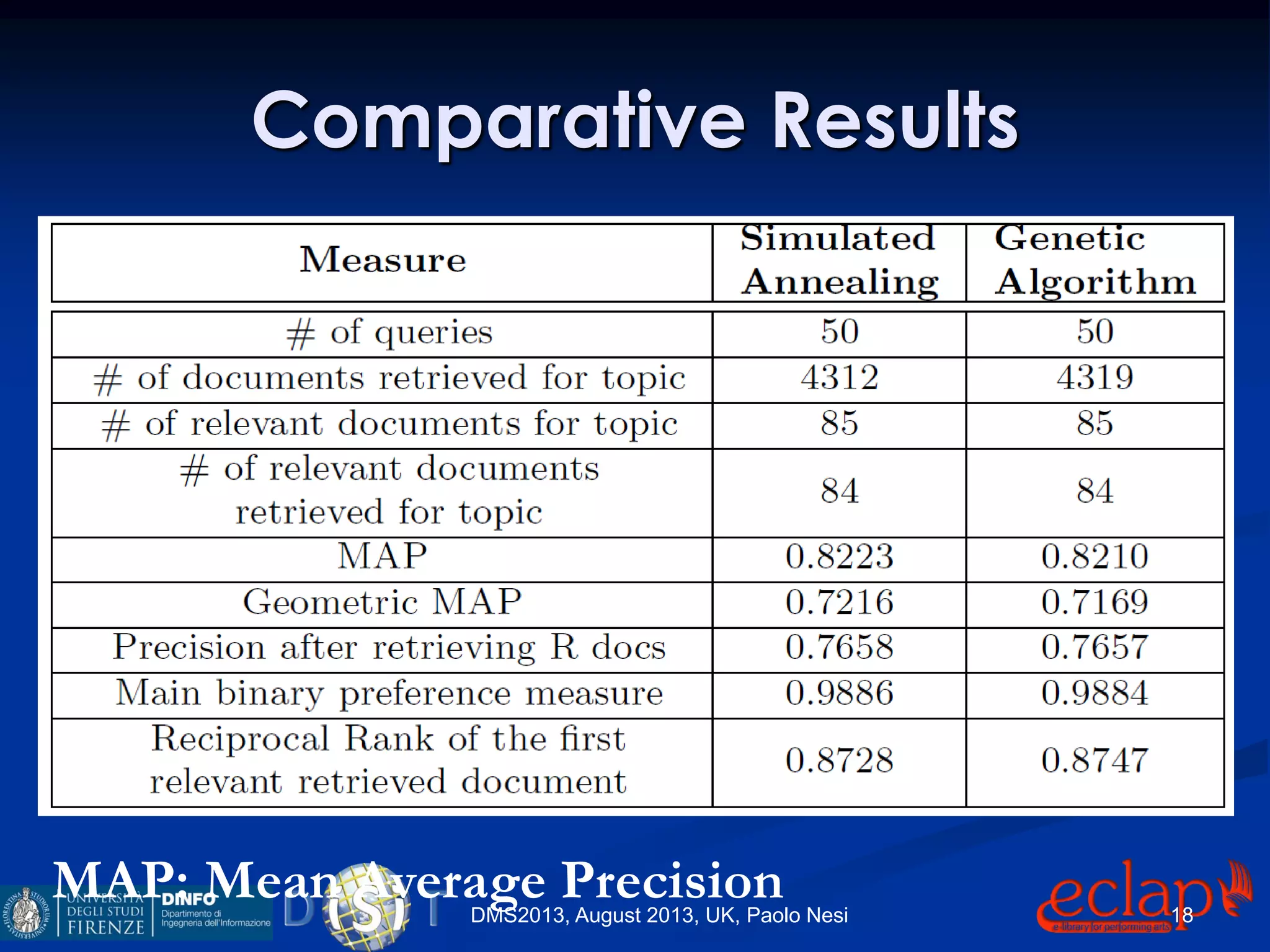
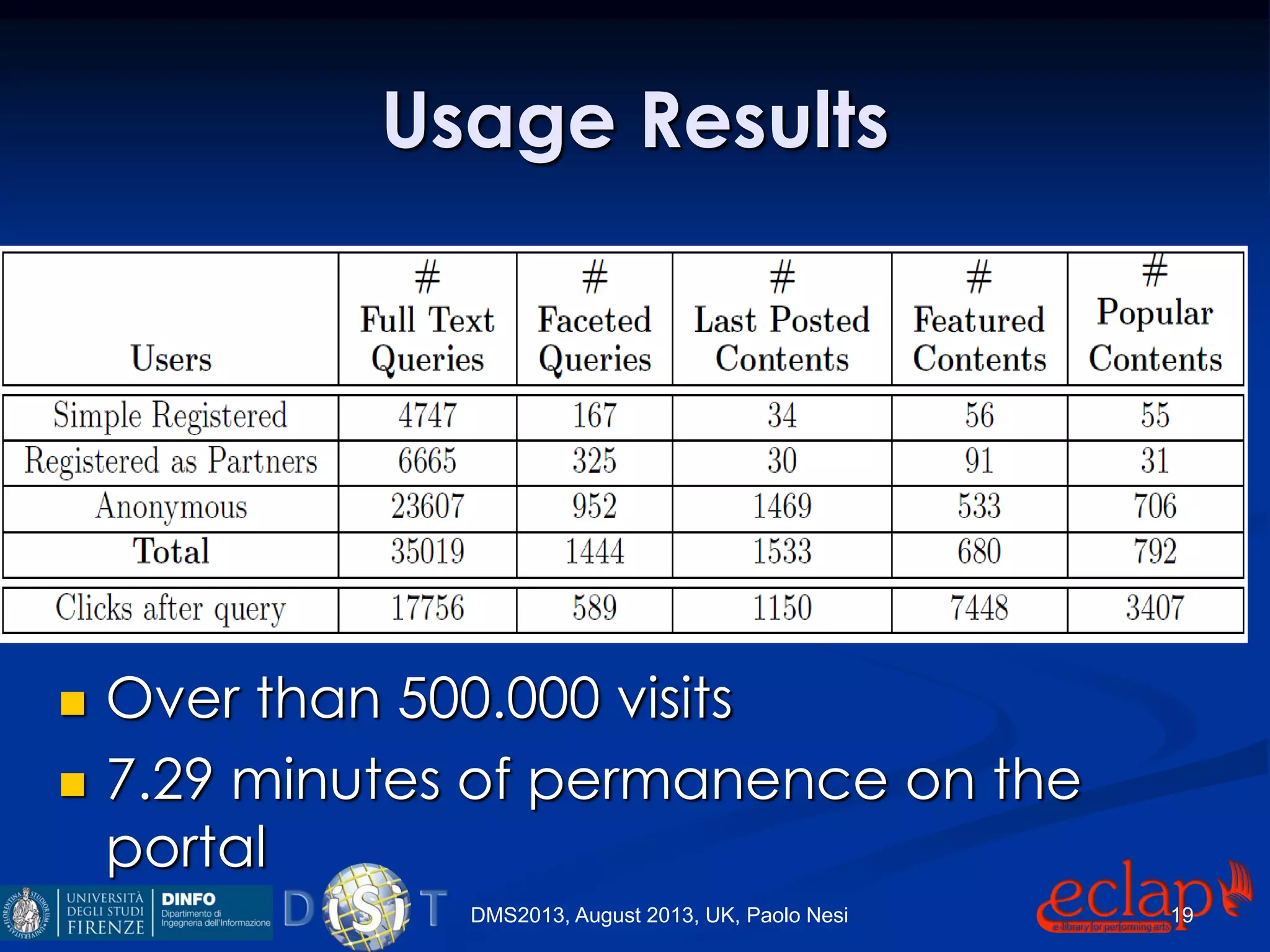
The document discusses an indexing and searching solution for the Eclap social network focused on the performing arts, leveraging multilingual and crossmedia content. It outlines the goals, technical requirements, and methodologies for improving search capabilities, including fuzzy search and faceted search, while assessing user engagement and satisfaction. Ultimately, it highlights improvements in search quality and user experience through advanced search techniques and algorithms.