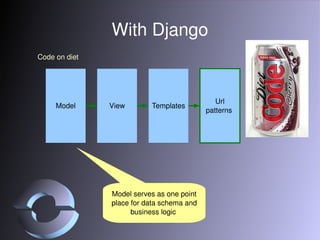
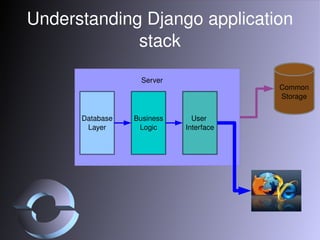
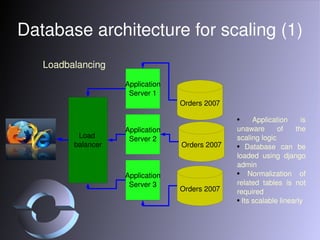
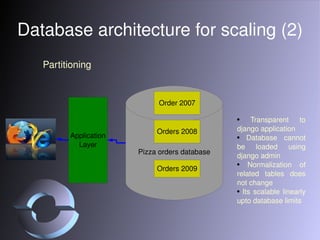
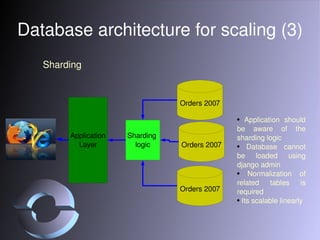
The document discusses strategies for scaling Django applications, including optimizing queries, schema design, caching, load balancing, database partitioning, and sharding. It provides examples of best practices for modeling data, debugging queries, and architectural approaches for scaling the database. Key recommendations include using appropriate field types, adding indexes strategically, and approaches that keep the application logic separated from database scaling.
![Pulling more out of Django application Supreet Sethi Email < [email_address] This talk is possible because of kindness of some clients, who let me use their machinery for my utterly wierd experiments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/django_database_optimization-090225021543-phpapp01/75/Django-Database-Optimization-1-2048.jpg)