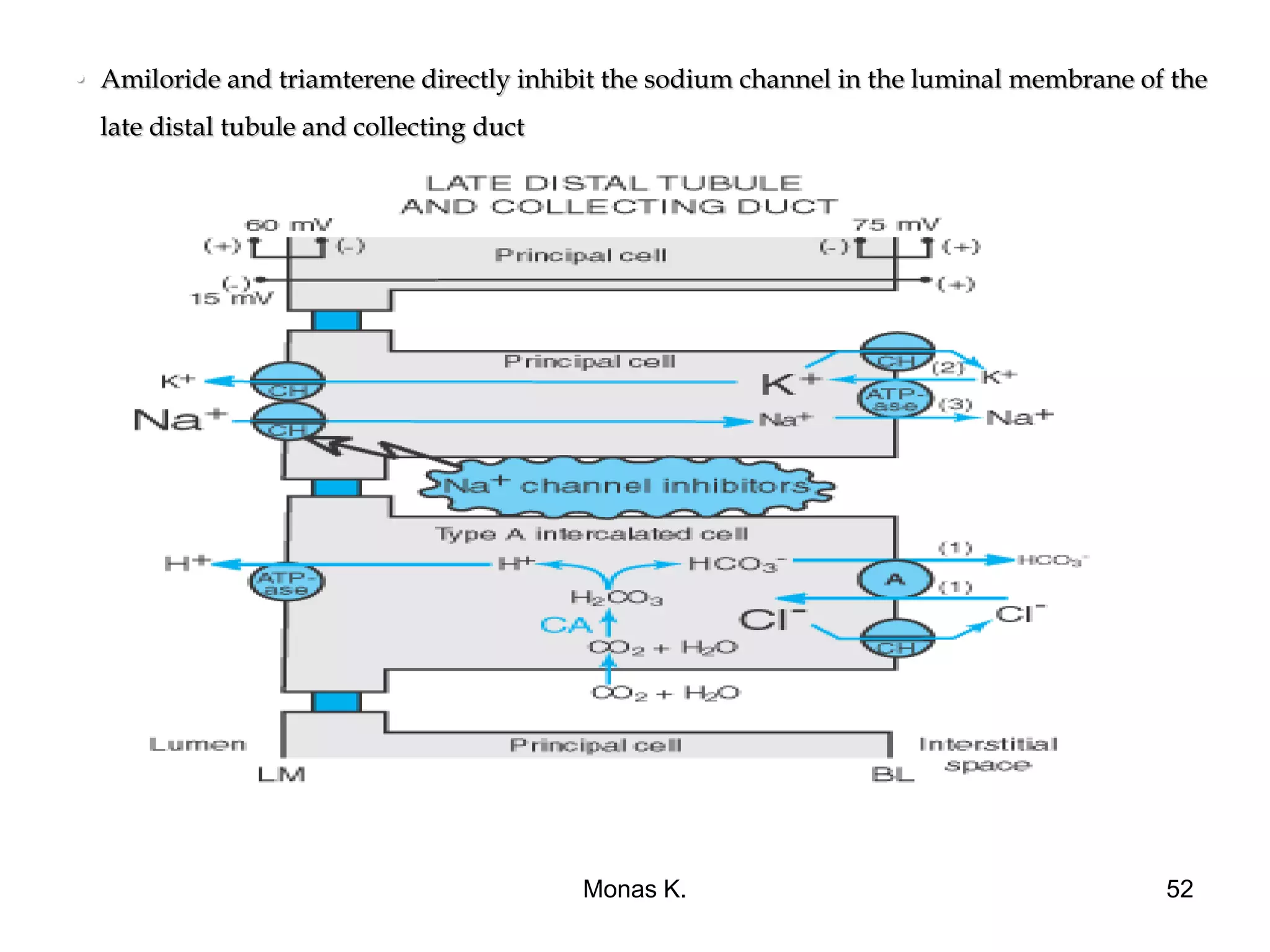
The document summarizes the pharmacology of diuretic agents. It discusses the renal anatomy and physiology, principles of diuretic action, and classification of diuretics. It then describes the mechanisms and sites of action of different classes of diuretics, including carbonic anhydrase inhibitors like acetazolamide, loop diuretics like furosemide, and their clinical indications and adverse effects. Loop diuretics are highly efficacious as they inhibit sodium reabsorption in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop, where a large solute load is normally reabsorbed.