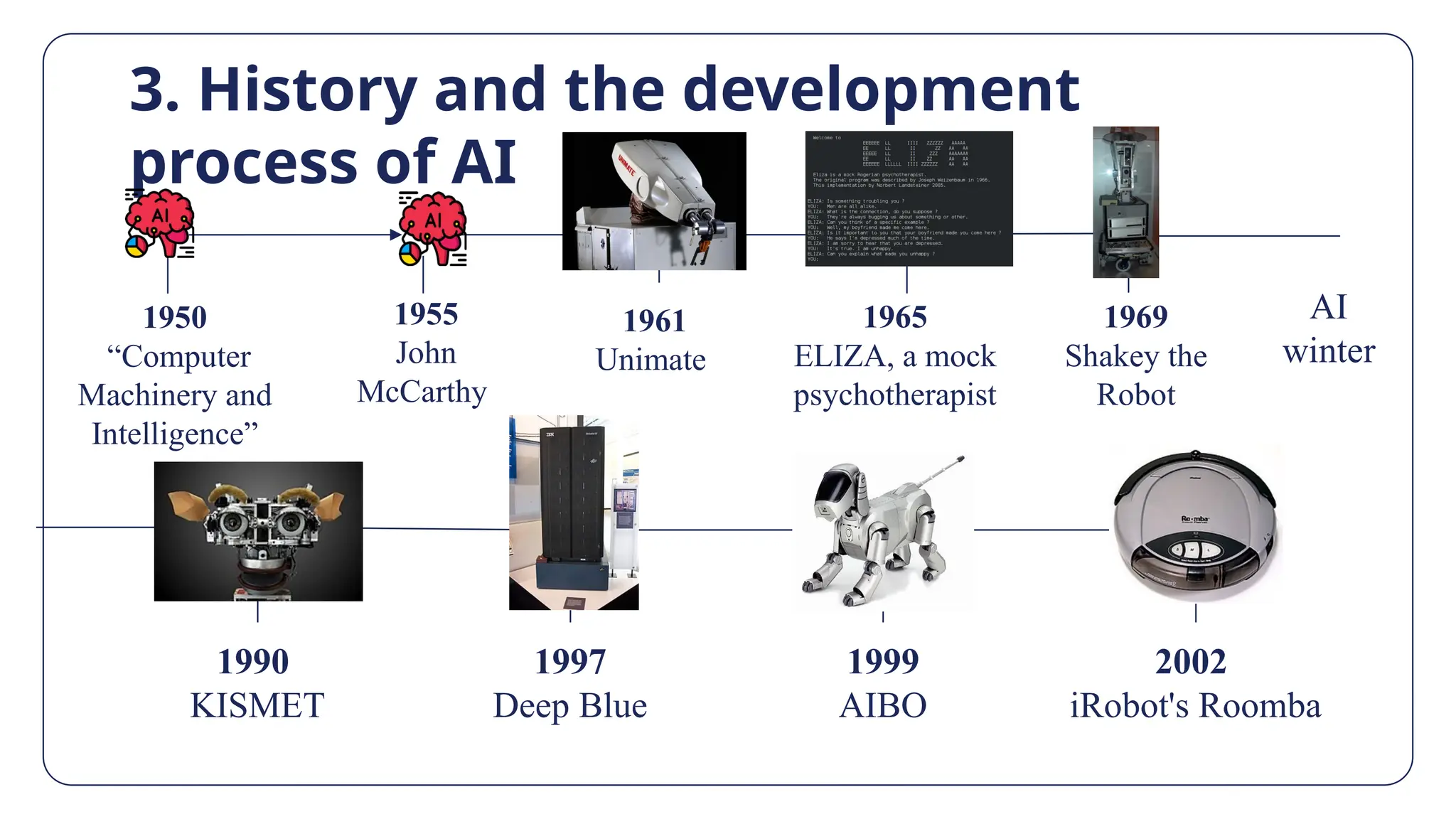
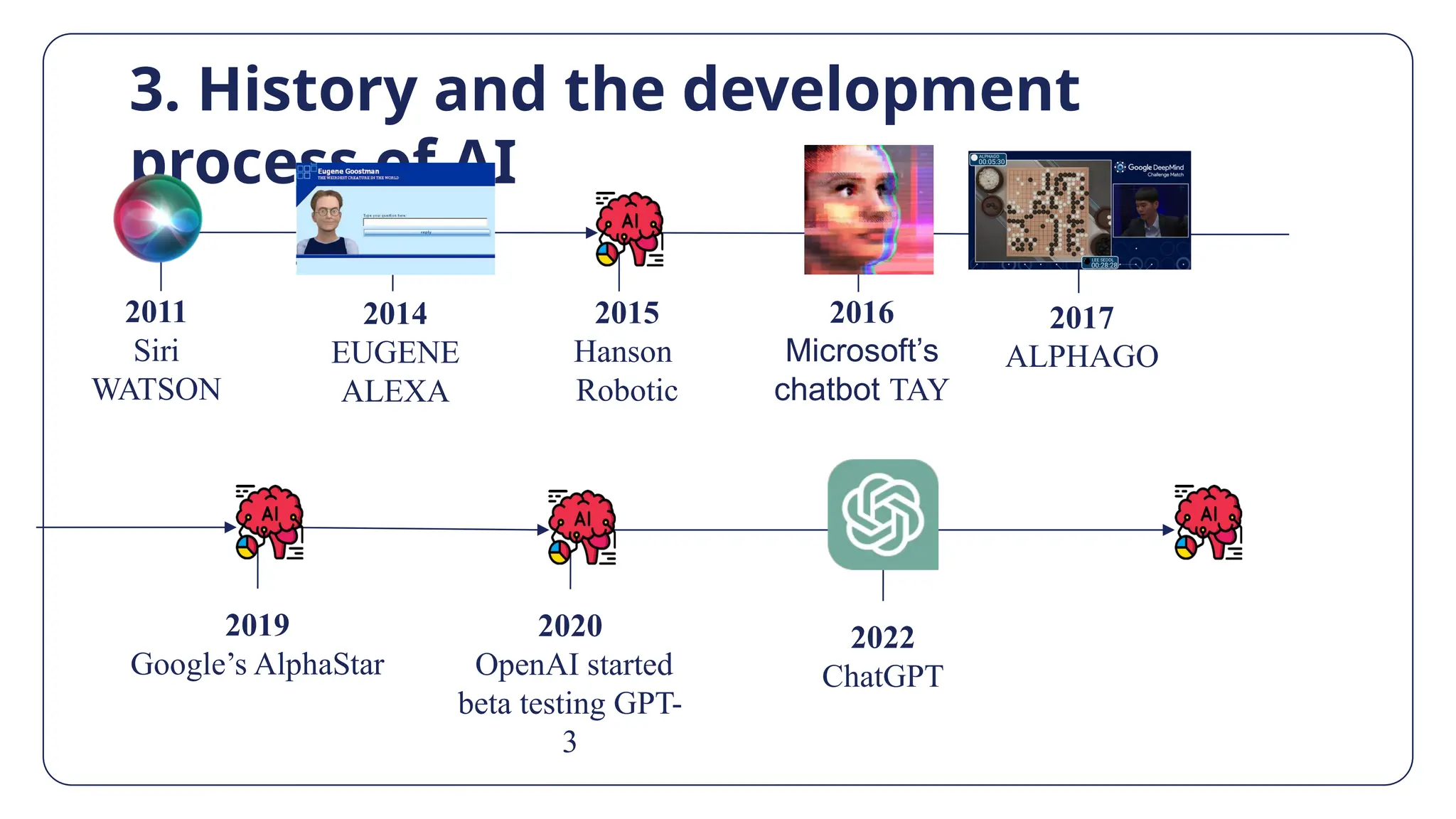
The document discusses artificial intelligence (AI), defining it as computer systems capable of performing tasks that traditionally required human intelligence. It covers the types, historical development, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of AI in various sectors such as healthcare, education, and business, highlighting its potential impacts on efficiency and user experience. Additionally, it addresses the challenges and ethical implications associated with AI technology.