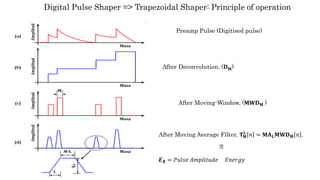
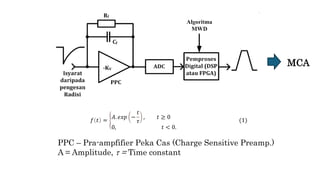
The document discusses a digital pulse processing technique utilizing moving window deconvolution (MWD) for enhanced signal resolution and reduced noise in pulse measurements. It explains the mathematical framework behind MWD, including algorithm components and comparisons between trapezoidal and triangular shaping methods. Key references are provided to foundational studies in digital pulse processing and signal conditioning.


![Digital Pulse Shaper => Trapezoidal Shaper
𝐴 𝑛 = 𝑥 𝑛 +
1
𝜏𝑠
𝑘=−∞
𝑛−1
𝑥 𝑘 = 𝑥 𝑛 − 1 −
1
𝜏𝑠
𝑥 𝑛 − 1 + 𝐴 𝑛 − 1 , 2 . . 𝐷𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑜𝑚𝑎𝑖𝑛
𝜏𝑠 = sampling time
Differentiation of (2) with moving window with width M yield MWD
equation:
𝐌𝐖𝐃𝐌 𝑛 = 𝐴 𝑛 − 𝐴 𝑛 − M = 𝑥 𝑛 − 𝑥 𝑛 − M +
1
𝜏𝑠
𝑘=𝑛−M
𝑛−1
𝑥 𝑘 (3).
With Deconvolution 𝐃𝐌 𝑛 = 𝑥 𝑛 − 𝑥[𝑛 − M] & Moving window 𝑛 =
𝑘=𝑛−M
𝑛−1
𝑥[𝑘] 𝐌𝐀𝐌
Eq.(3) deduced to:-
𝐌𝐖𝐃𝐌 𝑛 = 𝐃𝐌 𝑛 +
1
𝜏𝑠
𝐌𝐀𝐌 𝑛
MWD does not filter the noise? Need low-pass filter i.e., Moving Average
with sampling L (𝐌𝐀𝐋). Pulse , 𝐓𝐌
𝐋
𝑛 = 𝐌𝐀𝐋𝐌𝐖𝐃𝐌 𝑛 .
if L = M -> Triangular Shaper, L M Trapezoid Shaper (Flat top width
= M-L)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalpulseprocessor-240702003242-f6d87a1c/85/Digital-Pulse-Processor-for-processing-signal-from-radiation-detectors-pptx-4-320.jpg)