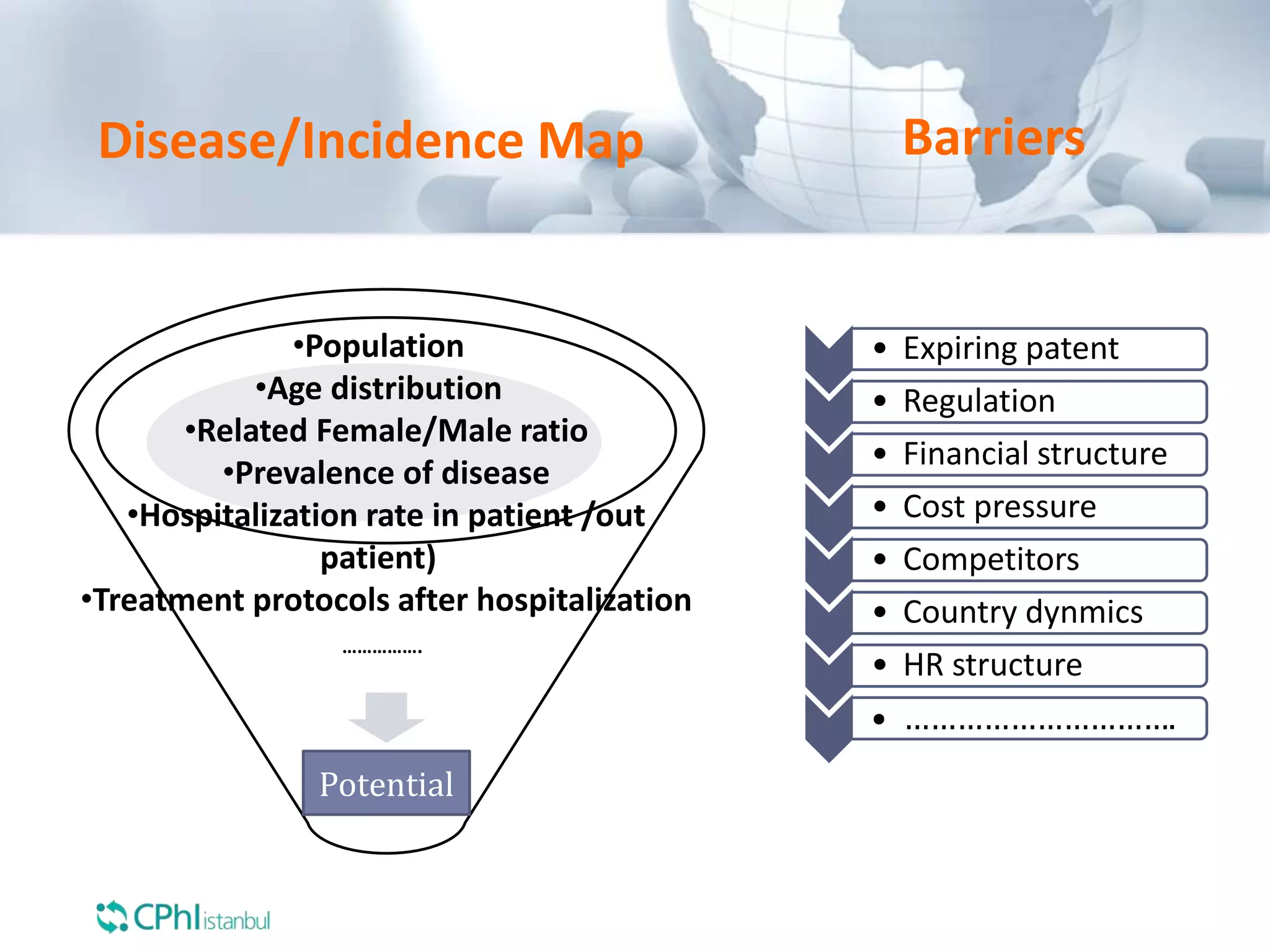
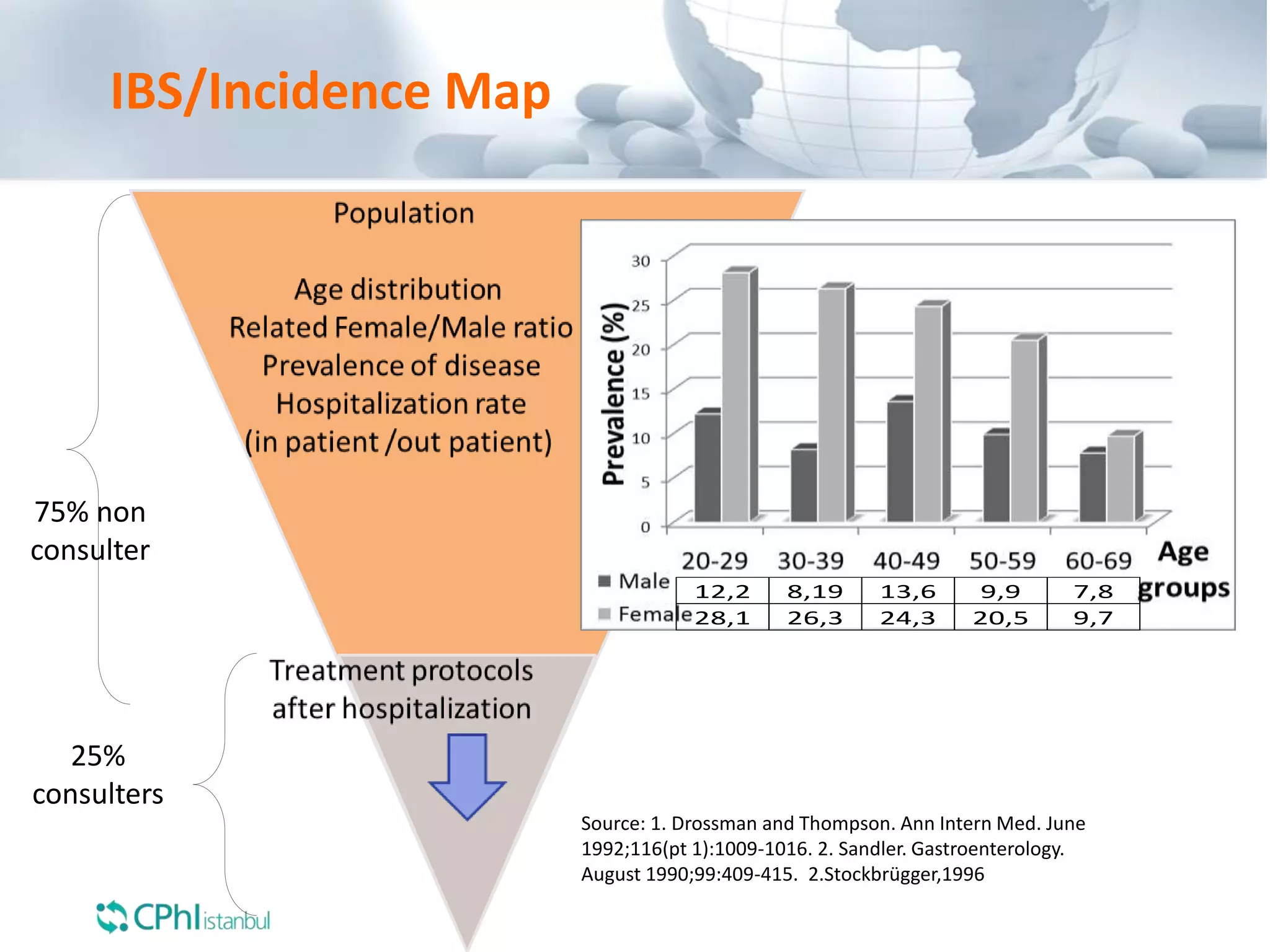
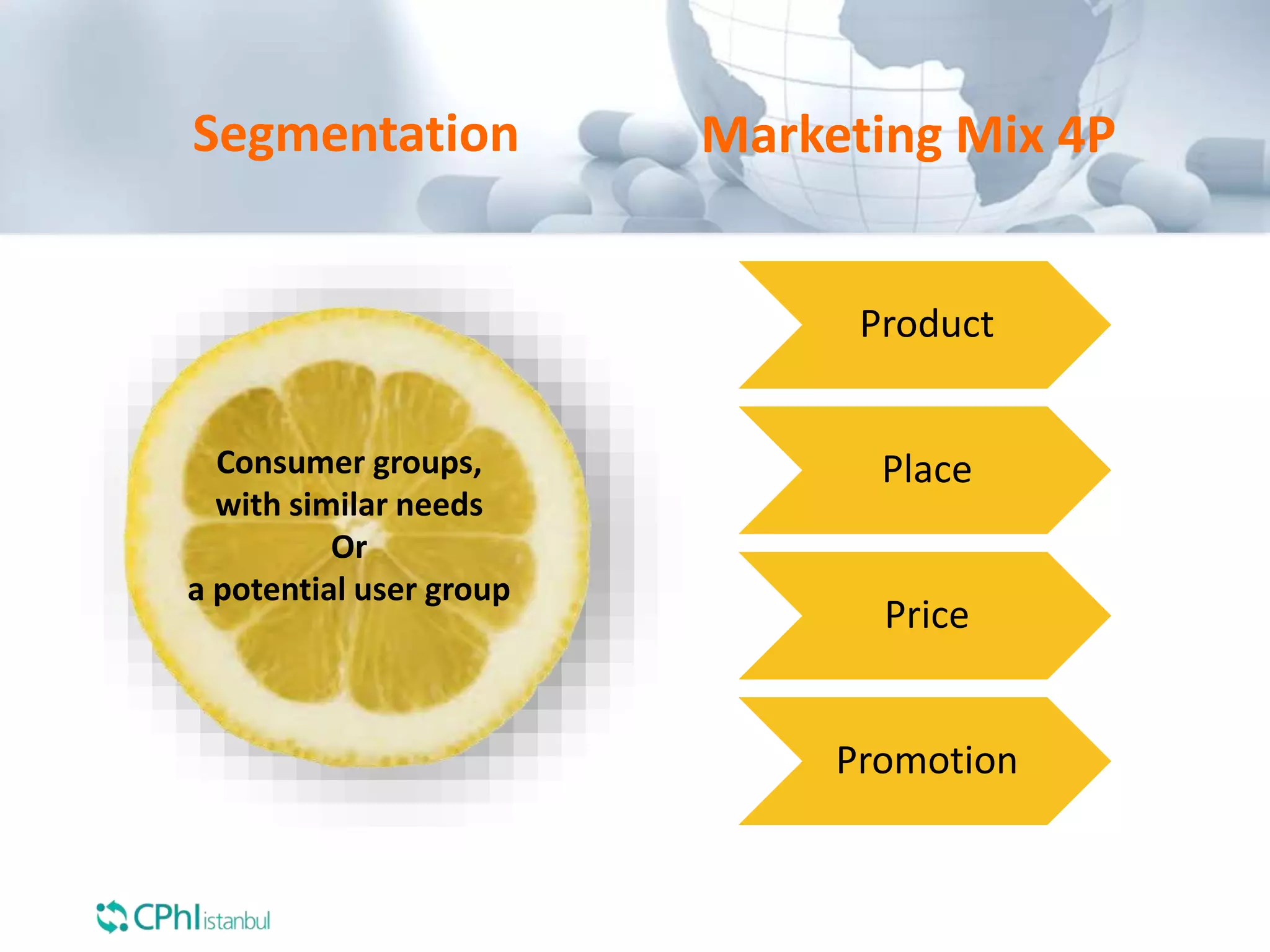
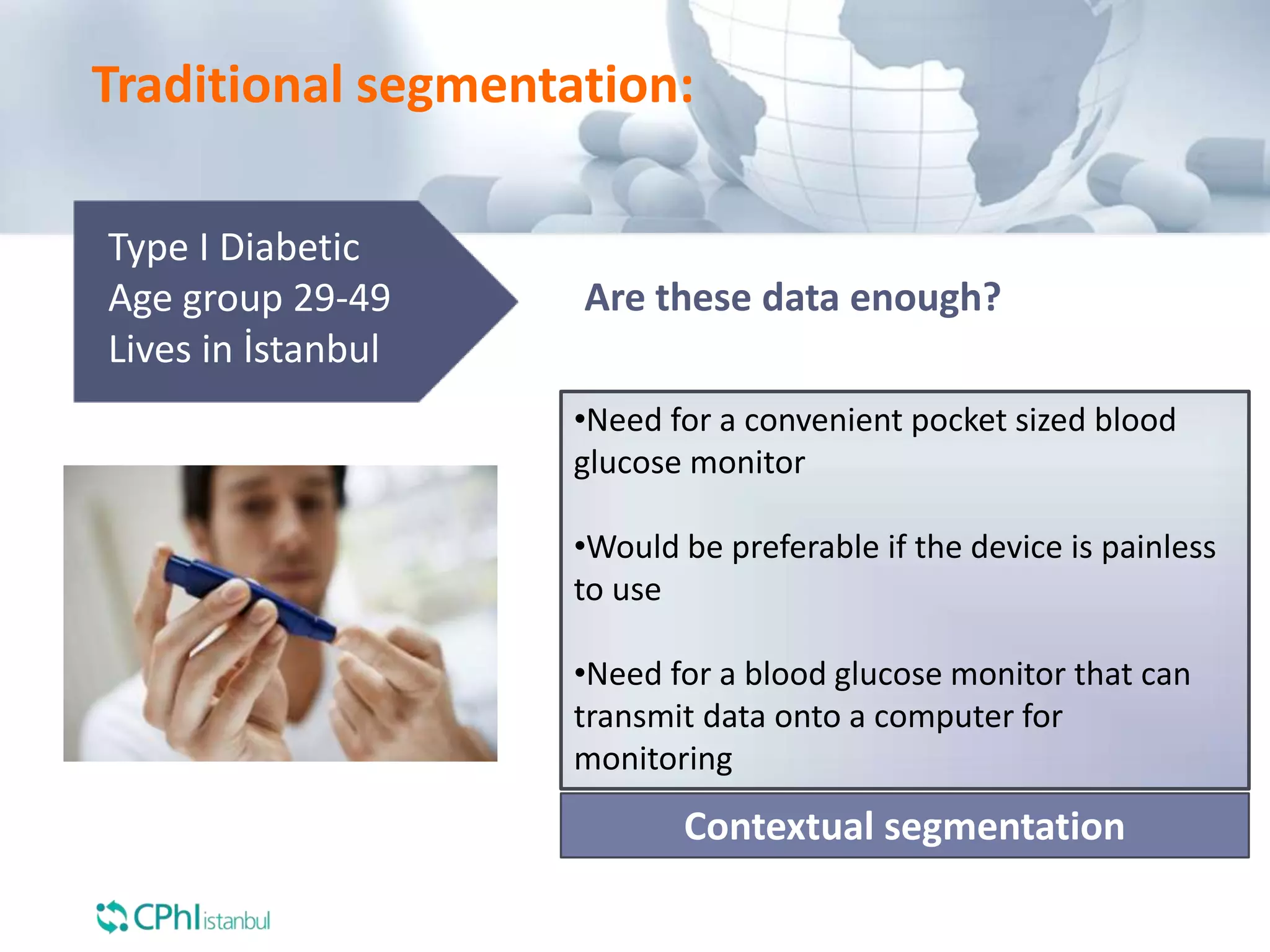
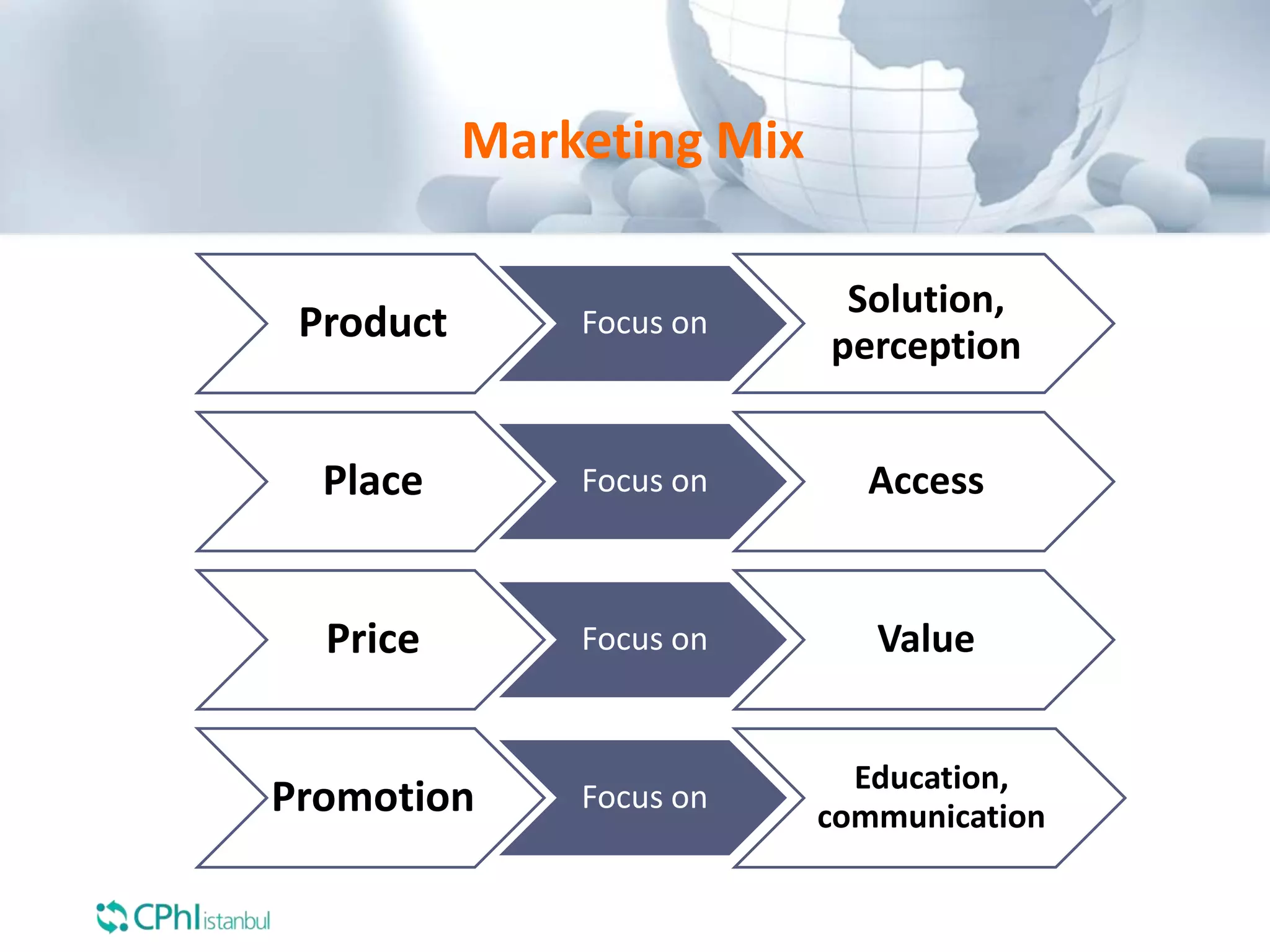
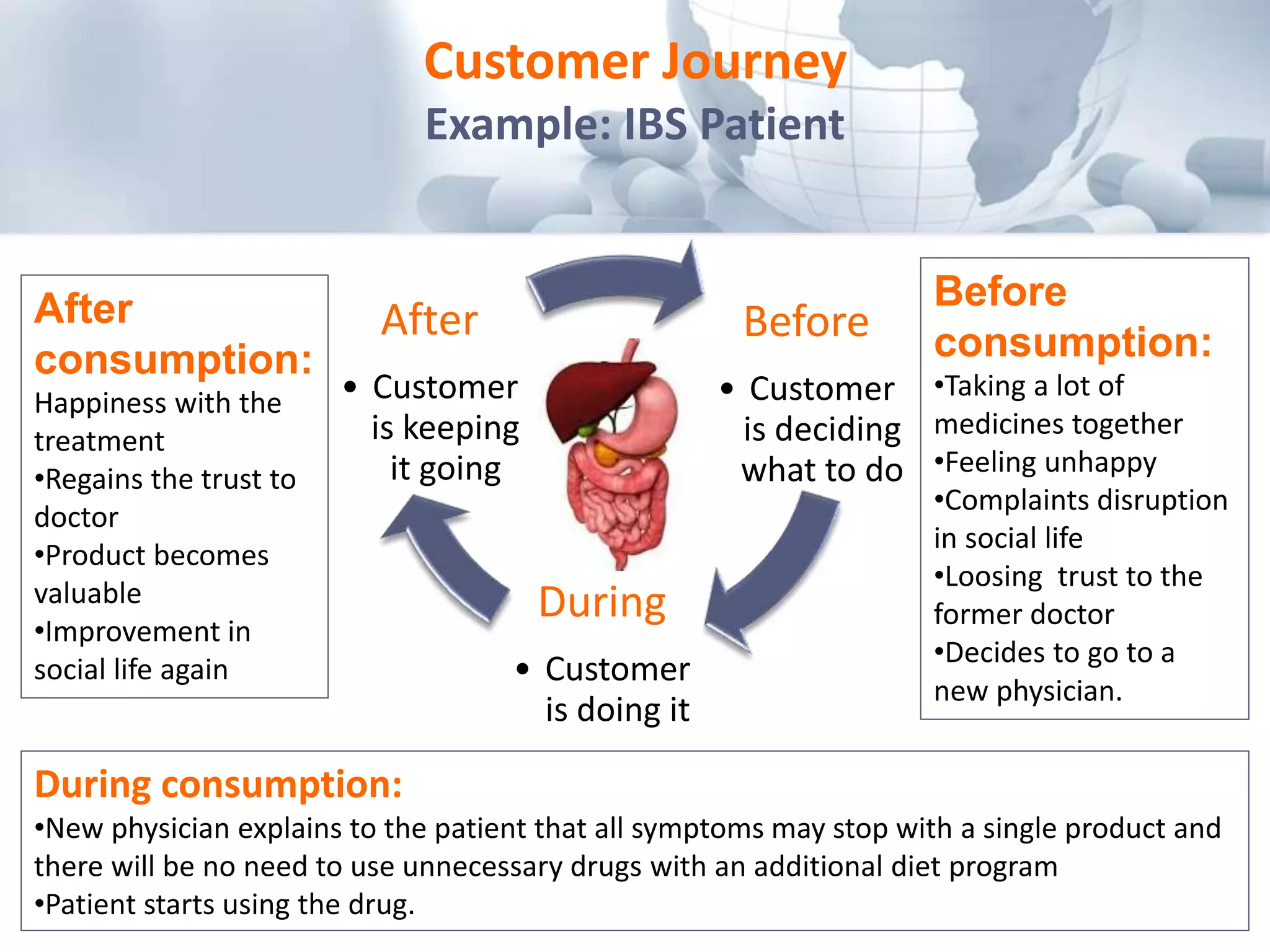
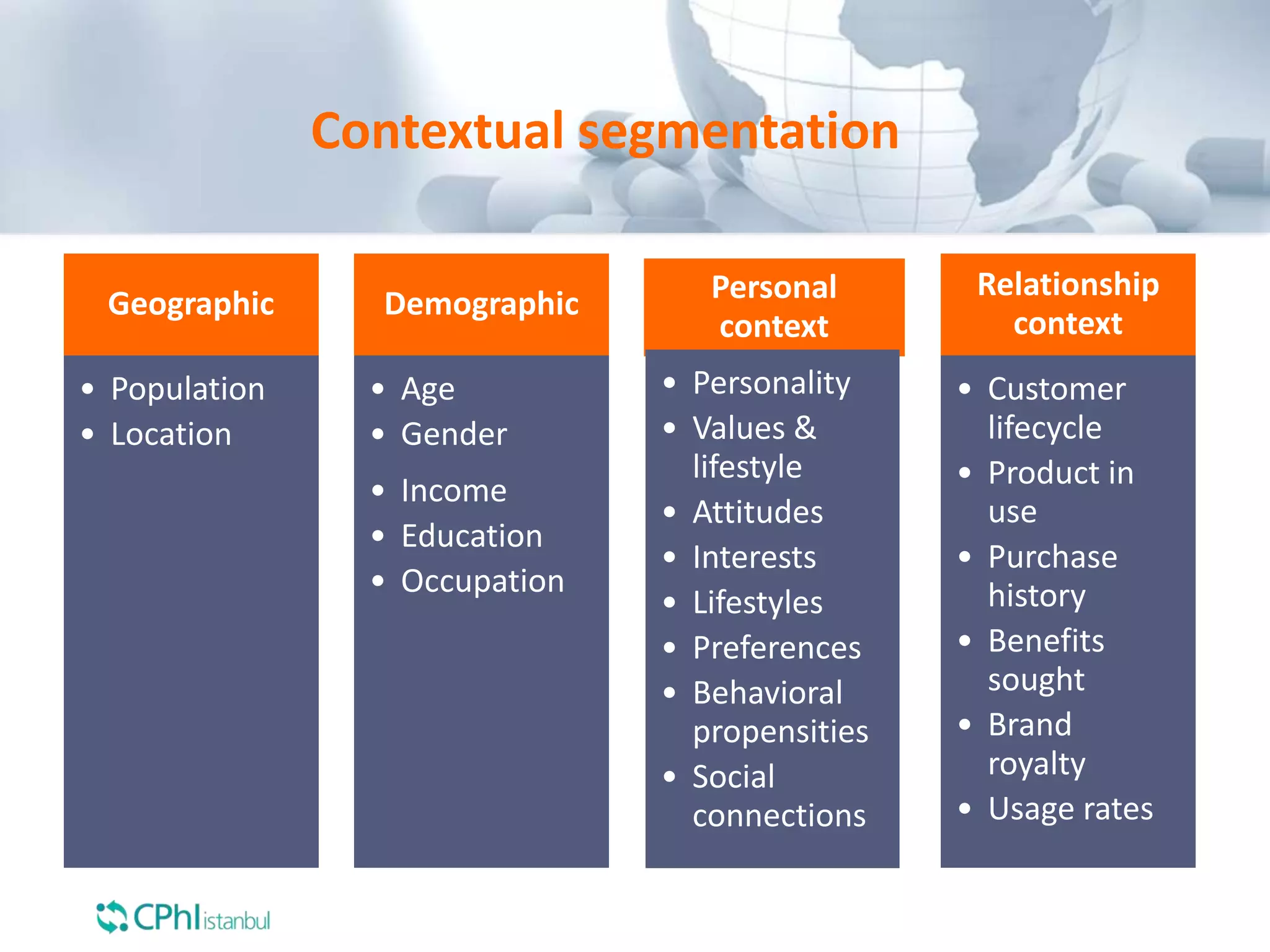
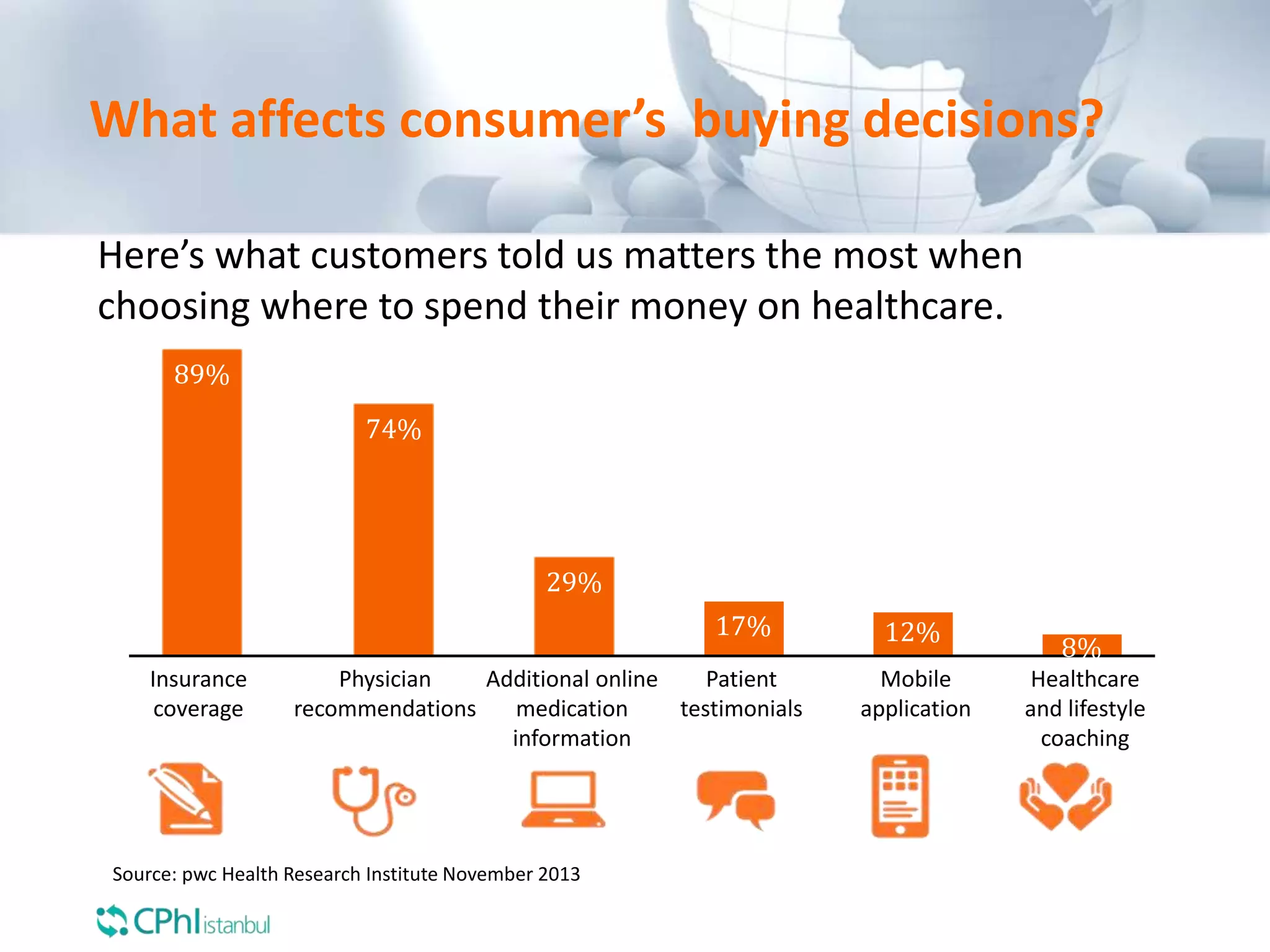
The document discusses the perception of generic products in emerging markets, highlighting their low prices relative to original products and the challenges faced in marketing and consumer trust. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer needs and expectations through contextual segmentation and provides strategies for successful product positioning. Additionally, it notes that consumer satisfaction and the ability to demonstrate product value are vital for success in these markets.