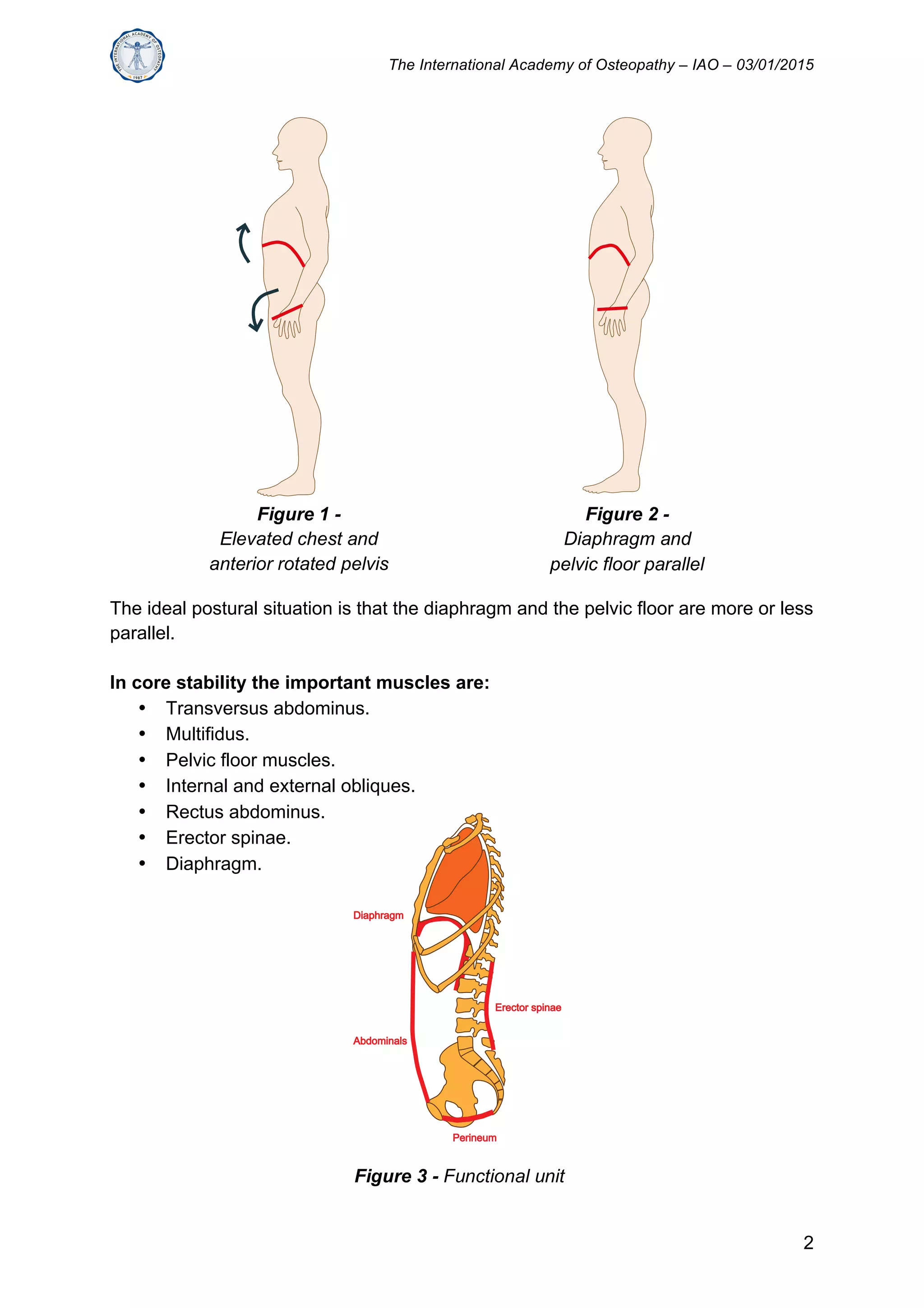
The document discusses the relationship between diaphragm function and core stability. It states that a weak diaphragm does not provide proper support for the spine, leading to postural issues. Good diaphragm function requires coordinated activity of the abdominal wall and intra-abdominal pressure during breathing to support the lumbar spine. Evaluating diaphragm and breathing function is important for assessing core stability and treating low back pain. Treatment should address bony, articular, ligamentary, muscular and fascial aspects of the core to improve coordination between structures like the diaphragm and pelvic floor.