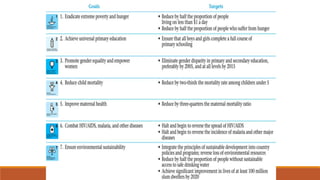
Development economics is a branch of economics that deals with reducing poverty and encouraging prosperity in low-income countries. It examines factors like health, education, markets, and policies that impact economic growth and development, which is a long-term process of not just economic indicators improving but also standards of living. Development economics provides theories to understand developing economies and help improve lives globally.