This document discusses different models and indicators of development. It covers:
1. Economic, social, and demographic indicators used to measure development, including GDP, education, health, and life expectancy.
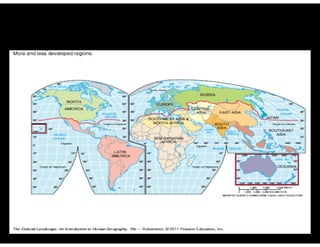
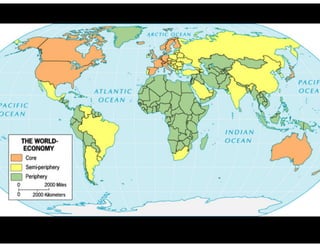
2. Models of development including self-sufficiency, Rostow's stages of growth theory, Wallerstein's world systems analysis of core/periphery/semi-periphery, and structuralist and dependency theories.
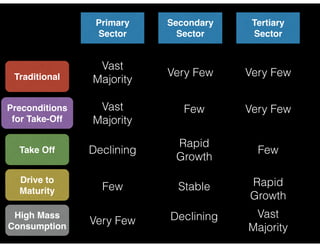
3. Rostow's model outlines traditional, preconditions for take-off, take-off, drive to maturity, and mass consumption stages and faces some criticisms for being too simplistic.