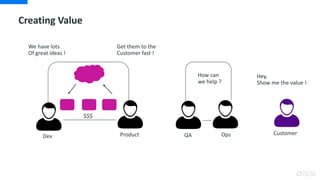
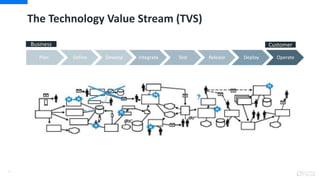
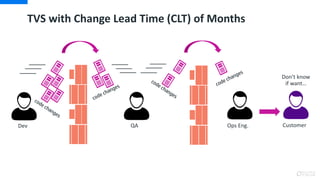
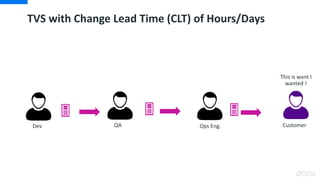
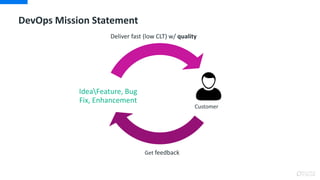
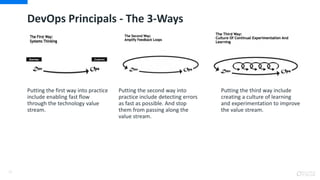
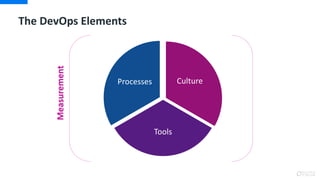
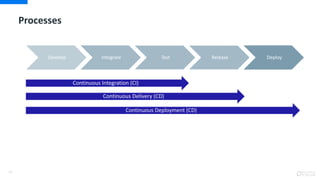
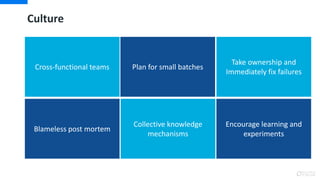
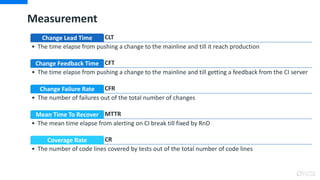
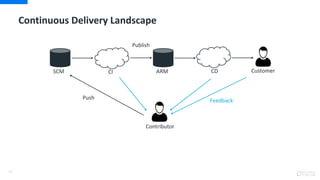
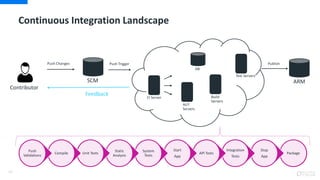
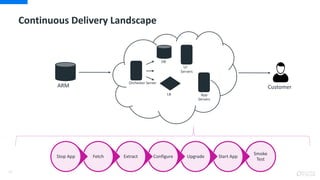
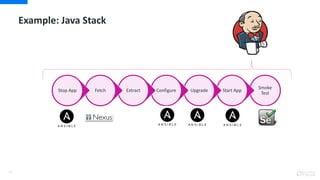
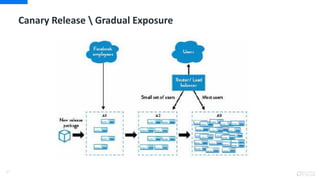
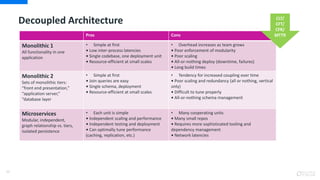
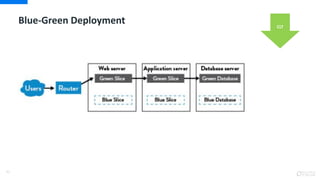
DevOps is an approach that aims to unify software development (Dev) and software operation (Ops) practices to reduce the time between code changes and deployment to production. Some key aspects of DevOps include:
- Cross-functional teams that include both developers and operations staff
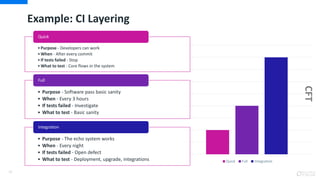
- Automating testing, builds, and deployments to speed up the delivery process
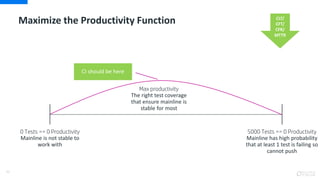
- Continuous integration, delivery, and deployment to get code changes to users faster
- Monitoring and measuring key metrics like change lead time to track progress